
A cable modem is a type of network bridge that provides bi-directional data communication via radio frequency channels on a hybrid fibre-coaxial (HFC), radio frequency over glass (RFoG) and coaxial cable infrastructure. Cable modems are primarily used to deliver broadband Internet access in the form of cable Internet, taking advantage of the high bandwidth of a HFC and RFoG network. They are commonly deployed in the Americas, Asia, Australia, and Europe.
A digital video recorder (DVR) is an electronic device that records video in a digital format to a disk drive, USB flash drive, SD memory card, SSD or other local or networked mass storage device. The term includes set-top boxes (STB) with direct to disk recording, portable media players and TV gateways with recording capability, and digital camcorders. Personal computers are often connected to video capture devices and used as DVRs; in such cases the application software used to record video is an integral part of the DVR. Many DVRs are classified as consumer electronic devices; such devices may alternatively be referred to as personal video recorders (PVRs), particularly in Canada. Similar small devices with built-in displays and SSD support may be used for professional film or video production, as these recorders often do not have the limitations that built-in recorders in cameras have, offering wider codec support, the removal of recording time limitations and higher bitrates.
Vonage Holdings Corp. is an American cloud communications provider operating as a subsidiary of Ericsson. Headquartered in Holmdel Township, New Jersey, the organization was founded in 1998 as Min-X as a provider of residential telecommunications services based on voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP). In 2001, the organization changed its name to Vonage.
Hybrid fiber-coaxial (HFC) is a broadband telecommunications network that combines optical fiber and coaxial cable. It has been commonly employed globally by cable television operators since the early 1990s.
Cox Communications, Inc. is an American digital cable television provider, telecommunications and home automation services. It is the third-largest cable television provider in the United States, serving approximately 6.5 million customers, including 2.9 million digital cable subscribers, 3.5 million Internet subscribers, and almost 3.2 million digital telephone subscribers, making it the seventh-largest telephone carrier in the country. Cox is headquartered at 6205 Peachtree Dunwoody Rd in Sandy Springs, Georgia, U.S., in the Atlanta metropolitan area. It is a privately owned subsidiary of Cox Enterprises.

CableCARD is a special-use PC Card device that allows consumers in the United States to view and record digital cable television channels on digital video recorders, personal computers and television sets on equipment such as a set-top box not provided by a cable television company. The card is usually provided by the local cable operator, typically for a nominal monthly fee.
Pace plc was a British company which developed set-top boxes (STBs), advanced residential gateways, software and services for the pay-TV and broadband services industry. Pace's customers included cable, telco, satellite and IPTV operators. The company was listed on the London Stock Exchange until December 2015, when the company received the last of the regulatory clearances needed to allow a merger with Arris Group to proceed. In 2019, Arris was subsequently acquired by network infrastructure provider CommScope.

Scientific Atlanta, Inc. was a Georgia, United States–based manufacturer of cable television, telecommunications, and broadband equipment. Scientific Atlanta was founded in 1951 by a group of engineers from the Georgia Institute of Technology, and was purchased by Cisco Systems in 2005 for $6.9 billion after Cisco received antitrust clearance for the purchase. The Cisco acquisition of Scientific Atlanta was ranked in the top 10 of largest technology acquisitions in history and was Cisco's largest acquisition to date. Prior to the purchase, Scientific Atlanta had been a Fortune 500 company and was one of the top 25 largest corporations in Georgia.

