Arezzo is a city and comune in Italy and the capital of the province of the same name located in Tuscany. Arezzo is about 80 kilometres southeast of Florence at an elevation of 296 metres (971 ft) above sea level. It is also 30 km west of Città di Castello. In 2013 the population was about 99,000.

Santa Maria Novella is a church in Florence, Italy, situated just across from the main railway station named after it. Chronologically, it is the first great basilica in Florence, and is the city's principal Dominican church.

The Basilica of Saint Francis of Assisi is the mother church of the Roman Catholic Order of Friars Minor Conventual in Assisi, a town in the Umbria region in central Italy, where Saint Francis was born and died. It is a Papal minor basilica and one of the most important places of Christian pilgrimage in Italy. With its accompanying friary, Sacro Convento, the basilica is a distinctive landmark to those approaching Assisi. It has been a UNESCO World Heritage site since 2000.

The Basilica of San Petronio is a minor basilica and church of the Archdiocese of Bologna located in Bologna, Emilia Romagna, northern Italy. It dominates Piazza Maggiore. The basilica is dedicated to the patron saint of the city, Saint Petronius, who was the bishop of Bologna in the fifth century. Construction began in 1390 and its main facade has remained unfinished since. The building was transferred from the city to the diocese in 1929; the basilica was finally consecrated in 1954. It has been the seat of the relics of Bologna's patron saint only since 2000; until then they were preserved in the Santo Stefano church of Bologna.

Parma Cathedral is a Roman Catholic cathedral in Parma, Emilia-Romagna (Italy), dedicated to the Assumption of the Blessed Virgin Mary. It is the episcopal seat of the Diocese of Parma. It is an important Italian Romanesque cathedral: the dome, in particular, is decorated by a highly influential illusionistic fresco by Renaissance painter Antonio da Correggio.

The Basilica of Saint Mary of the Angels is a Papal minor basilica situated in the plain at the foot of the hill of Assisi, Italy, in the frazione of Santa Maria degli Angeli.

Genoa Cathedral, Cathedral of Saint Lawrence is a Roman Catholic cathedral in the Italian city of Genoa. It is dedicated to Saint Lawrence, and is the seat of the Archbishop of Genoa. The cathedral was consecrated by Pope Gelasius II in 1118 and was built between the twelfth century and the fourteenth century as fundamentally a medieval building, with some later additions. Secondary naves and side covers are of Romanesque style and the main facade is Gothic from the early thirteenth century, while capitals and columns with interior corridors date from the early fourteenth century. The bell tower and dome were built in the sixteenth century.

Sant'Orso, or Saint-Ours, is a collegiate church in Aosta, northern Italy, dedicated to Saint Ursus of Aosta. The original church had a single hall, delimited by a semicircular apse. It was entirely rebuilt during the 9th century, during the Carolingian age. Later, bishop Anselm of Aosta further renovated the church, introducing a basilica plan with three naves with wooden trusses. These were replaced by Gothic cross vaults in the 15th century.

The Pontifical Basilica of Saint Anthony of Padua is a Roman Catholic church and minor basilica in Padua, Veneto, Northern Italy, dedicated to St. Anthony. Although the Basilica is visited as a place of pilgrimage by people from all over the world, it is not the titular cathedral of the city, a title belonging to the Cathedral-Basilica of St. Mary of Padua. The basilica is known locally as "il Santo". It is one of the eight international shrines recognized by the Holy See.

Padua Cathedral is a Roman Catholic cathedral and minor basilica in Padua, northern Italy. The cathedral, dedicated to the Assumption of the Virgin Mary, is the seat of the bishop of Padua.

The Duomo of Monza often known in English as Monza Cathedral is the main religious building of Monza, in northern Italy. Unlike most duomos it is not in fact a cathedral, as Monza has always been part of the Diocese of Milan, but is in the charge of an archpriest who has the right to certain episcopal vestments including the mitre and the ring. The church is also known as the Basilica of San Giovanni Battista from its dedication to John the Baptist.

The Basilica of Sant'Abbondio is a Romanesque-style 11th-century Roman Catholic basilica church located in Como, region of Lombardy, Italy.

Pistoia Cathedral is the main religious building of Pistoia, Tuscany, central Italy, located in the Piazza del Duomo in the centre of the city. It is the seat of the Bishop of Pistoia and is dedicated to Saint Zeno of Verona.

The basilica of Santo Stefano encompasses a complex of religious edifices in the city of Bologna, Italy. Located on Piazza Santo Stefano, it is locally known as Sette Chiese and Santa Gerusalemme. It has the dignity of minor basilica.
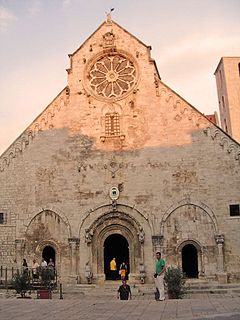
Ruvo Cathedral is a Roman Catholic cathedral in Ruvo di Puglia, a city in Apulia, southern Italy, dedicated to the Assumption of the Virgin Mary. Formerly the episcopal seat of the Diocese of Ruvo, it is now a co-cathedral in the Diocese of Molfetta-Ruvo-Giovinazzo-Terlizzi. The building is an important example of late Apulian Romanesque architecture, built between the 12th and 13th centuries, with several later alterations.

Ancona Cathedral is a Roman Catholic cathedral in Ancona, central Italy, dedicated to Saint Cyriacus of Ancona. It is the seat of the Archbishop of Ancona. The building is an example of mixed Romanesque-Byzantine and Gothic elements, and stands on the site of the former acropolis of the Greek city, the Guasco hill which overlooks Ancona and its gulf.

Otranto Cathedral is a Roman Catholic cathedral in the Italian city of Otranto, dedicated to the Annunciation of the Virgin Mary. It is the archiepiscopal seat of the Archdiocese of Otranto. The cathedral was consecrated in 1088. It is 54 metres long by 25 metres wide and is built on 42 monolithic granite and marble columns from unknown quarries. Its plan is a three-aisled nave with an apsidal east end. On either side of the west facade are two lancet windows.

The Basilica di San Giulio is a Roman Catholic church on the small Isola San Giulio in the center of Lake Orta, province of Novara, north-western Italy. It has the status of a minor basilica. Although the island is part of the Orta San Giulio municipality, the basilica belongs to the San Giacomo parish, including the island and a portion of the west coast of the lake in San Maurizio d'Opaglio municipality.
Sarsina Cathedral is a Roman Catholic cathedral in Sarsina, a municipality in the province of Forlì-Cesena, region of Emilia-Romagna, Italy, dedicated to the Annunciation of the Virgin Mary. Formerly the seat of the Bishops of Sarsina, since 1986 it has been a co-cathedral of the Diocese of Cesena-Sarsina.

The Abbazia di Santa Maria a Pie’ di Chienti or Abbey of Santa Maria at Pie’ di Chienti was a former Roman Catholic monastery and church located in a rural site on the north bank of the Chienti river, just outside of the town of Montecosaro Scalo, in the province of Macerata, region of Marche, Italy. The church is also known as the Santissima Annunziata.