
Lithuania is a Northern country on the south-eastern shore of the Baltic Sea, a member of the United Nations Organisation, the Organisation for Security and Cooperation in Europe, the European Union, the North Atlantic Treaty Organisation, the World Trade Organisation. Currently, Lithuania maintains diplomatic relations with 186 states Lithuania became a member of the United Nations on 18 September 1991, and is a signatory to a number of its organizations and other international agreements. It is also a member of the Organization for Security and Cooperation in Europe, NATO and its adjunct North Atlantic Coordinating Council, the Council of Europe, and the European Union. Lithuania gained membership in the World Trade Organization on 31 May 2001.

The Council of the Baltic Sea States (CBSS) is a regional intergovernmental organisation working on three priority areas: Regional Identity, Safe & Secure Region and Sustainable & Prosperous Region. These three priority areas aim to address the themes of sustainable development, environment, sustainable maritime economy, education, labour, culture, youth engagement, civil security, children's rights and trafficking in human beings.

Agenda 21 is a non-binding action plan of the United Nations with regard to sustainable development. It is a product of the Earth Summit held in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, in 1992. It is an action agenda for the UN, other multilateral organizations, and individual governments around the world that can be executed at local, national, and global levels. One major objective of the Agenda 21 initiative is that every local government should draw its own local Agenda 21. Its aim initially was to achieve global sustainable development by 2000, with the "21" in Agenda 21 referring to the original target of the 21st century.

The Baltic states or the Baltic countries is a modern unofficial geopolitical term, typically used to group three countries: Estonia, Latvia, and Lithuania. All three countries are members of NATO, the European Union, the Eurozone, and the OECD. The three sovereign states on the eastern coast of the Baltic Sea are sometimes referred to as the "Baltic nations", less often and in historical circumstances also as the "Baltic republics", the "Baltic lands", or simply the Baltics.

The terms Baltic Sea Region, Baltic Rim countries, and the Baltic Sea countries/states refer to slightly different combinations of countries in the general area surrounding the Baltic Sea, mainly in Northern and Eastern Europe.
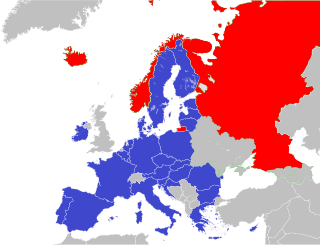
The Northern Dimension is a joint policy between four equal partners - the European Union, Russia, Norway and Iceland - regarding the cross-border and external policies geographically covering North-West Russia, the Baltic Sea and the Arctic regions, including the Barents region. The ND Policy was initiated in 1999 and renewed in 2006. The Northern Dimension addresses the specific challenges and opportunities arising in those regions and aims to strengthen dialogue and cooperation between the EU and its member states, the northern countries associated with the EU under the European Economic Area and Russia. A particular emphasis is placed on subsidiarity, and on ensuring the active participation of all stakeholders in the North, including regional organizations, local and regional authorities, the academic and business communities, and civil society.

Small Island Developing States (SIDS) are a group of developing countries that are small island countries which tend to share similar sustainable development challenges. These include small but growing populations, limited resources, remoteness, susceptibility to natural disasters, vulnerability to external shocks, excessive dependence on international trade, and fragile environments. Their growth and development is also held back by high communication, energy and transportation costs, irregular international transport volumes, disproportionately expensive public administration and infrastructure due to their small size, and little to no opportunity to create economies of scale. They consist of some of the most vulnerable countries to climate change.

The Baltic Assembly (BA) is a regional organisation that promotes intergovernmental cooperation between Estonia, Latvia, and Lithuania. It attempts to find a common position in relation to many international issues, including economic, political and cultural issues. The decisions of the assembly are advisory.

