
The People's Army of Vietnam (PAVN), officially the Vietnam People's Army, also recognized as the Vietnamese Army or the People's Army, is the national military force of the Socialist Republic of Vietnam and the armed wing of the ruling Communist Party of Vietnam (CPV). The PAVN is the backbone component of the Vietnam People's Armed Forces and includes: Ground Force, Navy, Air Force, Border Guard and Coast Guard. Vietnam does not have a separate and formally-structured Ground Force or Army service. Instead, all ground troops, army corps, military districts and special forces are designated under the umbrella term combined arms and are belonged to the Ministry of National Defence, directly under the command of the CPV Central Military Commission, the Minister of National Defence, and the General Staff of the Vietnam People's Army. The military flag of the PAVN is the National flag of the Socialist Republic of Vietnam defaced with the motto Quyết thắng added in yellow at the top left.

Võ Nguyên Giáp was a Vietnamese general, communist revolutionary and politician. Regarded as one of the greatest military strategists of the 20th century, Giáp led Vietnamese communist forces to victories in wars against Japan, France, South Vietnam and the United States, and China. Giáp was the military commander of the Việt Minh and the People's Army from 1941 to 1972, minister of defense of the Democratic Republic of Vietnam and the Socialist Republic of Vietnam in 1946–1947 and from 1948 to 1980, and deputy prime minister from 1955 to 1991. He was a member of the Politburo of the Communist Party of Vietnam.

The Battle of Điện Biên Phủ was a climactic confrontation of the First Indochina War that took place between 13 March and 7 May 1954. It was fought between the French Union's colonial Far East Expeditionary Corps and Viet Minh communist revolutionaries.
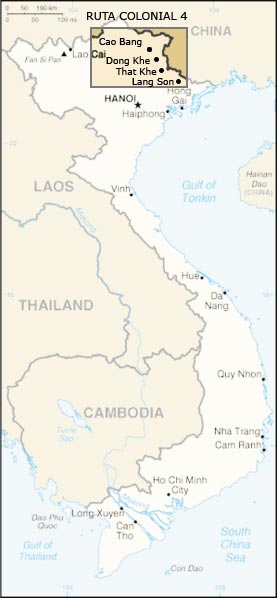
The Battle of Route Coloniale 4, also called the Autumn-Winter Border Campaign by the Viet Minh, was a battle of the First Indochina War. It took place along Route Coloniale 4, a road used to supply the French military base at Cao Bằng. French military traffic along the road had previously been subject to an ongoing series of ambushes during 1947–1949.

The First Indochina War was fought between France and Việt Minh, and their respective allies, from 19 December 1946 until 21 July 1954. Việt Minh was led by Võ Nguyên Giáp and Hồ Chí Minh. Most of the fighting took place in Tonkin in Northern Vietnam, although the conflict engulfed the entire country and also extended into the neighboring French Indochina protectorates of Laos and Cambodia.
This article deals with the history of the French air force in colonial territories from World War II to the post-colonial period.
The Battle of Mạo Khê, occurring from March 23 to March 28, 1951, was a significant engagement in the First Indochina War between the French Union and the Việt Minh. The French Union forces, led by World War II hero Jean de Lattre de Tassigny, inflicted a defeat on Việt Minh forces, which were commanded by General Võ Nguyên Giáp. The French Union victory, however, was not decisive and the Việt Minh would attack again shortly afterwards.

Operation Lorraine was a French military operation of the First Indochina War.
The Battle of Hòa Bình was fought during the First Indochina War. It occurred from 10 November 1951 to 25 February 1952, when French Union forces attempted to lure the Việt Minh out into the open and to force it to fight on French terms.

The Battle of Nà Sản was fought between French Union forces and the Nationalist forces of the Việt Minh at Nà Sản, Sơn La Province, during the First Indochina War for control of the T’ai region.

Bernard de Lattre de Tassigny was a French Army officer, who fought during World War II and the First Indochina War. Bernard de Lattre received several medals during his military career, including the Médaille militaire. He was killed in action at the age of 23, fighting near Ninh Binh. At the time of his death, his father, General Jean de Lattre de Tassigny, was the overall commander of French forces in Indochina. Bernard's death received widespread newspaper coverage, with headlines drawing attention to the death of the son of a general. His mother worked to preserve the memory of her son, as well as that of her more famous husband who died in 1952. Their legacy includes an open-air memorial chapel and centre in Wildenstein, Alsace, France. The death of Bernard de Lattre is mentioned in histories of the First Indochina War, and it has been compared to the deaths of other sons of generals and military leaders.
The 308th Infantry Division is a division of the People's Army of Vietnam (PAVN), first formed in August 1950 in southern China from the previous Regimental Group 308.

