The BC-610 was a radio transmitter based on the Hallicrafters HT-4 and was used by the U.S. Army Signal Corps during World War II.
Contents

The BC-610 was a radio transmitter based on the Hallicrafters HT-4 and was used by the U.S. Army Signal Corps during World War II.

In the early 1940s, the U.S. military sought a high-powered radio transmitter capable of infallible voice communications over 100 miles (160 km), sturdy enough to work in all conditions, flexible enough to be able to cover a wide range of frequencies, self-powered and able to operate in motion or at fixed locations. The Hallicrafters HT-4 transmitter was chosen from units available from various U.S. radio manufacturers. The HT-4 was designed for amateur radio use and had been commercially available for several years at a price of approximately $700, rivaling the cost of a car. It was considered compact and stable for its era and could deliver in excess of 300 watts of power for voice or MCW communications and 400 watts during Morse code operation. As was typical in physically large vacuum tube equipment, the manual cautions power output is less at higher frequencies. It was quartz crystal controlled, but could be used over a wide range of frequencies through use of the master-oscillator power amplifier. [1]
Modifications requested by the Signal Corps were performed by Hallicrafters' engineers working with U.S. Army technicians at Fort Monmouth. They made a new version of the HT-4, which was known as the BC-610 transmitter, a part of the SCR-299 mobile communications unit, and production began in 1942. General Dwight Eisenhower credited the SCR-299 in the reorganization of U.S. forces, which led to their victory against the Nazis at Kasserine Pass. The SCR-299 was also used in the Invasion of Sicily and later, Italy. [1]
A BC-610 transmitter was used by double agent Juan Pujol García during WWII as part of Operation Fortitude. Clear reception by the Germans of messages transmitted by García, code name GARBO, were so crucial to the Allied deception that use of the relatively high-powered transmitter was deemed necessary. [2]
Over 25,000 units were produced by Hallicrafters and other allied companies. In 1944, a short subject film was produced by the Jam Handy Organization and sponsored by the Hallicrafters Company detailing how the HT-4 transmitter was adapted for military service and dramatizing its use by the U.S. military during World War II. [3] [4]

The "A" through "I" models are the same basic unit with relatively minor component and cosmetic differences. [6]

A walkie-talkie, more formally known as a handheld transceiver (HT) or handheld radio, is a hand-held, portable, two-way radio transceiver. Its development during the Second World War has been variously credited to Donald Hings, radio engineer Alfred J. Gross, Henryk Magnuski and engineering teams at Motorola. First used for infantry, similar designs were created for field artillery and tank units, and after the war, walkie-talkies spread to public safety and eventually commercial and jobsite work.

The SCR-270 was one of the first operational early-warning radars. It was the U.S. Army's primary long-distance radar throughout World War II and was deployed around the world. It is also known as the Pearl Harbor Radar, since it was an SCR-270 set that detected the incoming raid about 45 minutes before the December 7, 1941, attack on Pearl Harbor commenced.

The United States Army Signal Corps (USASC) is a branch of the United States Army that creates and manages communications and information systems for the command and control of combined arms forces. It was established in 1860, the brainchild of Major Albert J. Myer, and had an important role in the American Civil War. Over its history, it had the initial responsibility for portfolios and new technologies that were eventually transferred to other U.S. government entities. Such responsibilities included military intelligence, weather forecasting, and aviation.

The Hallicrafters Company manufactured, marketed, and sold radio equipment, and to a lesser extent televisions and phonographs, beginning in 1932. The company was founded by William J. Halligan and based in Chicago, Illinois, United States.

The AN/ARC-5 Command Radio Set is a series of radio receivers, transmitters, and accessories carried aboard U.S. Navy aircraft during World War II and for some years afterward. It is described as "a complete multi-channel radio transmitting and receiving set providing communication and navigation facilities for aircraft. The LF-MF-HF components are designed to transmit and receive voice, tone-modulated, and continuous wave (cw) signals." Its flexible design provided AM radiotelephone voice communication and Modulated continuous wave (MCW) and Continuous wave (CW) Morse code modes, all of which are typical capabilities in other Navy aircraft communication sets of the period. It was an improvement of the Navy's ARA/ATA command set. Similar units designated SCR-274-N were used in U.S. Army aircraft. The Army set is based on the ARA/ATA, not the later AN/ARC-5. The ARA/ATA and SCR-274-N series are informally referred to as "ARC-5", despite small differences that render all three series incompatible. Like the AN/ARC-5, the ARA/ATA and SCR-274-N had AM voice communication and two-way MCW and CW Morse code capability.

