- Pluto - map features
- Pluto - Baret Montes
| Feature type | Mountain range |
|---|---|
| Location | Western Sputnik Planitia, Pluto |
| Coordinates | 14°36′N157°48′E / 14.600°N 157.800°E |
| Discoverer | New Horizons |
| Eponym | Jeanne Baret |
Baret Montes is a chain of mountains on the surface of the dwarf planet Pluto. It is located near the western border of Sputnik Planitia in Tombaugh Regio. These mountains were first viewed by the New Horizons spacecraft. It features large ridges that are formed by the compression of methane and water ice. [1]
The mountains are named after Jeanne Baret, a French explorer and first woman to have completed a circumnavigation voyage of the globe. [2] [3] The New Horizons team suggested this name in 2015, and it was officially approved by the International Astronomical Union in April 2018.

A mountain range or hill range is a series of mountains or hills arranged in a line and connected by high ground. A mountain system or mountain belt is a group of mountain ranges with similarity in form, structure, and alignment that have arisen from the same cause, usually an orogeny. Mountain ranges are formed by a variety of geological processes, but most of the significant ones on Earth are the result of plate tectonics. Mountain ranges are also found on many planetary mass objects in the Solar System and are likely a feature of most terrestrial planets.

Maxwell Montes is a mountain range on the planet Venus, of which Skadi Mons is the highest.

The geology of Pluto consists of the characteristics of the surface, crust, and interior of Pluto. Because of Pluto's distance from Earth, in-depth study from Earth is difficult. Many details about Pluto remained unknown until 14 July 2015, when New Horizons flew through the Pluto system and began transmitting data back to Earth. When it did, Pluto was found to have remarkable geologic diversity, with New Horizons team member Jeff Moore saying that it "is every bit as complex as that of Mars". The final New Horizons Pluto data transmission was received on 25 October 2016. In June 2020, astronomers reported evidence that Pluto may have had a subsurface ocean, and consequently may have been habitable, when it was first formed.
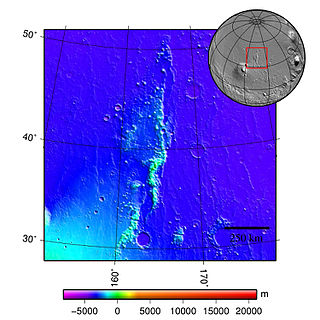
The Phlegra Montes are a system of eroded Hesperian–Noachian-aged massifs and knobby terrain in the mid-latitudes of the northern lowlands of Mars, extending northwards from the Elysium Rise towards Vastitas Borealis for nearly 1,400 km (870 mi). The mountain ranges separate the large plains provinces of Utopia Planitia (west) and Amazonis Planitia (east), and were named in the 1970s after a classical albedo feature. The massif terrains are flanked by numerous parallel wrinkle ridges known as the Phlegra Dorsa.

Tombaugh Regio, sometimes nicknamed "Pluto's heart" after its shape, is the largest bright surface feature of the dwarf planet Pluto. It lies just north of Pluto's equator, to the northeast of Belton Regio and to the northwest of Safronov Regio, which are both dark features. Its western lobe, a 1,000 km (620 mi)-wide plain of nitrogen and other ices lying within a basin, is named Sputnik Planitia. The eastern lobe consists of high-albedo uplands thought to be coated by nitrogen transported through the atmosphere from Sputnik Planitia, and then deposited as ice. Some of this nitrogen ice then returns to Sputnik Planitia via glacial flow. The region is named after Clyde Tombaugh, the discoverer of Pluto.

Belton Regio is a prominent surface feature of the dwarf planet Pluto. It is an elongated dark region along Pluto's equator, 2,990 km (1,860 mi) long and one of the darkest features on its surface.

The geology of Charon encompasses the characteristics of the surface, crust, and interior of Pluto's moon Charon. Like the geology of Pluto, almost nothing was known of Charon's geology until the New Horizons of the Pluto system on 14 July 2015. Charon's diameter is 1,208 km (751 mi)—just over half that of Pluto. Charon is sufficiently massive to have collapsed into a spheroid under its own gravity.

