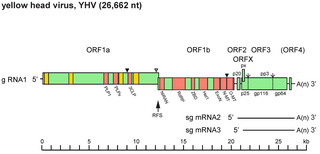
Okavirus is a genus of enveloped positive-strand RNA viruses which infect crustaceans. Host organisms are mostly shrimp. It is the only genus in the family Roniviridae. Viruses associated with the genus include: gill-associated virus (GAV) which causes reddening, biofouling with exoparasites, emaciation, and massive mortality; and yellow head virus (YHV) which causes yellow head, arrest of feeding, and massive mortality. The name is derived from the 'Oka' or lymphoid organ in which the viruses are commonly detected and in which pathology occurs during acute infections. Lymphoid organs are anatomical structures common to penaeid shrimp. There are three species in this genus.

Barnaviridae is a family of non-enveloped, positive-strand RNA viruses. Cultivated mushrooms serve as natural hosts. The family has one genus, Barnavirus, which contains one species: Mushroom bacilliform virus. Diseases associated with this family includes La France disease.
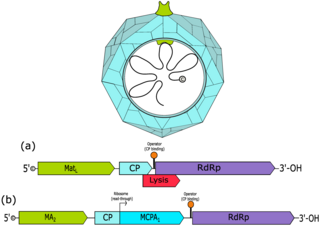
Fiersviridae is a family of positive-strand RNA viruses which infect prokaryotes. Bacteria serve as the natural host. They are small viruses with linear, positive-sense, single-stranded RNA genomes that encode four proteins. All phages of this family require bacterial pili to attach to and infect cells. The family has 185 genera, most discovered by metagenomics. In 2020, the family was renamed from Leviviridae to its current name.
Closterovirus, also known as beet yellows viral group, is a genus of viruses, in the family Closteroviridae. Plants serve as natural hosts. There are 17 species in this genus. Diseases associated with this genus include: yellowing and necrosis, particularly affecting the phloem. This genus has a probably worldwide distribution and includes among other viral species the Beet yellows virus and Citrus tristeza virus, rather economically important plant diseases. At least some species require vectors such as aphids or mealybugs for their transmission from plant to plant.

Totivirus is a genus of double-stranded RNA viruses in the family Totiviridae. Fungi serve as natural hosts. The name of the group derives from Latin toti which means undivided or whole. There are seven species in this genus.
Marnaviridae is a family of positive-stranded RNA viruses in the order Picornavirales. The first species of this family that was isolated is Heterosigma akashiwo RNA virus (HaRNAV) in the genus Marnavirus, that infects the toxic bloom-forming Raphidophyte alga, Heterosigma akashiwo. Using a sequence-based framework an additional twenty marine RNA viruses have been added to the family.

Benyvirus is a genus of viruses, in the family Benyviridae. Plant serve as natural hosts. There are four species in this genus. Diseases associated with this genus include: BNYVV: rhizomania.
Sadwavirus is a genus of viruses in the order Picornavirales, in the family Secoviridae. Plants serve as natural hosts. There are three subgenera and five species in this genus. Diseases associated with this genus include: satsuma dwarf virus disease which causes spoon-shaped leaves on citrus tree. Symptoms are enations, multiple flushing, stunting or dwarfing, reduction in number and size of leaves and fruits. The name of this genus comes from one of its species: Satsuma dwarf virus.
Cilevirus is a genus of viruses in the family Kitaviridae. Plants serve as natural hosts. There are two species: Citrus leprosis virus C and Citrus leprosis virus C2.
Aureusvirus is a genus of viruses, in the family Tombusviridae. Plants serve as natural hosts. There are six species in this genus.
Bymovirus is a genus of viruses, in the family Potyviridae. Plants serve as natural hosts. There are six species in this genus.
Tritimovirus is a genus of viruses, in the family Potyviridae. Plants serve as natural hosts. There are six species in this genus.

Alvernaviridae is a family of non-enveloped positive-strand RNA viruses. Dinoflagellates serve as natural hosts. There is one genus in this family, Dinornavirus, which contains one species: Heterocapsa circularisquama RNA virus 01. Diseases associated with this family include host population control, possibly through lysis of the host cell.
Permutotetraviridae is a family of viruses. Lepidopteran insects serve as natural hosts. The family contains one genus that has two species. Diseases associated with this family include: infection outcome varies from unapparent to lethal.
Alphanecrovirus is a genus of viruses, in the family Tombusviridae. Plants serve as natural hosts. There are four species in this genus.
Aparavirus is a genus of viruses in the order Picornavirales, in the family Dicistroviridae. Invertebrates, honeybee, and bumblebees serve as natural hosts. There are six species in this genus. Diseases associated with this genus include: ABPV: paralysis. This virus plays a role in sudden collapse of honey bee colonies infested with the parasitic mite varroa destructor.
Alphamononivirus is a genus of enveloped, positive-strand RNA viruses in the order Nidovirales which infect planarian flatworms. Member virus planarian secretory cell nidovirus (PSCNV) has the largest known nonsegmented RNA genome of 41.1kb of any RNA virus. The genus is monotypic. It contains the subgenus Dumedivirus, which contains only one species, Planidovirus 1. Alphamononivirus is also the only member of the subfamily Mononivirinae, which in turn is the only member of family Mononiviridae, which likewise is the only member of the Monidovirineae suborder.

Solemoviridae is a family of non-enveloped, positive-strand RNA viruses which infect plants. Solemoviridae is a member of the order Sobelivirales.

Variarterivirinae is a subfamily of enveloped, positive-strand RNA viruses which infect vertebrates. The subfamily is in the family Arteriviridae and order Nidovirales. The subfamily contains three genera.

Simarterivirinae is a subfamily of enveloped, positive-strand RNA viruses which infect vertebrate. The subfamily is in the family Arteriviridae and order Nidovirales. The subfamily contains six genera.










