
Bartonella is a genus of Gram-negative bacteria. It is the only genus in the family Bartonellaceae. Facultative intracellular parasites, Bartonella species can infect healthy people, but are considered especially important as opportunistic pathogens. Bartonella species are transmitted by vectors such as ticks, fleas, sand flies, and mosquitoes. At least eight Bartonella species or subspecies are known to infect humans.
Bartonellosis is an infectious disease produced by bacteria of the genus Bartonella. Bartonella species cause diseases such as Carrión's disease, trench fever, cat-scratch disease, bacillary angiomatosis, peliosis hepatis, chronic bacteremia, endocarditis, chronic lymphadenopathy, and neurological disorders.

Haplogroup H (Y-DNA), also known as H-L901/M2939 is a Y-chromosome haplogroup.
Coproporphyrinogen-III oxidase, mitochondrial is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the CPOX gene. A genetic defect in the enzyme results in a reduced production of heme in animals. The medical condition associated with this enzyme defect is called hereditary coproporphyria.

ACADSB is a human gene that encodes short/branched chain specific acyl-CoA dehydrogenase (SBCAD), an enzyme in the acyl CoA dehydrogenase family.
Bartonella quintana, originally known as Rochalimaea quintana, and "Rickettsia quintana", is a bacterium transmitted by the human body louse that causes trench fever. This bacterial species caused outbreaks of trench fever affecting 1 million soldiers in Europe during World War I.

Pancreatic Stone Protein (PSP), also known as Lithostathine-1-alphaislet cells regeneration factor (ICRF) or islet of Langerhans regenerating protein (REG) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the REG1A gene as a single polypeptide of 144 amino acids further cleaved by trypsin to produced a 133 amino acid protein that is O-linked glycosylated on threonine 27. This protein is a type I subclass member of the Regenerating protein family. The Reg protein family is a multi protein family grouped into four subclasses, types I, II, III and IV based on the primary structures of the proteins. Reg family members REG1B, REGL, PAP and this gene are tandemly clustered on chromosome 2p12 and may have arisen from the same ancestral gene by gene duplication. The PSP is mostly produced in Human by the acinar cells of the pancreas and is secreted in the duodenum by the same pathway that pancreatic exocrine enzymes. It has C-terminal C-type lectin domain whose binding partner is currently unknown.

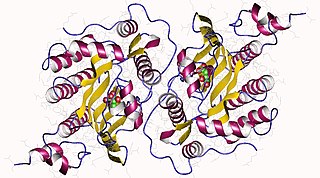
Cob(I)yrinic acid a,c-diamide adenosyltransferase, mitochondrial is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the MMAB gene.
Faecalibacterium is a genus of bacteria. Its sole known species, Faecalibacterium prausnitzii is gram-positive, mesophilic, rod-shaped, anaerobic and is one of the most abundant and important commensal bacteria of the human gut microbiota. It is non-spore forming and non-motile. These bacteria produce butyrate and other short-chain fatty acids through the fermentation of dietary fiber.

Human coronavirus HKU1 (HCoV-HKU1) is a species of coronavirus in humans. It causes an upper respiratory disease with symptoms of the common cold, but can advance to pneumonia and bronchiolitis. It was first discovered in January 2004 from one man in Hong Kong. Subsequent research revealed it has global distribution and earlier genesis.
Human coronavirus 229E (HCoV-229E) is a species of coronavirus which infects humans and bats. It is an enveloped, positive-sense, single-stranded RNA virus which enters its host cell by binding to the APN receptor. Along with Human coronavirus OC43, it is one of the viruses responsible for the common cold. HCoV-229E is a member of the genus Alphacoronavirus and subgenus Duvinacovirus.
Bartonella alsatica is a proteobacterium. Like other Bartonella species, it can cause disease in animals. It is small, aerobic, oxidase-negative, and Gram-negative. Its rod-like cells were localized within wild rabbit erythrocytes when first described. The type strain is IBS 382T. It is associated with cases of lymphadenitis and endocarditis.
Bartonella koehlerae is a proteobacterium first isolated from cats. Its genome consists of 1.7-1.8 Mb.
Bartonella bovis is a pathogenic bacteria first isolated from European ruminants. It is small, fastidious, aerobic, oxidase-negative, gram-negative and rod-shaped. Its type strain is 91-4T.
Bartonella capreoli is a pathogenic bacteria first isolated from European ruminants. It is small, fastidious, aerobic, oxidase-negative, gram-negative and rod-shaped. Its type strain is IBS 193T.
Bartonella australis is a Gram-negative bacterium of the genus Bartonella which was isolated from eastern grey kangaroos.
Bartonella silvatica is an oxidase- and catalase-negative bacterium from the genus Bartonella isolated from the blood of the large Japanese field mouse Apodemus speciosus.
Bartonella vinsonii is a gram-negative bacteria from the genus Bartonella which was isolated from dogs Rochalimaea vinsonii was reclassified to Bartonella vinsonii. B. vinsonii contains three validly published subspecies B. vinsonii subsp. arupensis, B. vinsonii subsp. berkhoffii, and B. vinsonii subsp. vinsonii, and one effectively published B. vinsonii subsp. yucatanensis. B. vinsonii subsp. vinsonii has been isolated from voles and B. vinsonii subsp. berkhofli was isolated from a dog with endocarditis. B. vinsonii subsp. berkhoffii can cause diseases in humans. Those two subspecies are named after J. William Vinson and Herman A. Berkhoff.
Bartonella washoensis is a bacterium from the genus Bartonella which was first isolated from a dog with mitral valve endocarditis. Bartonella washoensis can infect squirrels but also can cause meningitis in humans.

The history of coronaviruses is a reflection of the discovery of the diseases caused by coronaviruses and identification of the viruses. It starts with the first report of a new type of upper-respiratory tract disease among chickens in North Dakota, U.S., in 1931. The causative agent was identified as a virus in 1933. By 1936, the disease and the virus were recognised as unique from other viral disease. They became known as infectious bronchitis virus (IBV), but later officially renamed as Avian coronavirus.







