
Mantidae is one of the largest families in the order of praying mantises, based on the type species Mantis religiosa; however, most genera are tropical or subtropical. Historically, this was the only family in the order, and many references still use the term "mantid" to refer to any mantis. Technically, however, "mantid" refers only to members of the family Mantidae, and not the 14 remaining families of mantises. Some of the most recent classifications have promoted a number of the mantid subfamilies to the rank of family, e.g. Iridopterygidae, Sibyllidae, Tarachodidae, Thespidae, and Toxoderidae, while other classifications have reduced the number of subfamilies without elevating to higher rank.

Empusidae is a family of plant-mimicking mantises, consisting of 10 genera, holding almost 30 species. Unlike many other mantis families, the Empusidae are a monophyletic lineage. Empusidae mantises are ambush predators, with mouthparts adapted to feeding on other insects and small animals. The majority of Empusidae species are distributed throughout Africa, but they are also found in Southeast Asia and in the southern parts of Europe.

Amorphoscelidae is a family of mantises in the order Mantodea.

Acontista is a genus of mantises in the family Acanthopidae.

Amorphoscelis is a genus of praying mantis in the family Amorphoscelidae; records of occurrence are from Africa and tropical Asia.
Bantia is a genus of mantises in the family Thespidae.
Bantia fusca is a species of praying mantis in the genus Bantia in the family Thespidae.
Bantia marmorata is a species of praying mantis in the family Thespidae.
Bantia metzi is a species of praying mantis in the family Thespidae.

Bantia michaelisi is a species of praying mantis in the family Thespidae.
Bantia nana is a species of praying mantis in the family Thespidae.
Bantia pygmaea is a species of praying mantis in the family Thespidae.
Bantia simoni is a species of praying mantis in the family Thespidae.
Bantia werneri is a species of praying mantis in the family Thespidae.
Cilnia chopardi is a species of praying mantis in the family Miomantidae.
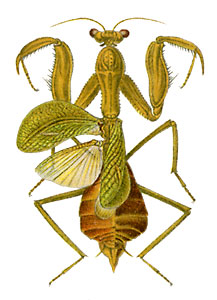
Cilnia is a genus of praying mantises in the family Miomantidae that is native to Africa.

Thespidae is a family of Neotropical insects in the order Mantodea. Following a major revision of this order in 2019, the old-world subfamilies Haaniinae and Hoplocoryphinae, previously placed here, have been upgraded to family level.

The bark mantises and ground mantises are praying mantids now placed in the family Eremiaphilidae that are native to the Afrotropics. They are generally light brown but more silvery on the wings. The wings are attractively reticulated, and the veins may be mottled dark and pale. The head is wider than the pronotum, which is rounded anteriorly, and doesn't overlap with the rear of the head. The pronotum is depressed, with its sides more or less parallel, and only a weak supra-coxal bulge is present. The anterior tibia are flattened and greatly expanded longitudinally, and the tibial claw does not fit into a pit between the 1st and 2nd external spines of the anterior femora, as in a few mantis groups.

Mantises are an order (Mantodea) of insects that contains over 2,400 species in about 460 genera in 33 families. The largest family is the Mantidae ("mantids"). Mantises are distributed worldwide in temperate and tropical habitats. They have triangular heads with bulging eyes supported on flexible necks. Their elongated bodies may or may not have wings, but all Mantodea have forelegs that are greatly enlarged and adapted for catching and gripping prey; their upright posture, while remaining stationary with forearms folded, has led to the common name praying mantis.










