
The BaruLema'a is a traditional armor from Indonesia.

The BaruLema'a is a traditional armor from Indonesia.
The Baru Lema'a is made in the form of a vest. It consists of the braided, coarse fibers of the Iluk plant. The fibers are braided and the strands are connected again side by side. It has neither sleeves nor a collar. In the neck area a surface is protruding which is similar to two connected circles. This serves to protect the neck from blows. The vest is heavy and inflexible. It is used by ethnic groups from Indonesia. [1]

Zylon is a trademarked name for a range of thermoset liquid-crystalline polyoxazole. This synthetic polymer material was invented and developed by SRI International in the 1980s and manufactured by Toyobo. In generic usage, the fiber is referred to as PBO.

A folk costume expresses an identity through costume, which is usually associated with a geographic area or a period of time in history. It can also indicate social, marital or religious status. If the costume is used to represent the culture or identity of a specific ethnic group, it is usually known as ethnic costume. Such costumes often come in two forms: one for everyday occasions, the other for traditional festivals and formal wear.

A sarong or sarung is a large tube or length of fabric, often wrapped around the waist, worn in Southeast Asia, South Asia, Western Asia, Northern Africa, East Africa, West Africa, and on many Pacific islands. The fabric often has woven plaid or checkered patterns, or may be brightly colored by means of batik or ikat dyeing. Many modern sarongs have printed designs, often depicting animals or plants. Different types of sarongs are worn in different places in the world, notably the lungi in the Indian subcontinent and the izaar in the Arabian Peninsula.

A kebaya is an upper garment traditionally worn by women in Southeast Asia, notably in Indonesia, Malaysia, Brunei, and Singapore. Outside of Southeast Asia, it is worn by Javanese, Malays and Portuguese Eurasians in Australian Cocos Islands and Christmas Island, coastal India and Sri Lanka, Macau as well as South Africa.

Baju Melayu is a traditional Malay costume, originated from the court of Malacca Sultanate and is traditionally worn by men in Brunei, Malaysia, Singapore, parts of Indonesia, southern Philippines, and southern Thailand. It literally translates as Malay dress and consists of two main parts. The first being the baju itself which has a raised stiff collar known as the cekak musang collar. The second part is the trousers called seluar. The two parts are made out of the same type of fabric which is usually cotton, or a mixture of polyester and cotton. A skirt-type adornment is also commonly worn with the Baju Melayu, which is either the kain samping, made out of songket, tenun cloth or the kain sarung, made out of cotton or a polyester mix. Both are loops of fabric that are folded around the wearer's waist. Jet-black or dark-colored headgear called the songkok can also worn to complete the attire.

On horses, the mane is the hair that grows from the top of the neck of a horse or other equine, reaching from the poll to the withers, and includes the forelock or foretop. It is thicker and coarser than the rest of the horse's coat, and naturally grows to roughly cover the neck. Heredity plays a role, giving some horses a longer, thicker mane, and others a shorter, thinner one.

Pakaian is the term for clothing in Malaysia's national language. It is referring to things to wear such as shirts, pants, shoes etc. Since Malaysia is a multicultural nation: Malay, Chinese, Indian and hundred of other indigenous groups of Malay peninsula and Borneo, each has its own traditional and religious articles of clothing all of which are gender-specific and may be adapted to local influences and conditions. Previously, traditional clothes were worn daily. However, by excluding Baju Melayu, Baju Kurung and Baju Kebaya, many are now only worn on special occasions such as marriage ceremonies and cultural events.

Baju Kurung is a traditional costume of Malays and traditionally worn by women in Brunei, Indonesia, Malaysia, Singapore and southern Thailand. This type of traditional costume is the national dress of Brunei and Malaysia. In Indonesia, it is also one of the regional dresses, seen most on the island of Sumatra, where many ethnic Malay and Minangkabau women wear it.

The national costume of Indonesia is the national costume that represents the Republic of Indonesia. It is derived from Indonesian culture and Indonesian traditional textile traditions. Today the most widely recognized Indonesian national costumes include batik and kebaya, although originally those costumes mainly belong within the island of Java and Bali, most prominently within Javanese, Sundanese and Balinese culture. Since Java has been the political and population center of Indonesia, folk costume from the island has become elevated into national status.

Kemben is an Indonesian female torso wrap historically common in Java, Bali, and other part of Indonesian archipelago. It is made by wrapping a piece of kain (clothes), either plain, batik printed, velvet, or any type of fabrics, covering the chest wrapped around the woman's torso.

The Baju Lamina is a mail and plate armor from the Nusantara archipelago.
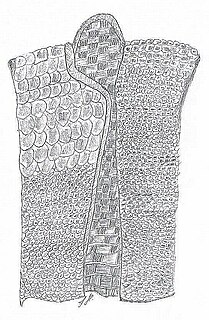
The Baju Empurau is an armour from Indonesia.

The Baju Rantai is a type of armor from Nusantara archipelago.
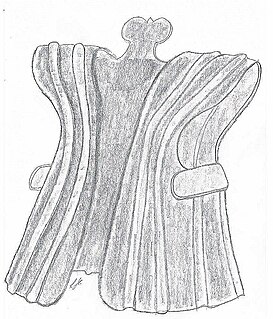
Baru Öröba is a traditional armor of the Nias people in Indonesia. The earliest examples of this type of armor were made out of crocodile skin. After crocodile can no longer be found on Nias, the material is replaced with hammered metal.

Making Mathematics with Needlework: Ten Papers and Ten Projects is an edited volume on mathematics and fiber arts. It was edited by sarah-marie belcastro and Carolyn Yackel, and published in 2008 by A K Peters, based on a meeting held in 2005 in Atlanta by the American Mathematical Society.

The bodo blouse, locally known as Baju Bodo, is a sheer and transparent short sleeved loose blouse, a traditional costume for women of the Bugis and Makassar peoples of South Sulawesi, Indonesia. A bodo blouse is traditionally combined with a matching woven sarong that covered the waist below the body.

Karambalangan is a type of personal armor from Java. It is a metal coating worn in front of the chest or breastplate.

Kawaca is a term for war attire mentioned in Old Javanese texts. Its name comes from the Sanskrit kawaca which means armor, cuirass, a type of chain mail, any kind of cover, corset, jacket.

Siping-siping, simping-simping, or sisimping, is a type of armor used in Java. It is a short sleeveless jacket made of scale-shaped metal plates.