
Cue sports are a wide variety of games of skill played with a cue, which is used to strike billiard balls and thereby cause them to move around a cloth-covered table bounded by elastic bumpers known as cushions. Cue sports are also collectively referred to as billiards, though this term has more specific connotations in some varieties of English.

The foot is an anatomical structure found in many vertebrates. It is the terminal portion of a limb which bears weight and allows locomotion. In many animals with feet, the foot is a separate organ at the terminal part of the leg made up of one or more segments or bones, generally including claws and/or nails.

A bunion, also known as hallux valgus, is a deformity of the MTP joint connecting the big toe to the foot. The big toe often bends towards the other toes and the joint becomes red and painful. The onset of bunions is typically gradual. Complications may include bursitis or arthritis.

A callus is an area of thickened and sometimes hardened skin that forms as a response to repeated friction, pressure, or other irritation. Since repeated contact is required, calluses are most often found on the feet and hands, but they may occur anywhere on the skin. Some degree of callus, such as on the bottom of the foot, is normal.

Pes cavus, also known as high arch, is an orthopedic condition that presents as a hollow arch underneath the foot with a pronounced high ridge at the top when weight bearing.

Pointe technique is part of classical ballet involving a technique that concerns pointe work, in which a ballet dancer supports all body weight on the tips of fully extended feet when wearing pointe shoes. A dancer is said to be en pointe when the body is supported in this manner, and a fully extended vertical foot is said to be en pointe when touching the floor, even when not bearing weight.
Navicular syndrome, often called navicular disease, is a syndrome of lameness problems in horses. It most commonly describes an inflammation or degeneration of the navicular bone and its surrounding tissues, usually on the front feet. It can lead to significant and even disabling lameness.

High-heeled shoes, also known as high heels, are a type of shoe with an upward-angled sole. The heel in such shoes is raised above the ball of the foot. High heels cause the legs to appear longer, make the wearer appear taller, and accentuate the calf muscle.
Metatarsalgia, literally 'metatarsal pain' and colloquially known as a stone bruise, is any painful foot condition affecting the metatarsal region of the foot. This is a common problem that can affect the joints and bones of the metatarsals.

Morton's neuroma is a benign neuroma of an intermetatarsal plantar nerve, most commonly of the second and third intermetatarsal spaces, which results in the entrapment of the affected nerve. The main symptoms are pain and/or numbness, sometimes relieved by ceasing to wear footwear with tight toe boxes and high heels. The condition is named after Thomas George Morton, though it was first correctly described by a chiropodist named Durlacher.

A rack is a piece of equipment that is used to place billiard balls in their starting positions at the beginning of a pocket billiards game. Rack may also be used as a verb to describe the act of setting billiard balls in their starting positions, or as a noun to describe a set of balls that are in their starting positions.
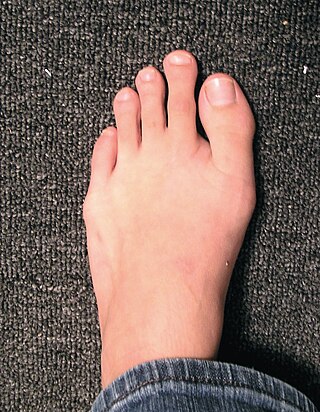
Morton's toe is the condition of having a first metatarsal bone that is shorter than the second metatarsal. It is a type of brachymetatarsia. This condition is the result of a premature closing of the first metatarsal's growth plate, resulting in a short big toe, giving the second toe the appearance of being long compared to the first toe.

Tiptoe describes the human body posture and locomotion of removing the heel(s) of one or both feet from the ground. The term is mostly used colloquially when the weight is placed on the balls of the feet rather than literally on the tips of the toes; literal tip-toeing is difficult but possible, as in the pointe technique of ballet. In running, landing on the ball of the foot is known as forefoot strike.
Hallux rigidus or stiff big toe is degenerative arthritis and stiffness due to bone spurs that affects the metatarsophalangeal joints (MTP) at the base of the hallux.

Tailor's bunion, also known as digitus quintus varus or bunionette, is a condition caused as a result of inflammation of the fifth metatarsal bone at the base of the little toe.

March fracture is the fracture of the distal third of one of the metatarsal bones occurring because of recurrent stress. It is more common in soldiers, but also occurs in hikers, organists, and other people whose duties entail much standing. March fractures most commonly occur in the second and third metatarsal bones of the foot. It is a common cause of foot pain, especially when people suddenly increase their activities.

Diabetic shoes are specially designed shoes, or shoe inserts, intended to reduce the risk of skin breakdown in diabetics with existing foot disease and relieve pressure to prevent diabetic foot ulcers.

Comparative foot morphology involves comparing the form of distal limb structures of a variety of terrestrial vertebrates. Understanding the role that the foot plays for each type of organism must take account of the differences in body type, foot shape, arrangement of structures, loading conditions and other variables. However, similarities also exist among the feet of many different terrestrial vertebrates. The paw of the dog, the hoof of the horse, the manus (forefoot) and pes (hindfoot) of the elephant, and the foot of the human all share some common features of structure, organization and function. Their foot structures function as the load-transmission platform which is essential to balance, standing and types of locomotion.

Syndesmosis procedure is one of the more than twenty bunion surgeries currently being performed. While the majority of bunion surgeries involve the breaking and shifting of bones, syndesmosis procedure is one of few surgical techniques that use a soft-tissue or non-osteotomy (non-bone-breaking) approach to afford the same correction. More than 130 different surgical techniques have been described for correction of one single condition of the foot: the bunion deformity.

The toe box is the section of footwear that surrounds the toes on closed-toe shoes. Toe boxes that are too tight can cause injuries and foot deformities, whereas wider toe boxes may be used to treat or prevent common foot conditions such as Morton's neuroma. Toe boxes come in a variety of shapes and styles of construction, some of which are a matter of fashion, and some of which are designed for specialized functions.


















