
Brown algae are a large group of multicellular algae comprising the class Phaeophyceae. They include many seaweeds located in colder waters of the Northern Hemisphere. Brown algae are the major seaweeds of the temperate and polar regions. Many brown algae, such as members of the order Fucales, commonly grow along rocky seashores. Most brown algae live in marine environments, where they play an important role both as food and as a potential habitat. For instance, Macrocystis, a kelp of the order Laminariales, may reach 60 m (200 ft) in length and forms prominent underwater kelp forests that contain a high level of biodiversity. Another example is Sargassum, which creates unique floating mats of seaweed in the tropical waters of the Sargasso Sea that serve as the habitats for many species. Some members of the class, such as kelps, are used by humans as food.

The Sargasso Sea is a region of the Atlantic Ocean bounded by four currents forming an ocean gyre. Unlike all other regions called seas, it has no land boundaries. It is distinguished from other parts of the Atlantic Ocean by its characteristic brown Sargassum seaweed and often calm blue water.

Sargassum is a genus of brown macroalgae (seaweed) in the order Fucales of the Phaeophyceae class. Numerous species are distributed throughout the temperate and tropical oceans of the world, where they generally inhabit shallow water and coral reefs, and the genus is widely known for its planktonic (free-floating) species. Most species within the class Phaeophyceae are predominantly cold-water organisms that benefit from nutrients upwelling, but the genus Sargassum appears to be an exception. Any number of the normally benthic species may take on a planktonic, often pelagic existence after being removed from reefs during rough weather. Two species have become holopelagic—reproducing vegetatively and never attaching to the seafloor during their lifecycles. The Atlantic Ocean's Sargasso Sea was named after the algae, as it hosts a large amount of Sargassum.

Arame, sea oak is a species of kelp, of the brown algae, best known for its use in Japanese cuisine.

Masseira is a unique form of traditional farming practised in Póvoa de Varzim and Esposende in Portugal.

Quião Beach is an extensive maritime beach of Póvoa de Varzim, Portugal, located just South of Cape Santo André in the area of A Ver-o-Mar. It has fine to medium sand and several rocky outcrops. The beach is a coastal dune habitat and a rich and diverse marine ecosystem, including large honeycomb reefs. It has a popular beach restaurant, Praia do Mestre.

Ecklonia cava, is an edible marine brown alga species found in the ocean off Japan and Korea.

Sargassum muticum, commonly known as Japanese wireweed or japweed, is a large brown seaweed of the genus Sargassum. It is an invasive seaweed with high growth rate. It has an efficient dispersion thanks to its floats.

Phlorotannins are a type of tannins found in brown algae such as kelps and rockweeds or sargassacean species, and in a lower amount also in some red algae. Contrary to hydrolysable or condensed tannins, these compounds are oligomers of phloroglucinol (polyphloroglucinols). As they are called tannins, they have the ability to precipitate proteins. It has been noticed that some phlorotannins have the ability to oxidize and form covalent bonds with some proteins. In contrast, under similar experimental conditions three types of terrestrial tannins apparently did not form covalent complexes with proteins.
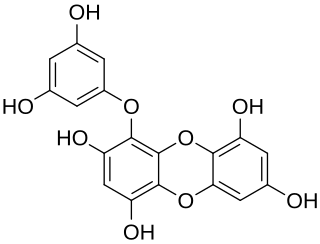
Eckol is a phlorotannin isolated from brown algae in the family Lessoniaceae such as species in the genus Ecklonia such as E. cava or E. kurome or in the genus Eisenia such as Eisenia bicyclis.
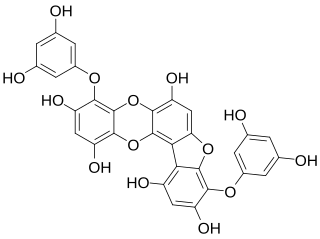
Phlorofucofuroeckol A is a phlorotannin isolated from brown algae species such as Eisenia bicyclis, Ecklonia cava, Ecklonia kurome or Ecklonia stolonifera.
Ecklonia stolonifera is a brown alga species in the genus Ecklonia found in the Sea of Japan. It is an edible species traditionally eaten in Japan.
Ecklonia kurome is a brown alga species in the genus Ecklonia found in the Sea of Japan.
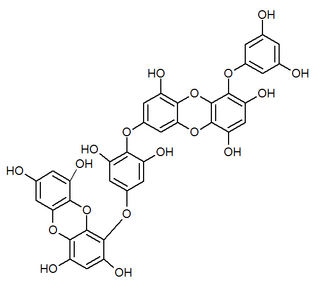
Dieckol is a phlorotannin that can be found in arame, in Ecklonia cava or in Ecklonia stolonifera.
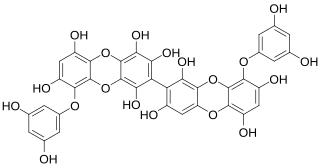
8,8'-Bieckol is an eckol-type phlorotannin found in the brown algae Ecklonia cava and Ecklonia kurome.

Eckstolonol is a phlorotannin found in the edible brown algae arame and turuarame.
Sargassum ringgoldianum is a brown alga species in the genus of Sargassum. The ethanol extract of S. ringgoldianum contains phlorotannins of the bifuhalol type, which shows an antioxidative activity.
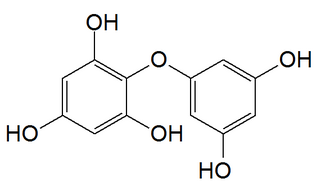
Diphlorethol is a phlorotannin found in the brown alga Cystophora retroflexa. It falls under the phlorethols class of phlorotannins due to the ether bond that connects its two phloroglucinol units.

Fucosterol is a sterol isolated from algae such as Ecklonia cava or Ecklonia stolonifera.
















