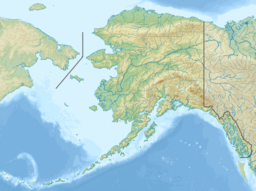
Sitka is a unified city-borough in the southeast portion of the U.S. state of Alaska. It was under Russian rule from 1799 to 1867. The city is situated on the west side of Baranof Island and the south half of Chichagof Island in the Alexander Archipelago of the Pacific Ocean. As of the 2020 census, Sitka had a population of 8,458, the fifth-most populated city in the state.

The Alexander Archipelago is a 300-mile (480 km) long archipelago in North America lying off the southeastern coast of Alaska. It contains about 1,100 islands, the tops of submerged coastal mountains that rise steeply from the Pacific Ocean. Deep channels and fjords separate the islands and cut them off from the mainland. The islands shelter the northern part of the Inside Passage as it winds its way among them.

The Kvichak River (Yup'ik: Kuicaraq) is a large river, about 50 miles (80 km) long, in southwestern Alaska in the United States. It flows southwest from Lake Iliamna to Kvichak Bay, an arm of Bristol Bay, on the Alaska Peninsula. The communities of Igiugig and Levelock lie along the Kvichak River. The Kvichak is navigable along its entire length, and is used as a short cut by boats getting between Cook Inlet and Bristol Bay via the Lake Iliamna portage.

Baranof Warm Springs is a small, primarily seasonally-occupied community located in the city and borough of Sitka, Alaska, on the eastern side of Baranof Island, from which it likely derives its name, in the Alexander Archipelago. It is occasionally referred to simply as Baranof. Baranof Warm Springs is located at 57°05′22″N134°49′59″W.

Baranof River is a glacially-fed river on the eastern side of Baranof Island, in the Alexander Archipelago, in the Alaska Panhandle. The source of the river is the unnamed icefields surrounding Peak 5390. Baranof River feeds into Baranof Lake, and the outlet of Baranof Lake that feeds into Warm Springs Bay is also commonly referred to as Baranof River as well.

Medvejie Lake is a long, narrow, snow-fed lake on Baranof Island just south of Sitka, Alaska in the Alaskan Panhandle, which drains into Silver Bay, eight miles (13 km) southeast of Sitka, on west coast of Baranof Island, Alexander Archipelago.

Mount Bassie is a large mountain in the center of Baranof Island, Alaska, United States, within the City and Borough of Sitka.

Warm Springs Bay is a 2.4 mile-long bay located just outside the small community of Baranof Warm Springs on Baranof Island in the Alexander Archipelago, Alaska. Warm Springs Bay receives the outflow of Baranof Lake and Baranof River. Warm Springs Bay is located at 57°04′49″N134°48′12″W.
Mount Furuhelm is a 3,620 foot peak located on Baranof Island just east and adjacent to Peak 5390 in Alaska. It is located at 57°03′00″N134°55′47″W.
Silver Bay, or Gaǥeit', in the Tlingit language, is a deep water fjord located southeast of Sitka, Alaska, United States, that indents Baranof Island. It was named through a United States Coast and Geodetic Survey translation of Bukhta Serebryanikova, a name published first by Captain Tebenkov of the Imperial Russian Navy in 1852.
The Tubutulik River is a waterway in the U.S. state of Alaska. The 25-mile (40 km) long river is situated on the Seward Peninsula. It flows southeastwards to the Kwiniuk Inlet at the northwestern end of Norton Bay, 25 miles (40 km) southwest of Koyuk in the Bering Sea. Its Inuit name was reported as "Tubuktulik" in 1849 by Capt. Mikhail Dmitrievich Tebenkov of the Imperial Russian Navy. Exploration for placer gold occurred in the Council district area where the river valley is located, and in 1898, mining commenced. The production was substantial and ranked second only to that of Nome.
Zubof Rock is a small island near Sitka, Alaska, United States, off the northeast coast of Baranof Island. Located in an area of Kelp Bay known as The Basin, it was entered into the United States Geological Survey's Geographic Names Information System on March 31, 1981. Its name dates back to 1895 as Zuboff, which was a Russian surname, as reported by Lieutenant Commander J. F. Moser of the United States Navy.

Baranof Island is an island in the northern Alexander Archipelago in the Alaska Panhandle, in Alaska. The name "Baranof" was given to the island in 1805 by Imperial Russian Navy captain U. F. Lisianski in honor of Alexander Andreyevich Baranov. It was called Sheet’-ká X'áat'l by the native Tlingit people. It is the smallest of the ABC islands of Alaska. The indigenous group native to the island, the Tlingit, named the island Shee Atika. Baranof island is home to a diverse ecosystem, which made it a prime location for the fur trading company, the Russian American Company. Russian occupation in Baranof Island impacted not only the indigenous population as well as the ecology of the island, but also led to the United States' current ownership over the land.

Nuss Lake is a small private lake in Klamath Falls, Oregon, United States. It is 0.2 sq mi (0.52 km2) in size, located approximately 6.6 miles from Altamont. The lake sits between the south skirt of Stukel Mountain and Olene Gap to the north.
Nikolay Yakovlevich Rosenberg was an officer of the Imperial Russian Navy who was appointed as Chief Manager of the Russian-American Company, effectively Governor of Russian America, serving from 1850 to 1853. He was replaced before the end of the usual 5-year term because of his difficulties in managing relations with the native Tlingit peoples, who were important to the Russian fur trade and their survival. He may also have been called back to Russia to serve in the Crimean War, which included naval actions.
Dogbone Lake is a lake in North Slope Borough, Alaska, in the United States.

Baranof Warm Springs are a series of ten geothermal mineral springs located in the small community of Baranof Warm Springs in Sitka, Alaska. The springs are surrounded by the Tongass National Forest.
Uganik Bay is a bay on the north coast of Kodiak Island, Alaska, extending southeast off Shelikof Strait. The community of Uganik is found at the west shore of the northeast arm of the bay.