Decarboxylation is a chemical reaction that removes a carboxyl group and releases carbon dioxide (CO2). Usually, decarboxylation refers to a reaction of carboxylic acids, removing a carbon atom from a carbon chain. The reverse process, which is the first chemical step in photosynthesis, is called carboxylation, the addition of CO2 to a compound. Enzymes that catalyze decarboxylations are called decarboxylases or, the more formal term, carboxy-lyases (EC number 4.1.1).

A dipeptide is an organic compound derived from two amino acids. The constituent amino acids can be the same or different. When different, two isomers of the dipeptide are possible, depending on the sequence. Several dipeptides are physiologically important, and some are both physiologically and commercially significant. A well known dipeptide is aspartame, an artificial sweetener.
In organic chemistry, a nitrile is any organic compound that has a −C≡N functional group. The name of the compound is composed of a base, which includes the carbon of the −C≡N, suffixed with "nitrile", so for example CH3CH2C≡N is called "propionitrile". The prefix cyano- is used interchangeably with the term nitrile in industrial literature. Nitriles are found in many useful compounds, including methyl cyanoacrylate, used in super glue, and nitrile rubber, a nitrile-containing polymer used in latex-free laboratory and medical gloves. Nitrile rubber is also widely used as automotive and other seals since it is resistant to fuels and oils. Organic compounds containing multiple nitrile groups are known as cyanocarbons.

In organic chemistry, an acyl halide is a chemical compound derived from an oxoacid by replacing a hydroxyl group with a halide group.
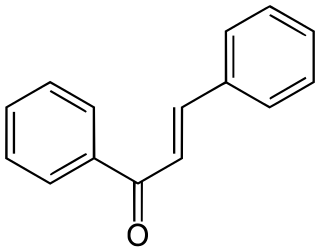
Chalcone is the organic compound C6H5C(O)CH=CHC6H5. It is an α,β-unsaturated ketone. A variety of important biological compounds are known collectively as chalcones or chalconoids. They are widely known bioactive substances, fluorescent materials, and chemical intermediates.
In organic chemistry, the Ugi reaction is a multi-component reaction involving a ketone or aldehyde, an amine, an isocyanide and a carboxylic acid to form a bis-amide. The reaction is named after Ivar Karl Ugi, who first reported this reaction in 1959.

Diethyl azodicarboxylate, conventionally abbreviated as DEAD and sometimes as DEADCAT, is an organic compound with the structural formula CH3CH2−O−C(=O)−N=N−C(=O)−O−CH2CH3. Its molecular structure consists of a central azo functional group, RN=NR, flanked by two ethyl ester groups. This orange-red liquid is a valuable reagent but also quite dangerous and explodes upon heating. Therefore, commercial shipment of pure diethyl azodicarboxylate is prohibited in the United States and is carried out either in solution or on polystyrene particles.
Organosulfur chemistry is the study of the properties and synthesis of organosulfur compounds, which are organic compounds that contain sulfur. They are often associated with foul odors, but many of the sweetest compounds known are organosulfur derivatives, e.g., saccharin. Nature is abound with organosulfur compounds—sulfur is vital for life. Of the 20 common amino acids, two are organosulfur compounds, and the antibiotics penicillin and sulfa drugs both contain sulfur. While sulfur-containing antibiotics save many lives, sulfur mustard is a deadly chemical warfare agent. Fossil fuels, coal, petroleum, and natural gas, which are derived from ancient organisms, necessarily contain organosulfur compounds, the removal of which is a major focus of oil refineries.