The SCR-284 was a World War II era combination transmitter and receiver used in vehicles or fixed ground stations.

The AN/ART-13 was a radio transmitter manufactured by Collins Radio that found widespread use during and after World War II in military aircraft.

The SCR-536 was a hand-held radio transceiver used by the US Army Signal Corps in World War II. It is popularly referred to as a walkie talkie, although it was originally designated a "handie talkie".
Signal Corps Radios were U.S. Army military communications components that comprised "sets". Under the Army Nomenclature System, the abbreviation SCR initially designated "Set, Complete Radio", but was later misinterpreted as "Signal Corps Radio."

The SCR-299 was a U.S. Signal Corps mobile military communications unit used during World War II.

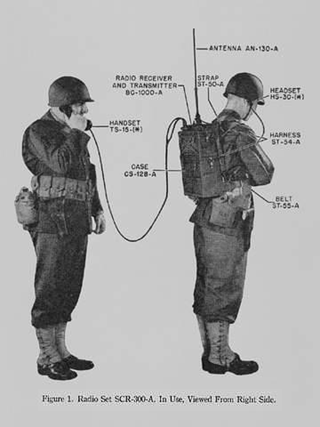
The SCR-300, designated AN/VRC-3 under the Joint Electronics Type Designation System, was a portable radio transceiver used by US Signal Corps in World War II. This backpack-mounted unit was the first radio to be nicknamed a "walkie talkie".

The SCR-694 was a portable two way radio set used by the U.S. military during World War II.

The SCR-277 was a mobile, trailer mounted radio range set for radio guidance of aircraft. It was standardized by the U.S. Army in June 1941.

The BC-342 was a World War II U.S. Army Signal Corps high frequency radio receiver. It was used primarily as part of field installations such as the SCR-188A, but could be used with mobile sets such as the 2 1/2 ton mounted SCR-399. First designed at Fort Monmouth, New Jersey by the U.S. Army Signal Corps, it was built by various manufacturers including RCA. Many of the later units that are encountered today were manufactured by the Farnsworth Television and Radio Corporation of Fort Wayne, Indiana. Variants include the low frequency coverage BC-344 receiver, and the battery or dynamotor powered BC-312 receiver.
The AN/MRN-1 was an instrument approach localizer used by the Army Air Force during and after World War II. It was standardized on 3 July 1942. It replaced the SCR-241, and was a component of SCS-51.
The AN/MRN-3 was a marker beacon set used by the Army Air Force during and after World War II, it was standardized 23 October 1943, and replaced SCR-241.

The SCR-245 Radio was a mobile MF/HF Signal Corps Radio used by the U.S. Army before and during World War II, for short range ground communications, It was one of the first crystal controlled sets used by the Army.

The SCR-508 radio was a mobile Signal Corps Radio used by the U.S. Army during World War II, for short range ground communications. The SCR-508 series radio represented the Army's commitment to both FM and crystal tuning, and was used extensively by armor and mechanized units. The turret bustle of late series light and medium tanks was designed around this radio.
During World War II, the German Army relied on an diverse array of communications to maintain contact with its mobile forces and in particular with its armoured forces. Most of this equipment received the generic prefix FuG for Funkgerät, meaning "radio device". Occasionally the shorted Fu designation were used and there were exceptions to both these systems. Number ranges were not unique across the services so sometimes different equipment used by different services had the same FuG prefix. This article is a list and a description of the radio equipment.

The VT-158, also known as the Zahl tube, was a vacuum tube invented by American physicist Harold A. Zahl in the 1930s and used during World War II and the Korean War. It allowed the radar technology at the time to detect low-flying planes by generating enough power to produce ultrahigh frequency energy.