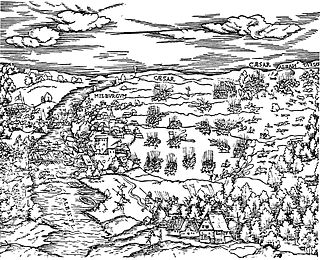
The Battle of Mühlberg took place near Mühlberg in the Electorate of Saxony in 1547, during the Schmalkaldic War. The Catholic princes of the Holy Roman Empire led by the Holy Roman Emperor Charles V decisively defeated the Lutheran Schmalkaldic League of Protestant princes under the command of Elector John Frederick I of Saxony and Landgrave Philip I of Hesse.

The Schmalkaldic War was fought within the territories of the Holy Roman Empire between the allied forces of Charles V, Holy Roman Emperor and Maurice, Duke of Saxony against the Lutheran Schmalkaldic League, with the forces directly loyal to Charles fighting under the command of Fernando Álvarez de Toledo, 3rd Duke of Alba.

The Sack of Rome, then part of the Papal States, followed the capture of Rome on 6 May 1527 by the mutinous troops of Charles V, Holy Roman Emperor, during the War of the League of Cognac. Charles V only intended to threaten military action to make Pope Clement VII come to his terms. However, most of the Imperial army were largely unpaid. Despite being ordered not to storm the city, they broke into the scarcely defended city and began looting, killing, and holding citizens for ransom without any restraint. Clement VII took refuge in Castel Sant'Angelo after the Swiss Guard were annihilated in a delaying rear guard action; he remained there until a ransom was paid to the pillagers.

The War of the League of Cognac (1526–30) was fought between the Habsburg dominions of Charles V—primarily the Holy Roman Empire and Spain—and the League of Cognac, an alliance including the Kingdom of France, Pope Clement VII, the Republic of Venice, the Kingdom of England, the Duchy of Milan, and the Republic of Florence.

Francesco Ferruccio was an Italian captain from Florence who fought in the Italian Wars.

The Battle of Ceresole took place on 14 April 1544, during the Italian War of 1542–1546, outside the village of Ceresole d'Alba in the Piedmont region of Italy. A French army, commanded by François de Bourbon, Count of Enghien, defeated the combined forces of the Holy Roman Empire and Spain, commanded by Alfonso d'Avalos d'Aquino, Marquis del Vasto. Despite having inflicted substantial casualties on the Imperial troops, the French subsequently failed to exploit their victory by taking Milan.

The Battle of Zenta, also known as the Battle of Senta, was fought on 11 September 1697, near Zenta, Kingdom of Hungary, between Ottoman and Holy League armies during the Great Turkish War. The battle was the most decisive engagement of the war, and it saw the Ottomans suffer an overwhelming defeat by an Imperial force half as large sent by Leopold I, Holy Roman Emperor.

The Battle of Montaperti was fought on 4 September 1260 between Florence and Siena in Tuscany as part of the conflict between the Guelphs and Ghibellines. The Florentines were routed. It was the bloodiest battle fought in Medieval Italy, with more than 10,000 fatalities. An act of treachery during the battle is recorded by Dante Alighieri in the Inferno section of the Divine Comedy.

The Battle of Luzzara took place in Lombardy on 15 August 1702 during the War of the Spanish Succession, between a combined French and Savoyard army under Louis Joseph, duc de Vendôme, and an Imperial force under Prince Eugene.

Fabrizio Maramaldo was an Italian Condottiero. An illiterate native of Naples or Calabria, his exact origins are unknown, though he hailed from the Kingdom of Naples, and was perhaps of Spanish origin. He fled Naples after having murdered his wife and sought protection at the Gonzaga under Federico II, Duke of Mantua, and in the Republic of Venice. In 1526 he was absolved of the crime of uxoricide by Charles V, the Holy Roman Emperor. He fought the Ottomans in Hungary, and the French in Piedmont. He suffered a grievous setback in the siege he laid to the city of Asti in 1526 where, after having breached the walls by cannon fire for a final assault, legend narrates that victory was snatched from his grasp by the intervention of the town's patron saint, St.Secondus of Asti who is said to have appeared in the sky. Fighting on the imperial side, he took part in the Sack of Rome the following year, and three years later, in the siege of Florence. He gained a reputation as a ruthless mercenary and ravager.

Ludovico de' Medici, also known as Giovanni delle Bande Nere was an Italian condottiero. He is known for leading the Black Bands and serving valiantly in military combat under his third cousins, Pope Leo X and Pope Clement VII, in the War of Urbino and the War of the League of Cognac, respectively.

The siege of Florence took place from 24 October 1529 to 10 August 1530, at the end of the War of the League of Cognac. At the Congress of Bologna, the Medici Pope Clement VII and Emperor Charles V agreed to restore the Medici family in Florence. A large Imperial and Spanish army under Philibert of Châlon, Prince of Orange and Pier Maria III de' Rossi surrounded the city and after a siege of nearly ten months, captured it. They overthrew the Republic of Florence and installed Alessandro de' Medici as the ruler of the city.

The Battle of Marciano occurred in the countryside of Marciano della Chiana, near Arezzo, Tuscany, on August 2, 1554, during the Italian War of 1551. The battle marked the defeat of the Republic of Siena in its war against the Duchy of Florence, and resulted in Siena losing its independence and being absorbed into the Duchy of Florence.

The Battle of Campo Tenese saw two divisions of the Imperial French Army of Naples led by Jean Reynier attack the left wing of the Royal Neapolitan Army under Roger de Damas. Though the defenders were protected by field fortifications, a French frontal attack combined with a turning movement rapidly overran the position and routed the Neapolitans with heavy losses. The action occurred at Campotenese, a little mountain village in the municipality of Morano Calabro in the north of Calabria. The battle was fought during the War of the Third Coalition, part of the Napoleonic Wars.

The Battle of Castiglione took place near Castiglione delle Stiviere in Lombardy, Italy on 9 September 1706 during the War of the Spanish Succession. A French army of 12,000 attacked a Hessian corps of 10,000 that was besieging the town and forced them to retreat with heavy losses.
The Battle of Landriano took place on 21 June 1529, between the French army under Francis de Bourbon, Comte de St. Pol and the Imperial–Spanish army commanded by Don Antonio de Leyva, Duke of Terranova in the context of the War of the League of Cognac. The French army was destroyed and the battle's strategic result was that the struggle between Francis I of France and Charles V, Holy Roman Emperor for control of northern Italy was temporarily at an end.
The siege of Saint-Dizier took place in the summer of 1544, during the Italian War of 1542–1546, when the Imperial army of Charles V attacked the French city of Saint-Dizier at the beginning of its advance into Champagne. After a two-month siege and the stubborn resistance by a small French garrison, the fortress fell to the Imperial army, personally led by Charles V.
Pasquino Corso, also known as Pasquino da Perugia or Pasquino di Sia was a Corsican Condottiero active during the Italian Wars which took place during the first half of the 16th century.

The Monument to Francesco Ferruccio is an equestrian statue dedicated to the Florentine military leader (1489–1530), who fought to repel the troops of the Habsburg Holy Roman Emperor Charles V, who had invaded Tuscany. The statue is located in the main central piazza Aiale of the hamlet of Gavinana, province of Pistoia, region of Tuscany, Italy.

