The geography of Pluto refers to the study and mapping of physical features across the dwarf planet Pluto. On 14 July 2015, the New Horizons spacecraft became the first spacecraft to fly by Pluto. During its brief flyby, New Horizons made detailed geographical measurements and observations of Pluto and its moons.
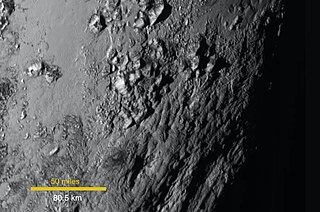
The Tenzing Montes are a range of icy mountains on Pluto, bordering the southwest region of Sputnik Planitia and the nearby Hillary Montes and Wright Mons. With peaks reaching 6.2 km in height, they are the highest mountain range on Pluto, and also the steepest, with a mean slope of 19.2 degrees.

Sputnik Planitia is a large, partially glaciated basin on Pluto. About 1,400 by 1,200 km in size, Sputnik Planitia is partially submerged in large, bright glaciers of nitrogen ice. Named after Earth's first artificial satellite, Sputnik 1, it constitutes the western lobe of the heart-shaped Tombaugh Regio. Sputnik Planitia lies mostly in the northern hemisphere, but extends across the equator. Much of it has a surface of irregular polygons separated by troughs, interpreted as convection cells in the relatively soft nitrogen ice. The polygons average about 33 km (21 mi) across. In some cases troughs are populated by blocky mountains or hills, or contain darker material. There appear to be windstreaks on the surface with evidence of sublimation. The dark streaks are a few kilometers long and all aligned in the same direction. The planitia also contains pits apparently formed by sublimation. No craters were detectable by New Horizons, implying a surface less than 10 million years old. Modeling sublimation pit formation yields a surface age estimate of 180000+90000
−40000 years. Near the northwest margin is a field of transverse dunes, spaced about 0.4 to 1 km apart, that are thought to be composed of 200-300 μm diameter particles of methane ice derived from the nearby Al-Idrisi Montes.

The Hillary Montes or are a mountain range that reach 3.5 km above the surface of the dwarf planet Pluto. They are located northwest of Tenzing Montes in the southwest border area of Sputnik Planitia in the south of Tombaugh Regio. The Hillary Montes were first viewed by the New Horizons spacecraft on 14 July 2015, and announced by NASA on 24 July 2015.

Vulcan Planitia, or Vulcan Planum, is the unofficial name given to a large plain on the southern hemisphere of Pluto's moon Charon. It discovered by New Horizons during its flyby of Pluto in July 2015. It is named after the fictional planet Vulcan in the science-fiction series Star Trek. The name is not approved by International Astronomical Union (IAU) as of 2024.

The Coleta de Dados Colles are a cluster of hills ("colles") on the smooth plains of Sputnik Planitia on Pluto. The hills are over 100 km from the major mountain ranges to the west, and appear to be blocks of water ice floating in the denser nitrogen ice of Sputnik Planitia. The hills were informally named on July 28, 2015, by the research team of the New Horizons mission after the first Brazilian satellite, the Satélite de Coleta de Dados. The ridge's name has yet to be recognized officially by the IAU.
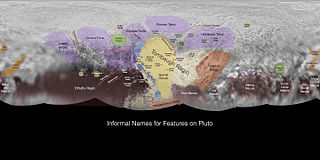
Luna Linea is a dark linear feature (linea) on the dwarf planet Pluto. It was discovered by the New Horizons craft in July 2015 and named after the Luna program, a Soviet space exploration program that was the first to visit the Moon. The name was officially approved by the International Astronomical Union (IAU) on 11 April, 2023.

Wright Mons is a large, roughly circular mountain and likely cryovolcano on the dwarf planet Pluto. Discovered by the New Horizons spacecraft in 2015, it is located southwest of Sputnik Planitia within Hyecho Palus, adjacent to the Tenzing Montes and Belton Regio. A relatively young geological feature, Wright Mons has attracted attention as one of the most apparent examples of recent geological activity on Pluto and borders numerous other similarly young features. Numerous semi-regular hills surround and partially construct the flanks of Wright Mons. Their nature remains unexplained, with few, if any, direct analogs elsewhere in the Solar System.

Nasreddin is a crater on Pluto's largest moon, Charon. The crater was first observed by NASA's New Horizons space probe on its flyby of Pluto in 2015. The name was chosen as a reference to Nasreddin, the hero of humorous folktales told throughout the Middle East, Southern Europe, and parts of Asia. The name was officially approved by the International Astronomical Union (IAU) on 11 April 2018.
Piccard Mons is a large, roughly circular mountain and likely cryovolcano on the dwarf planet Pluto. Discovered by the New Horizons spacecraft in 2015, it is located southeast of Wright Mons within the Tombaugh Regio, adjacent to the Safronov Regio and Elcano Montes.