In organic chemistry, a carbodiimide is a functional group with the formula RN=C=NR. On Earth they are exclusively synthetic, but in interstellar space the parent compound HN=C=NH has been detected by its maser emissions.
The Strecker amino acid synthesis, also known simply as the Strecker synthesis, is a method for the synthesis of amino acids by the reaction of an aldehyde with cyanide in the presence of ammonia. The condensation reaction yields an α-aminonitrile, which is subsequently hydrolyzed to give the desired amino acid. The method is used for the commercial production of racemic methionine from methional.
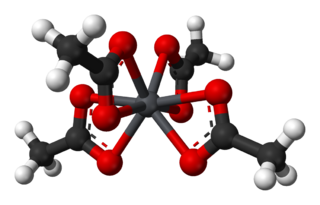
Lead(IV) acetate or lead tetraacetate is an metalorganic compound with chemical formula Pb(C2H3O2)4. It is a colorless solid that is soluble in nonpolar, organic solvents, indicating that it is not a salt. It is degraded by moisture and is typically stored with additional acetic acid. The compound is used in organic synthesis.
Acid–base extraction is a subclass of liquid–liquid extractions and involves the separation of chemical species from other acidic or basic compounds. It is typically performed during the work-up step following a chemical synthesis to purify crude compounds and results in the product being largely free of acidic or basic impurities. A separatory funnel is commonly used to perform an acid-base extraction.
In organic chemistry, a homologation reaction, also known as homologization, is any chemical reaction that converts the reactant into the next member of the homologous series. A homologous series is a group of compounds that differ by a constant unit, generally a methylene group. The reactants undergo a homologation when the number of a repeated structural unit in the molecules is increased. The most common homologation reactions increase the number of methylene units in saturated chain within the molecule. For example, the reaction of aldehydes or ketones with diazomethane or methoxymethylenetriphenylphosphine to give the next homologue in the series.

Pipecolic acid (piperidine-2-carboxylic acid) is an organic compound with the formula HNC5H9CO2H. It is a carboxylic acid derivative of piperidine and, as such, an amino acid, although not one encoded genetically. Like many other α-amino acids, pipecolic acid is chiral, although the S-stereoisomer is more common. It is a colorless solid.
Performic acid (PFA) is an organic compound with the formula CH2O3. It is an unstable colorless liquid which can be produced by mixing formic acid with hydrogen peroxide. Owing to its oxidizing and disinfecting action, it is used in the chemical, medical and food industries.

Oxazoline is a five-membered heterocyclic organic compound with the formula C3H5NO. It is the parent of a family of compounds called oxazolines, which contain non-hydrogenic substituents on carbon and/or nitrogen. Oxazolines are the unsaturated analogues of oxazolidines, and they are isomeric with isoxazolines, where the N and O are directly bonded. Two isomers of oxazoline are known, depending on the location of the double bond.

In organic chemistry, keto acids or ketoacids are organic compounds that contain a carboxylic acid group and a ketone group. In several cases, the keto group is hydrated. The alpha-keto acids are especially important in biology as they are involved in the Krebs citric acid cycle and in glycolysis.

Trichloroacetonitrile is an organic compound with the formula CCl3CN. It is a colourless liquid, although commercial samples often are brownish. It is used commercially as a precursor to the fungicide etridiazole. It is prepared by dehydration of trichloroacetamide. As a bifunctional compound, trichloroacetonitrile can react at both the trichloromethyl and the nitrile group. The electron-withdrawing effect of the trichloromethyl group activates the nitrile group for nucleophilic additions. The high reactivity makes trichloroacetonitrile a versatile reagent, but also causes its susceptibility towards hydrolysis.

N-Sulfinyl imines are a class of imines bearing a sulfinyl group attached to nitrogen. These imines display useful stereoselectivity reactivity and due to the presence of the chiral electron withdrawing N-sulfinyl group. They allow 1,2-addition of organometallic reagents to imines. The N-sulfinyl group exerts powerful and predictable stereodirecting effects resulting in high levels of asymmetric induction. Racemization of the newly created carbon-nitrogen stereo center is prevented because anions are stabilized at nitrogen. The sulfinyl chiral auxiliary is readily removed by simple acid hydrolysis. The addition of organometallic reagents to N-sulfinyl imines is the most reliable and versatile method for the asymmetric synthesis of amine derivatives. These building blocks have been employed in the asymmetric synthesis of numerous biologically active compounds.

Tris(2,2,2-trifluoroethyl) borate, also commonly referred to as the Sheppard amidation reagent, is a chemical compound with the formula B(OCH2CF3)3. This borate ester reagent is used in organic synthesis.












