Lake Garda is the largest lake in Italy. It is a popular holiday location in northern Italy, between Brescia and Milan to the west, and Verona and Venice to the east. The lake cuts into the edge of the Italian Alps, particularly the Alpine sub-ranges of the Garda Mountains and the Brenta Group. Glaciers formed this alpine region at the end of the last ice age. The lake and its shoreline are divided between the provinces of Brescia, Verona (south-east) and Trentino (north).

Nicolas Catinat was a French military commander and Marshal of France under Louis XIV.
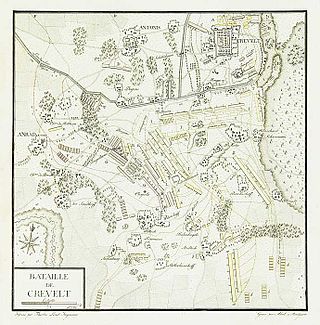
The Battle of Krefeld was fought at Krefeld near the Rhine on 23 June 1758 between a Prussian-Hanoverian army and a French army during the Seven Years' War.

Peschiera del Garda is a town and comune in the province of Verona, in Veneto, Italy. When Lombardy-Venetia was under Austrian rule, Peschiera was the northwest anchor of the four fortified towns constituting the Quadrilatero. The fortress is on an island in the river Mincio at its outlet from Lake Garda.

The Kingdom of Italy was a kingdom in Northern Italy that was a client state of Napoleon's French Empire. It was fully influenced by revolutionary France and ended with Napoleon's defeat and fall. Its government was assumed by Napoleon as King of Italy and the viceroyalty delegated to his stepson Eugène de Beauharnais. It covered some of Piedmont and the modern regions of Lombardy, Veneto, Emilia-Romagna, Friuli-Venezia Giulia, Trentino, South Tyrol, and Marche. Napoleon I also ruled the rest of northern and central Italy in the form of Nice, Aosta, Piedmont, Liguria, Tuscany, Umbria, and Lazio, but directly as part of the French Empire, rather than as part of a vassal state.

The First Battle of Custoza was fought on July 24 and 25, 1848, during the First Italian War of Independence between the armies of the Austrian Empire, commanded by Field Marshal Radetzky, and the Kingdom of Sardinia, led by King Charles Albert of Piedmont-Sardinia.

The Battle of Castiglione saw the French Army of Italy under General Napoleon Bonaparte attack an army of the Habsburg monarchy led by Feldmarschall Dagobert Sigmund von Wurmser on 5 August 1796. The outnumbered Austrians were defeated and driven back along a line of hills to the river crossing at Borghetto, where they retired beyond the Mincio River. The town of Castiglione delle Stiviere is located 10 kilometres (6 mi) south of Lake Garda in northern Italy. This battle was one of four famous victories won by Bonaparte during the War of the First Coalition, part of the French Revolutionary Wars. The others were Bassano, Arcole, and Rivoli.

The Battle of Marsaglia was a battle in the Nine Years' War, fought in Italy on 4 October 1693, between the French army of Marshal Nicolas Catinat and the army of the Grand Alliance under Duke Victor Amadeus II of Savoy.

The Battle of Torroella, also known as Battle of the river Ter, took place during the Nine Years' War, on 27 May 1694 along the banks and fords of the Ter River near the Puente Mayor in the vicinity of the important town of Girona, Catalonia, Spain.

The Quadrilatero is the traditional name of a defensive system of the Austrian Empire in the Lombardy-Venetia region of Italy, which connected the fortresses of Peschiera, Mantua, Legnago and Verona between the Mincio, the Po, and the Adige Rivers. The name refers to the fact that on a map the fortresses appear to form the vertices of a quadrilateral. In the period between the end of the Napoleonic Wars and the Revolutions of 1848, they were the only fully modernized and armed fortresses within the Empire.

The Battle of Bassano was fought on 8 September 1796, during the French Revolutionary Wars, in the territory of the Republic of Venice, between a French army under Napoleon Bonaparte and Austrian forces led by Count Dagobert von Wurmser. The engagement occurred during the second Austrian attempt to raise the siege of Mantua. It was a French victory; however, it was the last battle in Napoleon's perfect military career as two months later he would be defeated at the Second Battle of Bassano, ending his victorious streak. The Austrians abandoned their artillery and baggage, losing supplies, cannons, and battle standards to the French.

