
Charles IX was King of France from 1560 until his death in 1574. He ascended the French throne upon the death of his brother Francis II in 1560, and as such was the penultimate monarch of the House of Valois.

The House of Guise was a prominent French noble family that was involved heavily in the French Wars of Religion. The House of Guise was the founding house of the Principality of Joinville.

Gaspard de Coligny, seigneur de Châtillon, was a French nobleman, Admiral of France, and Huguenot leader during the French Wars of Religion. He served under kings Francis I and Henry II during the Italian Wars, attaining great prominence both due to his military skill and his relationship with his uncle, the king's favourite Anne de Montmorency. During the reign of Francis II he converted to Protestantism, becoming a leading noble advocate for the Reformation during the early reign of Charles IX.

Henri I de Lorraine, Duke of Guise, Prince of Joinville, Count of Eu, sometimes called Le Balafré ('Scarface'), was the eldest son of François, Duke of Guise, and Anna d'Este. His maternal grandparents were Ercole II d'Este, Duke of Ferrara, and Renée of France. Through his maternal grandfather, he was a descendant of Lucrezia Borgia and Pope Alexander VI.

Louis de Bourbon, 1st Prince of Condé was a prominent Huguenot leader and general, the founder of the Condé branch of the House of Bourbon. Coming from a position of relative political unimportance during the reign of Henri II, Condé's support for the Huguenots, along with his leading role in the conspiracy of Amboise and its aftermath, pushed him to the centre of French politics. Arrested during the reign of Francis II then released upon the latter's premature death, he would lead the Huguenot forces in the first three civil wars of the French Wars of Religion before being executed after his defeat at the Battle of Jarnac in 1569.

Anne de Montmorency, duc de Montmorency was a French noble, governor, royal favourite and Constable of France during the mid to late Italian Wars and early French Wars of Religion. He served under five French kings. He began his career in the latter Italian Wars of Louis XII, seeing service at Ravenna. When François, his childhood friend, ascended to the throne in 1515 he advanced as governor of the Bastille and Novara, then in 1522 was made a Marshal of France. He fought at the French defeat at La Bicocca in that year, and after assisting in rebuffing the invasion of Constable Bourbon he was captured at the disastrous Battle of Pavia. Quickly freed he worked to free first the king and then the king's sons. In 1526 he was made Grand Maître, granting him authority over the king's household, he was also made governor of Languedoc. He aided in the marriage negotiations for the king's son the duc d'Orléans to Catherine de’ Medici in 1533. In the mid 1530s he found himself opposed to the war party at court led by Admiral Chabot and therefore retired. He returned to the fore after the Holy Roman Emperor invaded Provence, leading the royal effort that foiled his invasion, and leading the counter-attack. In 1538 he was rewarded by being made Constable of France, this made him the supreme authority over the French military. For the next two years he led the efforts to secure Milano for France through negotiation with the Emperor, however this proved a failure and Montmorency was disgraced, retiring from court in 1541.

François de Lorraine, 2nd Duke of Guise, 1st Prince of Joinville, and 1st Duke of Aumale, was a French general and statesman. A prominent leader during the Italian War of 1551–1559 and French Wars of Religion, he was assassinated during the siege of Orleans in 1563.

François de Montmorency, 2nd Duke of Montmorency was a French noble, governor, diplomat and soldier during the latter Italian Wars and the early French Wars of Religion. The son of Anne de Montmorency, favourite of the king and Madeleine of Savoy, Montmorency began his political career during the coronation of Henri II in 1547. With the resumption of the Italian Wars in 1551 he fought at the capture of Chieri, the famous defence of Metz and the defence of Thérouanne. In the latter engagement he was captured by Imperial forces, and put up for ransom. He would spend the next three years in captivity before returning to France in 1556. Returning to the conflict immediately he participated in the disastrous Saint-Quentin campaign in which the French army was destroyed and his father captured. After serving as a lieutenant in Picardie he found himself gaining advantage on the death of Henri II, the new Guise regime compensating the Montmorency family for their seizure of the grand maître title with the provision of a Marshal baton to Montmorency.

France Antarctique was a French colony in Rio de Janeiro, in modern-day Brazil, which existed between 1555 and 1567, and had control over the coast from Rio de Janeiro to Cabo Frio. The colony quickly became a haven for Huguenots, and was ultimately destroyed by the Portuguese in 1567.

The Three Bishoprics constituted a government of the Kingdom of France consisting of the dioceses of Metz, Verdun, and Toul within the Lorraine region. The three dioceses had been Prince-bishoprics of the Holy Roman Empire until they were seized by King Henry II of France between April and June 1552. At the end of the Thirty Years' War, they were officially ceded to France by the 1648 Peace of Westphalia.

