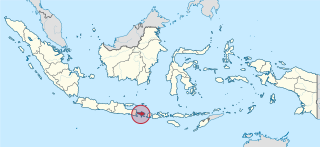
Bali is a province of Indonesia and the westernmost of the Lesser Sunda Islands. East of Java and west of Lombok, the province includes the island of Bali and a few smaller offshore islands, notably Nusa Penida, Nusa Lembongan, and Nusa Ceningan to the southeast. The provincial capital, Denpasar, is the most populous city in the Lesser Sunda Islands and the second-largest, after Makassar, in Eastern Indonesia. The upland town of Ubud in Greater Denpasar is considered Bali's cultural centre. The province is Indonesia's main tourist destination, with a significant rise in tourism since the 1980s. Tourism-related business makes up 80% of its economy.

Denpasar is the capital city of the province of Bali, Indonesia. Denpasar is the main gateway to the Bali island, the city is also a hub for other cities in the Lesser Sunda Islands.

Balinese Hinduism is the form of Hinduism practised by the majority of the population of Bali. This is particularly associated with the Balinese people residing on the island, and represents a distinct form of Hindu worship incorporating local animism, ancestor worship or Pitru Paksha, and reverence for Buddhist saints or Bodhisattava.

Ubud is a town on the Indonesian island of Bali in Ubud District, located amongst rice paddies and steep ravines in the central foothills of the Gianyar regency. Promoted as an arts and culture centre, it has developed a large tourism industry. It forms a northern part of the Greater Denpasar metropolitan area.

Besakih Temple is a pura complex in the village of Besakih on the slopes of Mount Agung in eastern Bali, Indonesia. It is the most important, largest, and holiest temple of Balinese Hinduism, and one of a series of Balinese temples. Perched nearly 1000 meters up the side of Gunung Agung, it is an extensive complex of 23 separate but related temples with the largest and most important being Pura Penataran Agung. The temple is built on six levels, terraced up the slope. The entrance is marked by a candi bentar, and beyond it, the Kori Agung is the gateway to the second courtyard.

Puputan is a Balinese term for a mass ritual suicide in preference to facing the humiliation of surrender. It originally seems to have meant a last desperate attack against a numerically superior enemy. Notable puputans in the history of Bali occurred in 1906 and 1908, when the Balinese were being subjugated by the Dutch.

The Dutch conquest of South Bali in 1906 was a Dutch military intervention in Bali as part of the Dutch colonial conquest of the Indonesian islands, killing an estimated 1,000 people. It was part of the final takeover of the Netherlands East-Indies. The campaign led to the deaths of the Balinese rulers of Badung and Tabanan kingdoms, their wives and children and followers. This conquest weakened the remaining independent kingdoms of Klungkung and Bangli, leading to their invasion two years later. It was the sixth Dutch military intervention in Bali.

Pura Ulun Danu Batur is a Hindu Balinese temple located on the island of Bali, Indonesia. As one of the Pura Kahyangan Jagat, Pura Ulun Danu Batur is one of the most important temples in Bali which acted as the maintainer of harmony and stability of the entire island. Pura Ulun Danu Batur represents the direction of the North and is dedicated to the god Vishnu and the local goddess Dewi Danu, goddess of Lake Batur, the largest lake in Bali. Following the destruction of the original temple compound, the temple was relocated and rebuilt in 1926. The temple, along with 3 other sites in Bali, form the Cultural Landscape of Bali Province which was inscribed as a World Heritage Site by UNESCO in 2012.

A Pura is a Balinese Hindu temple, and the place of worship for adherents of Balinese Hinduism in Indonesia. Puras are built following rules, style, guidance, and rituals found in Balinese architecture. Most puras are found on the island of Bali, where Hinduism is the predominant religion; however many puras exist in other parts of Indonesia where significant numbers of Balinese people reside. Mother Temple of Besakih is the most important, largest, and holiest temple in Bali. Many Puras have been built in Bali, leading it to be titled "the Island of a Thousand Puras".

