
Cochise was the leader of the Chiricahui local group of the Chokonen and principal nantan of the Chokonen band of a Chiricahua Apache. A key war leader during the Apache Wars, he led an uprising that began in 1861 and persisted until a peace treaty was negotiated in 1872. Cochise County is named after him.

Victorio was a warrior and chief of the Warm Springs band of the Tchihendeh division of the central Apaches in what is now the American states of Texas, New Mexico, Arizona, and the Mexican states of Sonora and Chihuahua.

The Apache Wars were a series of armed conflicts between the United States Army and various Apache tribal confederations fought in the southwest between 1849 and 1886, though minor hostilities continued until as late as 1924. After the Mexican–American War in 1846, the United States annexed conflicted territory from Mexico which was the home of both settlers and Apache tribes. Conflicts continued as American settlers came into traditional Apache lands to raise livestock and crops and to mine minerals.

The Battle of Summit Springs, on July 11, 1869, was an armed conflict between elements of the United States Army under the command of Colonel Eugene A. Carr and a group of Cheyenne Dog Soldiers led by Tall Bull, who was killed during the engagement. The US forces were assigned to retaliate for a series of raids in north-central Kansas by Chief Tall Bull's Dog Soldiers band of the Cheyenne. The battle happened south of Sterling, Colorado in Washington County near the Logan/Washington county line.

The Apache Scouts were part of the United States Army Indian Scouts. Most of their service was during the Apache Wars, between 1849 and 1886, though the last scout retired in 1947. The Apache scouts were the eyes and ears of the United States military and sometimes the cultural translators for the various Apache bands and the Americans. Apache scouts also served in the Navajo War, the Yavapai War, the Mexican Border War and they saw stateside duty during World War II. There has been a great deal written about Apache scouts, both as part of United States Army reports from the field and more colorful accounts written after the events by non-Apaches in newspapers and books. Men such as Al Sieber and Tom Horn were sometimes the commanding officers of small groups of Apache Scouts. As was the custom in the United States military, scouts were generally enlisted with Anglo nicknames or single names. Many Apache Scouts received citations for bravery.

The First Battle of Dragoon Springs was a minor skirmish between a small troop of Confederate dragoons of Governor John R. Baylor's Arizona Rangers, and a band of Apache warriors during the American Civil War. It was fought on May 5, 1862, near the present-day town of Benson, Arizona, in Confederate Arizona.

The Battle of the Mimbres River was a surprise attack launched by a troop of American militia against an encampment of Chiricahua Apaches along the western shore of the Mimbres River.
James Sumner was a United States Army soldier and a recipient of the United States military's highest decoration, the Medal of Honor, for his actions in the Indian Wars of the western United States. An English immigrant, Sumner served as a cavalryman during the Apache Wars of southeastern Arizona Territory. He was awarded the Medal of Honor for advancing through heavy fire in a skirmish against a group of Chiricahua Indians led by Cochise.

The Battle of Mount Gray was an engagement of the Apache Wars fought at the foothills of Gray Mountain on April 7, 1864. A troop of the United States Army's California Column attacked a superior force of Chiricahua Apaches at their camp and routed them from the field.
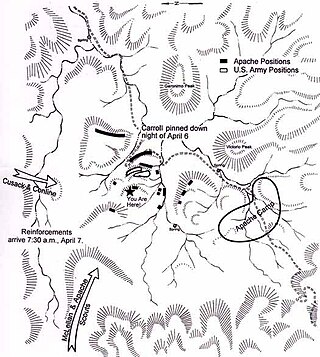
The Battle of Hembrillo Basin was fought April 5–8, 1880 between the United States Army against a combined band of Chiricahua and Mescalero Apaches led by Chief Victorio. Hembrillo Basin was the largest battle of Victorio's War, although casualties were light on both sides. Victorio held off an attack by superior numbers of army soldiers and Indian scouts, evacuated his women and children from the battlefield, and withdrew successfully. Hembrillo Basin is located on the White Sands Missile Range and access by the public is strictly regulated.

The Battle of Fort Buchanan was an Apache attack on the United States Army post of Old Fort Buchanan in southern Arizona Territory, which occurred on February 17, 1865. Though a skirmish, it ended with a significant Apache victory when they forced the small garrison of California Volunteers to retreat to the Santa Rita Mountains. Fort Buchanan was the only American military post conquered during the war against the Chiricahua.

The Bonneville Expedition was a military operation launched by the United States Army in 1857 at the beginning of the Chiricahua Apache Wars. Colonel Benjamin Bonneville, Lieutenant Colonel Dixon S. Miles, and Colonel William W. Loring commanded parties which headed west from Fort Fillmore, New Mexico Territory. The expedition quickly engaged Apaches in two small but significant battles, the first in the Black Range and the second along the Gila River near present-day Safford, Arizona.

The Battle of Devil's River was an 1857 Indian War skirmish which took place in Texas along the Devils River. A small force of United States Army cavalry defeated an overwhelming force of Comanche braves after an epic journey across the desert.

The Battle of Pecos River was fought in 1864 during the Navajo Wars. United States Army troops and Apache Scouts defeated a force of Navajo warriors next to the Pecos River in New Mexico. It is notable for being one of the many Indian war battles involving the California Column.

The Battle of Little Dry Creek was a skirmish during Geronimo's War. Chiricahua Apache warriors were raiding in the Arizona and New Mexico border area when they ambushed a larger force of United States Army troops and Navajo Scouts near Pleasanton.

Victorio's War, or the Victorio Campaign, was an armed conflict between the Apache followers of Chief Victorio, the United States, and Mexico beginning in September 1879. Faced with arrest and forcible relocation from his homeland in New Mexico to San Carlos Indian Reservation in southeastern Arizona, Victorio led a guerrilla war across southern New Mexico, west Texas and northern Mexico. Victorio fought many battles and skirmishes with the United States Army and raided several settlements until the Mexican Army killed him and most of his warriors in October 1880 in the Battle of Tres Castillos. After Victorio's death, his lieutenant Nana led a raid in 1881.
The Battle of Owyhee River took place during the Snake War in 1866 in response to Paiute attacks along the Owyhee River earlier that year.

The raid on Bear Valley was an armed conflict that occurred in 1886 during Geronimo's War. In late April, a band of Chiricahua Apaches attacked settlements in Santa Cruz County, Arizona over the course of two days. The Apaches raided four cattle ranches in or around Bear Valley, leaving four settlers dead, including a woman and her baby. They also captured a young girl, who was found dead several days after the event, and stole or destroyed a large amount of private property. When the United States Army learned of the attack, an expedition was launched to pursue the hostiles. In May, two small skirmishes were fought just across the international border in Sonora, Mexico but both times the Apaches were able to escape capture.

Pawnee Scouts were employed by the United States Army in the latter half of the 19th century. Like other groups of Indian scouts, Pawnee men were recruited in large numbers to aid in the ongoing conflicts between settlers and the Native Americans in the United States. Because the Pawnee people were at war with the Sioux and Cheyenne and had been under constant pressure and aggression by those tribes, some of them were more than willing to serve with the army for pay. A number of Pawnee served between 1864 and 1871. They were armed with rifles, revolvers and were issued scout uniforms.
The Battle of Devil's Creek was a military engagement during Geronimo's War, fought on May 22, 1885 near Alma, New Mexico. Though it was a minor skirmish, it was the first battle of the Geronimo campaign and ended after the Apaches were routed from their positions.
















