Related Research Articles

The Deutsche Reichsbahn had a standard passenger train tank engine with a wheel arrangement of 1'C1' or 2-6-2 and a low axle load, which was designated in their classification system as the DRG Class 64. The Class 64 was developed from 1926 onwards and it was built between 1928 and 1940. Many German manufacturers contributed to the series.

The Bavarian Class GtL 4/4 engines were superheated steam locomotives in service with the Royal Bavarian State Railways for duties on branch lines (Lokalbahnen).

The six-coupled P 5 of the Palatinate Railway (Pfalzbahn) was to replace the four-coupled locomotives in the Palatinate. They were given a leading Krauss-Helmholtz bogie and a trailing bogie in order to achieve satisfactory weight distribution.

The Class 85 was a German goods train tank engine and standard locomotive (Einheitslok) with the Deutsche Reichsbahn.

The German DRG Class 02 engines were standard (Einheitslokomotiven) express train locomotives with the Deutsche Reichsbahn-Gesellschaft. Number 02 001 was the first Einheitsdampflokomotive in the DRG to be completed.

The Class 62 engines were standard passenger train tank locomotives of Germany's Deutsche Reichsbahn-Gesellschaft (DRG).

The locomotives of the German DRG Class 81 were standard (Einheitsdampflokomotiven) goods train tank locomotives with the Deutsche Reichsbahn-Gesellschaft (DRG).
The German DRG Class 84s were standard goods train tank locomotives with the Deutsche Reichsbahn. A total of twelve engines were placed into service by the Reichsbahn between 1935 and 1937. The machines were given operating numbers 84 001–012. They were worked on the Müglitz Valley Railway (Müglitztalbahn) between Heidenau and Altenberg in the Ore Mountains (Erzgebirge), for which they were specially designed to negotiate tight curves. They were manufactured by the firms of Schwartzkopff and Orenstein & Koppel. One feature was that they were fitted with Schwartzkopff-Eckhardt II bogies.

The Prussian T 18 was the last class of tank locomotives developed for the Prussian state railways. They were originally intended for services on the island of Rügen as replacements for Class T 12 and T 10 engines. They emerged when a class of locomotive was conceived in 1912 that was to handle express and passenger trains in border areas or in shuttle services on short routes. A tank engine design with symmetrical running gear was envisaged because, unlike a tender locomotive, it could run equally fast forwards and backwards and could be operated on return journeys without having to be turned on a turntable. Its power and top speed were to be the same as those of the P 8. Robert Garbe designed this 4-6-4 (2′C2′) tank locomotive for 100 km/h with a 17-ton axle load and contracted the Vulkan Werke in Stettin to build it. It was given the designation T 18.

The first steam locomotives of the Baden Class VI c were delivered in 1914 by the Maschinenbau-Gesellschaft Karlsruhe for service in southwestern Germany with the Grand Duchy of Baden State Railway.
Locomotive numbers 1 to 3 on the Lübeck-Büchen railway in Germany were streamlined tank locomotives. The locomotives had a 2-4-2T wheel arrangement, a two-cylinder, superheated engine and were capable of push-pull operations. In order to ensure a symmetrical running gear, both carrying axles were built as Bissel bogies, which were fitted with return devices for improved running.

The Baden VI b was the first German tank locomotive with a 2-6-2 wheel arrangement. It was developed by the firm of Maffei for the Grand Duchy of Baden State Railways in order to provide faster services on the Höllentalbahn. As a result, the first six batches were given a firebox sloping to the rear. One striking feature was also the connecting pipe between the two steam domes.
The Prussian state railways grouped a variety of different types of passenger tank locomotive into its Prussian Class T 5. Several examples of the sub-classes T 5.1 and T 5.2 transferred into the Deutsche Reichsbahn as DRG Classes 71.0 and 72.0.

The Prussian Class T 10s were tank locomotives operated by the Prussian state railways. They were procured for duties between Frankfurt and Wiesbaden between 1909 and 1912. This 41-kilometre (25 mi) long route between the two termini was to be worked without turning the locomotive. Because the engine tended to derail, in practice it was turned whenever possible. On these engines, supplied by Borsig, the boiler from the Prussian P 6 and the running gear and drive from the Prussian P 8 were used. The boiler had to be positioned further forward than was usual on other locomotives in order to even out the distribution of weight, because the design omitted any trailing wheels. The first trial runs took place on 30 June 1909.
The Prussian T 9 was a class of German steam locomotive which included several types of tank engine, all with six coupled wheels and two carrying wheels operated by the Prussian state railways.
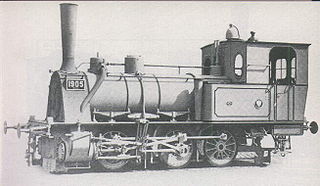
The Prussian Class T 3 steam locomotives procured for the Prussian state railways were 0-6-0 tank locomotives. Together with the Prussian T 2 they were the first locomotives that were built to railway norms. The first units were delivered by Henschel in 1882.

The Prussian Class T 12 is an early, German, passenger train, tank locomotive built for the Prussian state railways in large numbers. These locomotives were superheated variants of the T 11.

The Prussian T 8 were six-coupled superheated goods tank locomotives of the Prussian state railways. They were originally intended for suburban passenger service in Berlin, and for use on branch lines. Due to their poor running qualities, they were demoted to shunting and short-distance goods train service.

The Prussian T 7 was a group of goods tank locomotives of the Prussian State Railways with an 0-6-0T wheel arrangement. It was not a class in the modern sense of identical locomotives.
The Prussian G 4.2 was a class of compound 0-6-0 goods locomotive of the Prussian State Railways. It was a compound version of the G 3 and G 4.1 types by Henschel.
References
- Hütter, Ingo (2021). Die Dampflokomotiven der Baureihen 60 bis 91 der DRG, DRB, DB, und DR (in German). Werl: DGEG Medien. pp. 247–248. ISBN 978-3-946594-21-5.
- Weisbrod, Bäzold, Obermayer: Das große Typenbuch deutscher Dampflokomotiven. Transpress Verlag ISBN 3-344-70751-5
- Weisbrod, Manfred (1991). Dampflokomotiven deutscher Eisenbahnen, Von Privatbahnen zur DRG (EFA 1.5) (in German). Düsseldorf: Alba. pp. 102–104, 241. ISBN 3-87094-139-1.