Balinese architecture is a vernacular architecture tradition of Balinese people that inhabits the volcanic island of Bali, Indonesia. Balinese architecture is a centuries-old architectural tradition influenced by Balinese culture developed from Hindu influences through ancient Javanese intermediary, as well as pre-Hindu elements of native Balinese architecture.
The Kingdomship of Bali was a series of Hindu-Buddhist kingdoms that once ruled some parts of the volcanic island of Bali, in Lesser Sunda Islands, Indonesia. With a history of native Balinese kingship spanning from the early 10th to early 20th centuries, Balinese kingdoms demonstrated sophisticated Balinese court culture where native elements of spirit and ancestral reverence combined with Hindu influences—adopted from India through ancient Java intermediary—flourished, enriched and shaped Balinese culture.

Candi bentar, or split gateway, is a classical Javanese and Balinese gateway entrance commonly found at the entrance of religious compounds, palaces, or cemeteries in Indonesia. It is basically a candi-like structure split perfectly in two to create a passage in the center for people to walk through. In contrast to the very ornate shape and decoration of the main faces, the sides of the passage are left completely plain. The passage is usually elevated with a flight of stairs to reach it. A candi bentar is commonly found in Java, Bali, and Lombok.

Pura Kehen is a Balinese Hindu temple located in Cempaga, Bangli Regency, Bali. The temple is set on the foot of a wooded hill, about 2 kilometres (1.2 mi) north of the town center. Established at least in the 13th-century, Pura Kehen was the royal temple of the Bangli Kingdom, now the Regency of Bangli.

Pura Goa Lawah is a Balinese Hindu temple or a pura located in Klungkung, Bali, Indonesia. Pura Goa Lawah is often included among the Sad Kahyangan Jagad, or the "six sanctuaries of the world", the six holiest places of worship on Bali. Pura Goa Lawah is noted for built around a cave opening which is inhabited by bats, hence its name, the Goa Lawah or "bat cave".
Pura Dalem Sakenan is a pura located at the north-western shore of Serangan, a small island about 10 kilometres (6.2 mi) south of Denpasar, Bali. Pura Dalem Sakenan is dedicated to [rambut sedhana] and is associated with prosperity. Pura Dalem Sakenan is the focus temple of the 210-day Piodalan festival where in the past processions of pilgrims visited the island on foot or by traditional colorful wooden boats called jukung. With the construction of the bridge connecting the Serangan island with Bali as well as the reclamation of the island, the use of colorful jukung for pilgrimage has died out.
Pura Pulaki is a Balinese Hindu temple or a pura located to the west of Singaraja, Bali, Indonesia. The temple is set on flat land with rocky outcrops as the backdrop. Pura Pulaki is a pura segara or Balinese sea temples, set around the island to form a chain of temples which protect the island.

Pura Maospahit is a Balinese Hindu temple or pura located in Denpasar, Bali. The pura is known for its bare red brick architecture, reminiscent of the architecture of the 13th-century Majapahit Kingdom, hence the name. Pura Maospahit is the only pura in Bali which was built using a concept known as Panca Mandala where the most sacred area is situated at the center instead of at the direction of the mountain.

Pura Dalem Segara Madhu also known as Pura Dalem Jagaraga is a northern Balinese Hindu temple or pura located in the village of Jagaraga, Buleleng in northern Bali. It is about 11 km east of Singaraja. The village of Jagaraga is known historically as the place where the Dutch colonial government witnesses puputan or Balinese mass-suicide following their military attack on the kingdom of Bali in 1849. Pura Dalem Segara Madhu is known for its intensive wall decoration typical of northern Balinese architecture and for its unique western-influenced relief e.g. motifs of early 20th-century airplanes and automobiles.

Pura Dasar Buana is a Balinese Hindu temple or pura located in Gelgel, Bali, about 3 kilometres (1.9 mi) from Semarapura. Pura Dasar Buana is one of the Pura Dang Kahyangan Jagat, a temple which was built to honor a holy teacher of Hindu teaching. Pura Dasar Buana honored Mpu Ghana, a Brahmin who arrived to Bali from Javanese Majapahit to teach Hinduism in the island.

Bali Arts Festival or PKB is an annual arts festival in Bali, Indonesia that celebrates, preserves and develops Balinese art and culture. First held in 1979 it has become Indonesia's longest-running arts festival. The month-long event begins with an inaugural parade usually held on the grounds of the Bajra Sandhi Monument and continues in its main venue, Taman Werdhi Budaya Art Centre, Denpasar. Traditional Balinese artists perform daily, as do performers from other parts of Indonesia and other countries. The festival also features competitions, seminars, and exhibitions of art, handicrafts and authentic Balinese cuisine.



