Moxi was a line of high-definition digital video recorders produced by Moxi Digital Digeo and Arris International. Moxi was originally released only to cable operators, but in December 2008 it was released as a retail product. Moxi was removed from the market in November 2011. The former retail product, the Moxi HD DVR, provided a high-definition user interface with support for either two or three CableCARD TV tuners. Arris also offered a companion appliance, the Moxi Mate, which could stream live or recorded TV from a Moxi HD DVR.
The Technology and Engineering Emmy Awards, or Technology and Engineering Emmys, are one of two sets of Emmy Awards that are presented for outstanding achievement in engineering development in the television industry. The Technology and Engineering Emmy Awards are presented by the National Academy of Television Arts and Sciences (NATAS), while the separate Primetime Engineering Emmy Awards are given by its sister organization the Academy of Television Arts & Sciences (ATAS).
Arris International Limited is an American telecommunications equipment company engaged in data, video and telephony systems for homes and businesses. On April 4, 2019, Arris was acquired by network infrastructure provider CommScope.
Applied Micro Circuits Corporation was a fabless semiconductor company designing network and embedded Power ISA, and server processor ARM, optical transport and storage products.
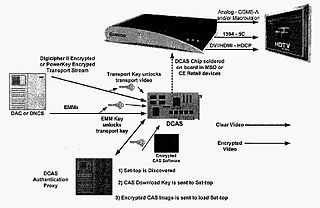
Downloadable Conditional Access System or DCAS was a proposal advanced by CableLabs for secure software download of a specific Conditional Access client which controls digital rights management (DRM) into an OCAP-compliant host consumer media device. The National Cable & Telecommunications Association (NCTA) proposed that DCAS be used as a substitute for physical CableCARDs, a standard also created by CableLabs for which products began appearing in August 2004 as part of industry compliance to the FCC mandate, which in turn is pursuant to the Telecommunications Act of 1996. DCAS is growing in popularity as a less expensive alternative for CableCARD, with major North American operator deployments from Cablevision and Charter. DCAS deployments can be expected to grow in the coming years, thanks to favorable regulatory view from the STELA Reauthorization Act of 2014 and FCC appointing a Downloadable Security Technical Advisory Committee, and wider support for key ladder (K-LAD) functionality from system-on-chip (SoC) vendors and set-top box manufacturers.

Switched video or switched digital video (SDV), sometimes referred to as switched broadcast (SWB), is a telecommunications industry term for a network scheme for distributing digital video via a cable. Switched video sends the digital video more efficiently freeing bandwidth. The scheme applies to digital video distribution both on typical cable TV systems using QAM channels, or on IPTV systems.
Tru2way is a brand name for interactive digital cable services delivered over the cable network. Services include interactive program guides, interactive ads, games, chat, web browsing, and T-Commerce. The brand also appears as <tru2way> and is used to market cable services, applications, and devices that support the tru2way cable architecture. Tru2way is the successor name for technology known as OpenCable. Major cable operators committed to deploy the tru2way platform in service areas covering more than 90 million U.S. homes by the end of 2008.

CommScope Holding Company, Inc. is an American network infrastructure provider based in Hickory, North Carolina. CommScope employs over 30,000 employees. The company joined the Nasdaq stock exchange on October 25, 2013.
Stingray Group Inc. is a Canadian music, media and technology company based in Montreal, Quebec, with offices in Toronto, Ontario, as well as in the United States, Mexico, the United Kingdom, the Netherlands, Germany and Australia.

RUCKUS Networks is a brand of wired and wireless networking equipment and software owned by CommScope. Ruckus offers Switches, Wi-Fi access points, CBRS access points, Controllers, Management systems, Cloud management, AAA/BYOD software, AI and ML analytics software, location software and IoT controller software products to mobile carriers, broadband service providers, and corporate enterprises. As a company, Ruckus invented and has patented wireless voice, video, and data technology, such as adaptive antenna arrays that extend signal range, increase data rates, and avoid interference, providing distribution of delay-sensitive content over standard 802.11 Wi-Fi.

Mellanox Technologies Ltd. was an Israeli-American multinational supplier of computer networking products based on InfiniBand and Ethernet technology. Mellanox offered adapters, switches, software, cables and silicon for markets including high-performance computing, data centers, cloud computing, computer data storage and financial services.
Harmonic Inc. is an American technology company that develops and markets video routing, server, and storage products for companies that produce, process, and distribute video content for television and the Internet.








