
Aconitum, also known as aconite, monkshood, wolfsbane, leopard's bane, devil's helmet, or blue rocket, is a genus of over 250 species of flowering plants belonging to the family Ranunculaceae. These herbaceous perennial plants are chiefly native to the mountainous parts of the Northern Hemisphere in North America, Europe, and Asia, growing in the moisture-retentive but well-draining soils of mountain meadows.
Pyrethrum was a genus of several Old World plants now classified in either Chrysanthemum or Tanacetum which are cultivated as ornamentals for their showy flower heads. Pyrethrum continues to be used as a common name for plants formerly included in the genus Pyrethrum. Pyrethrum is also the name of a natural insecticide made from the dried flower heads of Chrysanthemum cinerariifolium and Chrysanthemum coccineum. The insecticidal compounds present in these species are pyrethrins.

Delphinium is a genus of about 300 species of annual and perennial flowering plants in the family Ranunculaceae, native throughout the Northern Hemisphere and also on the high mountains of tropical Africa. The genus was erected by Carl Linnaeus.

Arnica is a genus of perennial, herbaceous plants in the sunflower family (Asteraceae). The genus name Arnica may be derived from the Greek arni, "lamb", in reference to the plants' soft, hairy leaves. Arnica is also known by the names mountain tobacco and, confusingly, leopard's bane and wolfsbane—two names that it shares with the entirely unrelated genus Aconitum.

Arnica montana, also known as wolf's bane, leopard's bane, mountain tobacco and mountain arnica, is a moderately toxic European flowering plant in the daisy family Asteraceae that has a large yellow flower head. The names "wolf's bane" and "leopard's bane" are also used for another plant, Aconitum, which is extremely poisonous.

Cicuta virosa, the cowbane or northern water hemlock, is a poisonous species of Cicuta, native to northern and central Europe, northern Asia and northwestern North America.

Eranthis is a genus of eight species of flowering plants in the buttercup family Ranunculaceae, native to southern Europe and east across Asia to Japan. The common name winter aconite comes from the early flowering time and the resemblance of the leaves to those of the related genus Aconitum, the true aconite. Like the notoriously toxic AconitumEranthis is poisonous, although its chemistry is different, the toxic compounds present being mainly cardiac glycosides of the bufadienolide group similar to those found in Adonis vernalis, rather than the virulent alkaloids of Aconitum.

Cicuta, commonly known as water hemlock, is a genus of four species of highly poisonous plants in the family Apiaceae. They are perennial herbaceous plants which grow up to 2.5 meters (8 ft) tall, having distinctive small green or white flowers arranged in an umbrella shape (umbel). Plants in this genus may also be referred to as cowbane or poison parsnip. Cicuta is native to temperate regions of the Northern Hemisphere, mainly North America and Europe, typically growing in wet meadows, along streambanks and other wet and marshy areas. These plants bear a close resemblance to other members in the family Apiaceae and may be confused with a number of edible or poisonous plants. The common name hemlock may also be confused with poison hemlock, or with the Hemlock tree.

Aconitum anthora, variously known as anthora, yellow monkshood, or healing wolfsbane, is a yellow flowering plant species of the genus Aconitum in the family Ranunculaceae.

Aconitum lycoctonum is a species of flowering plant in the genus Aconitum, of the family Ranunculaceae, native to much of Europe and northern Asia. It is found in lowlands to the subalpine zone, mainly in forests and shaded habitats. Along with A. napellus, A. lycoctonum is of the most common European species of the Aconitum genus. They are also grown ornamentally in gardens, thriving well in ordinary garden soil. As such, A. lycoctonum can be found in North America, especially in eastern Canada, often in old gardens or as garden escapees.

Doronicum is a genus of flowering plants in the sunflower family, known as leopard's bane. They are all herbaceous perennials native to Europe, southwest Asia and Siberia. They produce yellow, daisy-like flowerheads in spring and summer.

Doronicum orientale, the leopard's bane, is a European plant species in the family Asteraceae.

Staphisagria macrosperma, formerly known as Delphinium staphisagria, is a species of Staphisagria of the family Ranunculaceae. It used to belong to the subgenus or section Staphisagria of the genus Delphinium, but molecular evidence suggests Staphisagria should be a genus which is a sister group to the Aconitum-Delphinium clade. It is described botanically as a stoutly-stemmed, hairy biennial with large palmate leaves up to 6 inches (15 cm) across. The flowers are mauve-blue to blue, short-spurred, and up to 1 inch (2.5 cm) across, occurring in racemes. The plant grows to a height of 4–5 feet. It grows throughout the Mediterranean. All parts of this plant are highly toxic and should not be ingested in any quantity.
Leopard's bane or leopard's-bane may refer to:

Aconitum napellus, monkshood, aconite, Venus' chariot or wolfsbane, is a species of highly toxic flowering plants in the genus Aconitum of the family Ranunculaceae, native and endemic to western and central Europe. It is an herbaceous perennial plant growing to 1 m tall, with hairless stems and leaves. The leaves are rounded, 5–10 cm (2.0–3.9 in) diameter, palmately divided into five to seven deeply lobed segments. The flowers are dark purple to bluish-purple, narrow oblong helmet-shaped, 1–2 cm (0.39–0.79 in) tall. Plants native to Asia and North America formerly listed as A. napellus are now regarded as separate species. The plant is extremely poisonous in both ingestion and body contact. It is the most poisonous plant in all of Europe.

Doronicum grandiflorum is a European species of Doronicum, a member of the family Asteraceae.

Curio rowleyanus, syn. Senecio rowleyanus, is a flowering plant in the daisy family Asteraceae. It is a creeping, perennial, succulent vine native to the Cape Provinces of South Africa. In its natural environment its stems trail on the ground, rooting where they touch and form dense mats. It often avoids direct sunlight by growing in the shade of other plants and rocks. It is commonly known as string-of-pearls or string-of-beads.
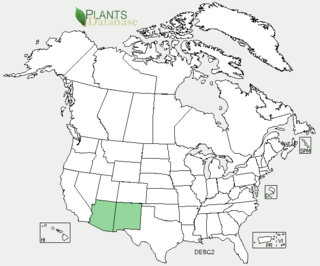
Delphinium scopulorum, commonly known as Rocky Mountain larkspur, is a species of wildflower in the genus Delphinium, which belongs to the buttercup family, Ranunculaceae. It is native to the Southwestern United States and found predominantly in upper-elevation moist meadows.

Doronicum plantagineum, the plantain-leaved leopard's-bane or plantain false leopardbane, is a European plant species in the sunflower family. It is native to southeastern Europe from Greece and Italy to Ukraine and the Czech Republic. There are reports of the species being naturalized in the State of Oregon in the northwestern United States.

Doronicum pardaliances, known as leopard's-bane, is a species of flowering plant in the family Asteraceae. Like other members of the genus Doronicum, it is a rhizomatous herbaceous perennial. It has upright stems growing to 80 cm (31 in), with heart-shaped basal leaves and yellow flowers, generally 3–4 cm (1.2–1.6 in) across. It is native to western Europe and was introduced to the British Isles, where it was first recorded in Northumberland in 1633.
















