
Aargau, more formally the Canton of Aargau, is one of the 26 cantons forming the Swiss Confederation. It is composed of eleven districts and its capital is Aarau.

The canton of Bern, or Berne, is one of the 26 cantons forming the Swiss Confederation. Its capital city, Bern, is also the de facto capital of Switzerland. The bear is the heraldic symbol of the canton, displayed on a red-yellow background.

Lenzburg Castle is a castle located above the old part of the town of Lenzburg in the Canton of Aargau, Switzerland. It ranks among the oldest and most important of Switzerland. The castle stands on the almost circular castle hill, which rises approximately 100 m (330 ft) over the surrounding plain but is only about 250 m (820 ft) in diameter. The oldest parts of the castle date to the 11th century, when the Counts of Lenzburg built it as their seat. The castle, its historical museum and the castle hill with its Neolithic burial grounds are listed as heritage sites of national significance.

Biberstein is a municipality in the district of Aarau of the canton of Aargau in Switzerland.

The County of Baden was a condominium of the Old Swiss Confederacy and is now part of the Swiss canton of Aargau. The county was established in 1415 after the Swiss conquest of the Aargau and was ruled as a shared condominium until 1798 when it became part of the short-lived Canton of Baden.
The Kyburg family was a noble family of grafen (counts) in the Duchy of Swabia, a cadet line of the counts of Dillingen, who in the late 12th and early 13th centuries ruled the County of Kyburg, corresponding to much of what is now Northeastern Switzerland.

Kasteln Castle is a castle in the municipality of Oberflachs in Canton Aargau, Switzerland. It is located west of the village on a rocky outcrop, surrounded by vineyards and woods. Today, it serves as a boarding school for students with behavioral problems. The immediately adjacent castle Ruchenstein was demolished in 1643, when the small fort was rebuilt into a Schloss Kasteln.

Schenkenberg Castle is a castle ruin above the municipality of Thalheim in the canton of Aargau in Switzerland. It was built in the 13th Century by the Habsburg dynasty, was the administrative seat for 260 years of a bailiwick of the city of Bern and fell into ruin in the 18th century.

Brunegg castle is a castle in the municipality of Brunegg in the canton of Aargau in Switzerland.

Aarburg Castle is a castle in the municipality of Aarburg in the canton of Aargau in Switzerland. It is located high above the town Aarburg on a steep, rocky hillside. The castle was built around a medieval castle, which controlled the narrow point on the Aare river and served as the seat of Aarburg Vogt. It is classified as a Swiss heritage site of national significance. Today it houses the Kantonale Jugendheim, for holding and rehabilitating juvenile offenders.

Burgdorf Castle is a castle in the municipality of Burgdorf in the canton of Bern in Switzerland. It is a Swiss heritage site of national significance.

Oberhofen Castle is a castle in the municipality of Oberhofen of the Canton of Bern in Switzerland. It is a Swiss heritage site of national significance.

Spiez Castle is a castle in the municipality of Spiez of the Swiss canton of Bern. It is a Swiss heritage site of national significance.

Wimmis Castle is a castle in the municipality of Wimmis of the Canton of Bern in Switzerland. It is a Swiss heritage site of national significance.

The ruins of Grünenberg Castle, Schnabelburg Castle and Langenstein Castle are a complex of three interconnected castles on a hill above the municipality of Melchnau in the canton of Bern in Switzerland. The three castles formed the center of power of the Barons of Grünenberg in the Oberaargau region during the High Middle Ages.

Fraubrunnen Abbey is a former Cistercian nunnery in the municipality of Fraubrunnen in the canton of Bern, Switzerland.
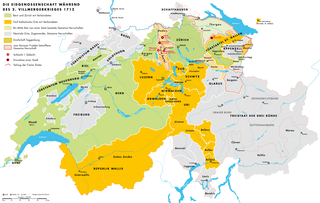
The Toggenburg War, also known as the Second War of Villmergen or the Swiss Civil War of 1712, was a Swiss civil war during the Old Swiss Confederacy from 12 April to 11 August 1712. The Catholic "inner cantons" and the Imperial Abbey of Saint Gall fought the Protestant cantons of Bern and Zürich as well as the abbatial subjects of Toggenburg. The conflict was a religious war, a war for hegemony in the Confederacy and an uprising of subjects. The war ended in a Protestant victory and upset the balance of political power within the Confederacy.

Bipp Castle is a partially ruined castle in the municipality of Oberbipp of the Canton of Bern in Switzerland.

Altenburg Castle is a castle in the village of Altenburg bei Brugg in the municipality of Brugg in the canton of Aargau in Switzerland. The castle and the Altenburg Roman ruins, which are integrated into it, are classified as Swiss heritage site of national significance.

Trostburg Castle is a small castle in the municipality of Teufenthal in the canton of Aargau in Switzerland.





















