
Negros Occidental, officially the Province of Negros Occidental, is a province in the Philippines located in the Negros Island Region. Its capital is the city of Bacolod, of which it is geographically situated and grouped under by the Philippine Statistics Authority, but remains politically independent from the provincial government and also one of the two regional centers in Negros Island Region. It occupies the northwestern half of the large island of Negros, and borders Negros Oriental, which comprises the southeastern half. Known as the "Sugarbowl of the Philippines", Negros Occidental produces more than half the nation's sugar output.

Silay, officially the City of Silay, is a 3rd class component city in the province of Negros Occidental, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 130,478 people.

Talisay, officially the City of Talisay, is a fourth class component city in the province of Negros Occidental, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 108,909 people.

Aniceto Ledesma Lacson is a Filipino revolutionary general, sugar farmer, and businessman. He is known as the first and only president of the Negros Republic from 1898 to 1901, and for leading the Negros Revolution alongside Juan Araneta.

The Negros Revolution, commemorated and popularly known as the Fifth of November or Negros Day, was a political movement that in 1898 created a government on Negros Island in the Philippines, ending Spanish control of the island and paving the way for a republican government run by the Negrense natives. The newly established Negros Republic lasted for approximately three months. American forces landed on the island unopposed on February 2, 1899, ending the island's independence. Negros was then annexed to the Philippine Islands on 20 April 1901.
Yves Leopold Germain Gaston was the patriarch of a large family with roots in the City of Silay, in the province of Negros Occidental, Philippines.

The Mariano Ramos Ancestral House is the home of the late Mariano Ramos, one of the first appointed Presidente Municipals of Bacolod, Philippines. The house was built in the 1930s with its architecture being a combination of Castilian and Tuscan styles. It comprises three storeys including the tower room, known as the torre or mirador.
The Negrenses are the native cultural group of the Philippine provinces of Negros Occidental, Negros Oriental and Siquijor.

Metro Bacolod is the 8th-most populous and the 6th-most densely populated metropolitan area out of the 12 metropolitan areas in the Philippines. This metropolitan area as defined by the National Economic and Development Authority (NEDA) has an estimated population of 840,170 inhabitants as of the 2020 official census by the Philippine Statistics Authority.

Ancestral houses of the Philippines or Heritage Houses are homes owned and preserved by the same family for several generations as part of the Filipino family culture. It corresponds to long tradition by Filipino people of giving reverence for ancestors and elders. Houses could be a simple house to a mansion. The most common ones are the "Bahay na Bato". Some houses of prominent families had become points of interest or museums in their community because of its cultural, architectural or historical significance. These houses that are deemed of significant importance to the Filipino culture are declared Heritage House by the National Historical Commission of the Philippines (NHCP), previously known as the National Historical Institute (NHI) of the Philippines. Preservation is of utmost importance as some ancestral houses have come into danger due to business people who buy old houses in the provinces, dismantle them then sell the parts as ancestral building materials for homeowners wishing to have the ancestral ambiance on their houses. These ancestral houses provide the current generation a look back of the country's colonial past through these old houses.
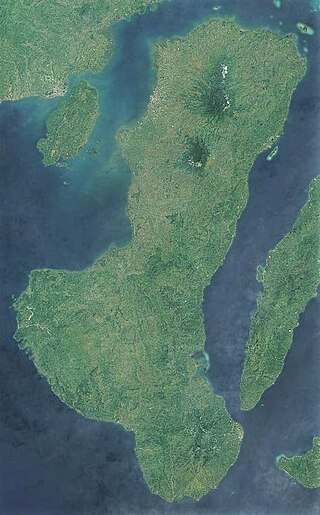
Negros is the fourth largest and third most populous island in the Philippines, with a total land area of 13,309 km2 (5,139 sq mi). The coastal zone of the southern part of Negros is identified as a site of highest marine biodiversity importance in the Coral Triangle.

The Cesar Lacson Locsin Ancestral House is a heritage house known to be the home of El Ideal Bakery, the oldest bakery along Rizal and Eusebio Streets, National Highway, Silay, Negros Occidental, Philippines. The bakery is known for its guapple pie and several other local delicacies and sweets.

Hacienda Rosalia, also known as Hacienda Santa Rosalia, is a compound where the ancestral home mansion of Gaston family and the Church of Cartwheels are located. It is situated in Manapla, Negros Occidental, Philippines. The mansion was built in 1930s.

The Lacson Ruins are the remains of the ancestral mansion of Don Mariano Ledesma Lacson and Maria Braga Lacson. It is situated in Talisay, Negros Occidental, Philippines. The mansion was built in early 1900s and inspired by Italian architecture.
The Museo Negrense de La Salle is located within the campus of the University of St. La Salle in Bacolod, Philippines beside the St. La Salle Coliseum. It is the only school-based museum in the Negros region.
The Dizon-Ramos Museum is situated in Bacolod, Negros Occidental, Philippines beside the Mariano Ramos Ancestral House.

The Silliman Hall is a building constructed in the Stick Style of American architecture in Dumaguete, Negros Oriental, Philippines. It was built in the early 1900s. It was converted to a museum in 1970. It is located in Dumaguete, Negros Oriental, Philippines.

Dr. Jose Corteza Locsin Ancestral House is a two-storey house built in the 1930s in Silay, Negros Occidental Philippines. It has been named as a Heritage Houses of the Philippines by the National Historical Commission of the Philippines. It was the home of Jose Locsin (1891–1977), a Filipino medical doctor and senator.
Philippines National Historic Landmarks is a registry of historic sites in the Philippines that have been officially declared by the Philippine Registry of Cultural Property.

The Tana Dicang House, also known as Balay ni Tana Dicang, is a stone house or bahay na bato in Talisay, Negros Occidental, Philippines. The house was named after its original female owner Enrica Lizares, nicknamed Dicang. "Tana”, a shortened version of kapitana, refers to Dicang's status as a female community leader.




