The United Nations Forum on Forests (UNFF) is a high-level intergovernmental policy forum. The forum includes all United Nations member states and permanent observers, the UNFF Secretariat, the Collaborative Partnership on Forests, Regional Organizations and Processes and Major Groups.
The Baltic Development Forum is an independent think-tank and non-profit high-level and agenda-setting networking organisation with strategic partners and sponsors from large companies, major cities, institutional investors, business associations and academia in the Baltic Sea Region. The network involves more than 8,000 decision-makers from all over the region and beyond.
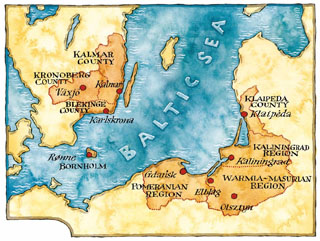
The Euroregion Baltic (ERB) refers to a cross-border Euroregion in the south-east of the Baltic Sea Region, consisting of eight regions of Denmark, Lithuania, Poland, Russia, and Sweden.

Estonia, officially the Republic of Estonia, is a country in Northern Europe. It is bordered to the north by the Gulf of Finland across from Finland, to the west by the Baltic Sea across from Sweden, to the south by Latvia, and to the east by Lake Peipus and Russia. The territory of Estonia consists of the mainland, the larger islands of Saaremaa and Hiiumaa, and over 2,200 other islands and islets on the eastern coast of the Baltic Sea, covering a total area of 45,339 square kilometres (17,505 sq mi). The capital city Tallinn and Tartu are the two largest urban areas of the country. The Estonian language is the autochthonous and the official language of Estonia; it is the first language of the majority of its population, as well as the world's second most spoken Finnic language.

The Northern Dimension Partnership in Public Health and Social Well-being (NDPHS) is an international networking platform for strengthening professional connections, sharing and co-creating knowledge, and developing joint activities in public health and social well-being. The Partnership is served by the NDPHS Secretariat that was established in 2012 as an international legal entity hosted by the Swedish Government located in Stockholm and funded jointly by the Partner Countries.

Nordic-Baltic Eight (NB8) is a regional co-operation format that includes Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Iceland, Latvia, Lithuania, Norway, and Sweden. Under NB8, regular meetings are held of the Baltic and Nordic countries' Prime Ministers, Speakers of Parliaments, Foreign Ministers, branch ministers, Secretaries of State and political directors of Foreign Ministries, as well as expert consultations where regional issues and current international topics are reviewed.

The Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) or Global Goals are a collection of 17 interlinked global goals designed to be a "shared blueprint for peace and prosperity for people and the planet, now and into the future". The SDGs were set up in 2015 by the United Nations General Assembly (UN-GA) and are intended to be achieved by 2030. They are included in a UN-GA Resolution called the 2030 Agenda or what is colloquially known as Agenda 2030. The SDGs were developed in the Post-2015 Development Agenda as the future global development framework to succeed the Millennium Development Goals which were ended in 2015.
Habitat III, the United Nations Conference on Housing and Sustainable Urban Development, took place in Quito, Ecuador, from 17 – 20 October 2016.

The Baltic Sea Parliamentary Conference (BSPC) was established in 1991 as a forum for political dialogue between parliamentarians from the Baltic Sea Region. BSPC aims at raising awareness and opinion on issues of current political interest and relevance for the Baltic Sea Region. It promotes and drives various initiatives and efforts to support a sustainable environmental, social and economic development of the Baltic Sea Region. It strives at enhancing the visibility of the Baltic Sea Region and its issues in a wider European context.

The Barents Euro-Arctic Council (BEAC) is the official body for inter-governmental co-operation in the Barents Region. It seeks solutions wherever and whenever the countries can achieve more together than by working on their own. Cooperation in the Barents Euro-Arctic Region was launched in 1993 on two levels: intergovernmental Barents Euro-Arctic Council (BEAC) and interregional Barents Regional Council (BRC). The overall objective of Barents cooperation has been sustainable development.

Tourism in Estonia refers to the overall state of the tourism industry in the Baltic nation of Estonia. It is a key part of the country's economy, contributing 7.8% to its GDP, and employing 4.3% of its population. In 2018, tourism and other related services counted for over 10.8 percent of Estonia's exports. Tourism is increasing rapidly in Estonia: the number of tourist arrivals—both domestic and international—has increased from 2.26 million in 2006 to 3.79 million in 2019. Estonia was also ranked the 15th-most safest country to visit in 2017, according to safedestinations.com, scoring 8.94 out of 10 on their list. In a 2018 report published by the OECD, they concluded that most international tourists come from places like Finland, Russia, Latvia, Germany, and Sweden.
