In the Battle of Rovereto on 4 September 1796 a French army commanded by Napoleon Bonaparte defeated an Austrian corps led by Paul Davidovich during the War of the First Coalition, part of the French Revolutionary Wars. The battle was fought near the town of Rovereto, in the upper Adige River valley in northern Italy.

The siege of Bouchain, following the Passage of the Lines of Ne Plus Ultra, was a siege of the War of the Spanish Succession, and the last major victory of John Churchill, 1st Duke of Marlborough. Marlborough and François Nicolas Fagel broke through the French defensive lines and took Bouchain after a siege of 34 days. Its capture left Cambrai the only French-held fortress between the allied army and Paris.

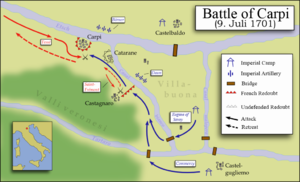
The Battle of Chiari was fought on 1 September 1701 during the War of the Spanish Succession. The engagement was part of Prince Eugene of Savoy's campaign to seize the Spanish controlled Duchy of Milan in the Italian peninsula, and had followed his victory over Marshal Catinat at the Battle of Carpi in July. Marshal Villeroi replaced Catinat as commander of the Franco–Spanish–Savoyard forces in the theatre, carrying with him orders from King Louis XIV to push the Imperialists out of Italy.

The Battle of Pfaffenhofen was fought on 15 April 1745 between France and Austria. The Austrians under Karl Josef Batthyány defeated the outnumbered French under General Ségur, ending the war in Bavaria.

The Veronese Easter was a rebellion during the Italian campaign of 1797, in which inhabitants of Verona and the surrounding areas revolted against the French occupying forces under Antoine Balland, while Napoleon Bonaparte was fighting in Austria. The uprising received its name through association with the anti-French uprising of the Sicilian Vespers of the 13th century. Incited by oppressive behaviour by the French, it began on the morning of 17 April 1797, the second day of Easter: the enraged population succeeded in defeating more than a thousand French soldiers in the first hour of fighting, forcing them to take refuge in the town's fortifications, which the mob then captured by force. The revolt ended on 25 April 1797 with the encirclement and capture of the town by 15,000 soldiers, who then forced it to pay a huge fine and hand over various assets, including artwork.

During the siege of Mantua, which lasted from 4 June 1796 to 2 February 1797 with a short break, French forces under the overall command of Napoleon Bonaparte besieged and blockaded a large Austrian garrison at Mantua for many months until it surrendered. This eventual surrender, together with the heavy losses incurred during four unsuccessful relief attempts, led indirectly to the Austrians suing for peace in 1797. The siege occurred during the War of the First Coalition, which is part of the French Revolutionary Wars. Mantua, a city in the Lombardy region of Italy, lies on the Mincio River.

The Battle of Borghetto, near Valeggio sul Mincio in the Veneto of northern Italy, took place during the War of the First Coalition, part of the French Revolutionary Wars. On 30 May 1796, a French army led by General Napoleon Bonaparte forced a crossing of the Mincio River in the face of opposition from an Austrian army commanded by Feldzeugmeister Johann Peter Beaulieu. This action compelled the Austrian army to retreat north up the Adige valley to Trento, leaving the fortress of Mantua to be besieged by the French.

The Battle of Verona was fought on 18 October 1805 between the French Army of Italy under the command of André Masséna and an Austrian army led by Archduke Charles, Duke of Teschen. By the end of the day, Massena seized a bridgehead on the east bank of the Adige River, driving back the defending troops under Josef Philipp Vukassovich. The action took place near the city of Verona in northern Italy during the War of the Third Coalition, part of the Napoleonic Wars.

The Republic of Venice was dissolved and dismembered by the French general Napoleon Bonaparte and the Habsburg Monarchy on 12 May 1797.