Jacques de Savoie, duc de Nemours was a French military commander, governor and Prince Étranger. Having inherited his titles at a young age, Nemours fought for king Henri II during the latter Italian Wars, seeing action at the siege of Metz and the stunning victories of Renty and Calais in 1554 and 1558. Already a commander of French infantry, he received promotion to commander of the light cavalry after the capture of Calais in 1558. A year prior he had accompanied François, Duke of Guise on his entry into Italy, as much for the purpose of campaigning as to escape the king's cousin Antoine of Navarre who was threatening to kill him for his extra-marital pursuit of Navarre's cousin.

Claude II de Lorraine, duc d'Aumale was a Prince étranger, military commander and French governor, during the latter Italian Wars and the early French Wars of Religion. The son of the first Duke of Guise he started his career in a pre-eminent position in French politics as a son of one of the leading families in the court of Henri II of France. Upon the death of his father in 1550, Aumale inherited the governorship of Burgundy from his father, and the duchy of Aumale from his brother who assumed the titles of Guise. Aumale was made colonel-general of the light horse by the new king and fought in Italy, Alsace and Picardie between 1551 and 1559. While leading the light cavalry during the defence of Metz he was captured, and held for the next two years, until his mother in law Diane de Poitiers paid his ransom. He achieved success at the siege of Volpiano and played an important role in the capture of Calais for which he was rewarded with the governorship of French Piedmont.

Gaspard de Saulx, sieur de Tavannes was a French Roman Catholic military leader during the Italian Wars and the French Wars of Religion. He served under four kings during his career, participating in the Siege of Calais (1558) and leading the royal army to victory in the third civil war at the Jarnac and Moncontour. A strong Catholic, he founded the confraternity of the holy ghost in 1567 which would be a template for other militant Catholic organisations across France. He died in 1573, shortly after the opening assassinations of the Massacre of Saint Bartholomew, which he had helped plan.
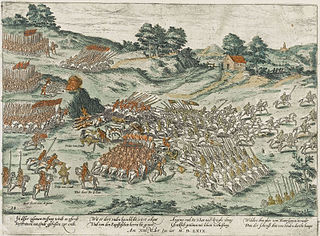
The Battle of Jarnac on 13 March 1569 was an encounter during the French Wars of Religion between the Catholic forces of Marshal Gaspard de Saulx, sieur de Tavannes, and the Huguenots led by Louis I de Bourbon, prince de Condé. The two forces met outside Jarnac between the right bank of the Charente and the high road between Angoulême and Cognac. The Huguenots were routed and Condé was killed after his surrender and his body paraded on an ass in Jarnac.

The Treaty of Chambord was an agreement signed on 15 January 1552 at the Château de Chambord between the Catholic King Henry II of France and three Protestant princes of the Holy Roman Empire led by Elector Maurice of Saxony. Based on the terms of the treaty, Maurice ceded the vicariate over the Three Bishoprics of Toul, Verdun, and Metz to France. In return, he was promised military and economic aid from Henry II in order to fight against the forces of Emperor Charles V of Habsburg.

François d'Andelot de Coligny was one of the leaders of French Protestantism during the French Wars of Religion. The son of Gaspard I de Coligny, he was the younger brother of Odet, cardinal de Châtillon and Gaspard de Coligny, the admiral.

Charles de Bourbon, Prince de la Roche-sur-Yon,, was a Prince of the Blood and provincial governor under three French kings. He fought in the latter Italian wars during the reign of Henri II, commanding an army during the 1554 campaign into the Spanish Netherlands.

François I de Clèves, was a French Prince étranger and military commander during the Italian Wars. He was the first duke of Nevers, his county being elevated to a duchy in 1539. In deference to the large amount of land he held in Champagne, and lands he was set to inherit there from his mother, François was made governor of Champagne in 1545.

The siege of Orléans was the final key military engagement of the first French War of Religion. Having lost the Battle of Dreux the rebel Huguenots fell back with their remaining forces to the city. François, Duke of Guise, the only non captive royal commander, moved to lay siege to the town, hoping its capitulation would bring about a total victory for the crowns forces. However, despite reducing the suburbs, he would be assassinated at the siege before he could bring it to a conclusion. As a result the captive Louis, Prince of Condé and Anne de Montmorency at Catherine de' Medici's direction were able to negotiate a compromise end to the first war in the Edict of Amboise.
Jacqueline de Montbel d'Entremont was a French courtier, possible artistic muse and Huguenot, known for her experiences during the French wars of religion. After her first husband's death, she converted to Protestantism and married Gaspard II de Coligny, who was later killed in the St. Bartholomew's Day Massacre.



