The Battle of the Day River took place between late May and early June 1951, around the Day River Delta in the Gulf of Tonkin. Part of the First Indochina War, the battle was the first conventional campaign of Võ Nguyên Giáp, and saw his Việt Minh People's Army of Vietnam (VPA) forces tackle the Catholic-dominated region of the Delta in order to break its resistance to Việt Minh infiltration. On the back of two defeats at similar ventures through March and April that year, Giap led three divisions in a pattern of guerrilla and diversion attacks on Ninh Bình, Nam Định, Phủ Lý and Phat Diem beginning on May 28 which saw the destruction of commando François, a naval commando.

General Lê Trọng Tấn was an officer of the People's Army of Vietnam (PAVN) during 1945 to 1986. During this period of his military career, Lê Trọng Tấn held several senior positions of the Army. Lê Trọng Tấn participated in the Viet Minh movement before the August Revolution in 1945 and gradually became one of the most important figures of the Vietnam People's Army during the Second Indochina War. Being one of the key figures of the North Vietnam armed forces in Vietnam War, Lê Trọng Tấn was Deputy Commander of the Viet Cong (VC) and second commander of the 1975 Spring Offensive that effectively ended the war. Afterwards, he became Chief of the General Staff and Deputy Minister of Defence of Vietnam until his death in December 1986. Lê Trọng Tấn was widely appreciated by his comrades, whom of which include general Võ Nguyên Giáp, as one of the finest commanders of the Vietnam People's Army.
The 320th Division or Đồng Bằng Division is a formation and one of the six original "Steel and Iron Divisions" of the People's Army of Vietnam (PAVN). It was established in January 1951.

On December 19, 1946, Viet Minh soldiers detonated explosives in Hanoi, and the ensuing battle, known as the Battle of Hanoi marked the opening salvo of the First Indochina War.
The Battle of Nghĩa Lộ, also called Ly Thuong Kiet Campaign by Việt Minh, was fought between the French army and the Việt Minh during the First Indochina War. Both general Giap and de Lattre waited eagerly for the battle due to the postponement that occurred when Giap's attack along the Day River were driven back in June 1951. Since Giap was the one controlling the tempo of this war for months, it took a huge turn during the pause after his defeat causing his military situation to become unstable. On 3 October, the Việt Minh 312th Division launched an attack on French forces in the town of Nghĩa Lộ and its vicinity which was led by the general Giap. This attack on Nghĩa Lộ occurred 95 miles west of Hanoi and only 65 miles past that of the western de Lattre Line. This village was the utmost importance to de Lattre because it served as the capital of the T'ai natives which had very strong ties with the French. The first attacked was carried out by two regiments of the 312th Division to the surrounding posts that acted as the main defense of the town in order to maintain military control. Since de Lattre was not present at the time, General Salan took the reins of the situation and quickly reinforced the surrounding posts with paratroopers carried by parachutes to fortify defenses. This quick strategy by General Salan was looked upon the saving grace of this battle since it repelled a secondary attack by two regiments of the 312th Division that same night. Additional reinforcements occurred during the 4th of October along with air support which led to General Giap to call off his attack which they then fled across the Red River. A year later on 17 October, the Việt Minh launched another attack on Nghĩa Lộ and succeeded in driving out the remaining French from the area.
The 312th Infantry Division is a division of the People's Army of Vietnam (PAVN), first formed in October 1950. It was one of the 6 original "Iron and Steel" Divisions of the Viet Minh.
The Battle of Nghĩa Lộ was a battle of the First Indochina War. In the fall of 1952 the French army encountered its most serious crisis since the disasters near the Chinese border at Cao Bằng, Đông Khê and RC 4 occurred in 1949 and 1950. The Battle of Nghĩa Lộ was the opening salvo in a series of offenses and counter-offenses in late 1952 during the First Indochina War. It was part of a Việt Minh offensive in the T’ai region of Tonkin in the vicinity of the Black River. The French countered with Operation Lorraine to attack Việt Minh rear supply bases in an attempt to cut off the offensive. The Việt Minh did not cease or divert the offensive to protect its supply bases. The Việt Minh continued its offensive attack against Nà Sản where there was an outpost and a short airstrip, both guarded by the French army. This series of battles lasted for three months between October 1952 and December 1952. These actions and the Việt Minh successes set the stage for the subsequent Invasion of Laos in April 1953.

Vương Thừa Vũ (1910-1980) was a lieutenant-general in the People's Army of Vietnam active during World War II, the First Indochina War, and the Vietnam War. He commanded Viet Minh forces in their early engagements at Hanoi in 1946, directing the city's two month-long defence against French forces. By 1949, during the Viet Minh's transition from guerrilla to regular warfare, he had risen to command the PAVN's first modern infantry division, the 308th, which he led into battle at Dien Bien Phu in 1954.










