
Lignite, often referred to as brown coal, is a soft, brown, combustible, sedimentary rock formed from naturally compressed peat. It has a carbon content around 25–35%, and is considered the lowest rank of coal due to its relatively low heat content. When removed from the ground, it contains a very high amount of moisture which partially explains its low carbon content. Lignite is mined all around the world and is used almost exclusively as a fuel for steam-electric power generation.

Freestone County is a county in the east-central part of the U.S. state of Texas. As of the 2020 census, its population was 19,435. Its county seat is Fairfield. The county was created in 1850 and organized the next year.
Energy Future Holdings Corporation is an electric utility company headquartered in Energy Plaza in Downtown Dallas, Texas, United States. The majority of the company's power generation is through coal and nuclear power plants. From 1998 to 2007, the company was known as TXU Corporation until its $45 billion leveraged buyout by Kohlberg Kravis Roberts, TPG Capital and Goldman Sachs Capital Partners. That purchase was the largest leveraged buyout in history. As of 2019, TXU Energy is a subsidiary of publicly traded Vistra Energy.
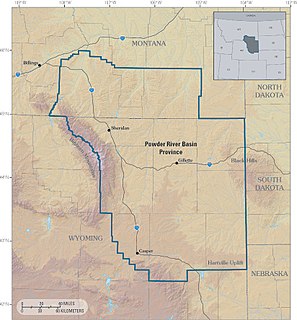
The Powder River Basin is a geologic structural basin in southeast Montana and northeast Wyoming, about 120 miles (190 km) east to west and 200 miles (320 km) north to south, known for its extensive coal reserves. The former hunting grounds of the Oglala Lakota, the area is very sparsely populated and is known for its rolling grasslands and semiarid climate.

Longannet power station was a large coal-fired power station in Fife, and the last coal-fired power station in Scotland. It was capable of co-firing biomass, natural gas and sludge. The station stood on the north bank of the Firth of Forth, near Kincardine on Forth.

The William H. Zimmer Power Station, located near Moscow, Ohio, is a 1.35-gigawatt coal power plant. Planned by Cincinnati Gas and Electric (CG&E), with Columbus & Southern Ohio Electric and Dayton Power & Light (DP&L) as its partners, it was originally intended to be a nuclear power plant. Although once estimated to be 97% complete, poor construction and quality assurance (QA) led to the plant being converted to coal-fired generation. The plant began operations in 1991. Today, the plant is owned and operated by Vistra Corp.

Centralia Big Hanaford power plant is a major coal-fired power plant supplemented with newer natural-gas-fired units. It is located east of Centralia, Washington, United States in Lewis County. As of 2006, it is the only commercial coal-fired power plant in the State of Washington. A bill signed in 2011 by governor Christine Gregoire, the TransAlta Energy Transition Bill, resulted in one coal boiler being shut down in 2020 and the other by the end of 2025.
Refined coal is the product of the coal-upgrading technology that removes moisture and certain pollutants from lower-rank coals such as sub-bituminous and lignite (brown) coals, raising their calorific values. Coal refining or upgrading technologies are typically pre-combustion treatments and/or processes that alter the characteristics of a coal before it is burned. The goals of pre-combustion coal-upgrading technologies are to increase efficiency and reduce emissions when coal is burned. Depending on the situation, pre-combustion technology can be used in place of or as a supplement to post-combustion technologies to control emissions from coal-fueled boilers. A primary benefit of refined coal is the capacity to reduce the net volume of carbon emissions that is currently emitted from power generators and would reduce the amount of emissions that is proposed to be managed via emerging carbon sequestration methodologies. Refined coal technologies have primarily been developed in the United States. Several similar technologies have been researched, developed and tested in Victoria, Australia, including the Densified coal technology developed to alter the chemical bonds of brown coal to create a product that is cleaner, stable, exportable and of sufficiently high calorific value to be a black coal equivalent.
The Monticello Steam Electric Station was a 1.8-gigawatt coal-fired power plant located southwest of Mount Pleasant, Texas in Titus County, Texas. It operated from 1974 to 2018.

Luminant is a Texas-based electric utility. It is a wholly owned subsidiary of Energy Future Holdings Corporation. Luminant's operations include electricity generation and wholesaling, mining, construction, and development. The company has capacity for the generation of 18,300 megawatts (MW) of electricity in 20 power plants spread across Texas, of which 2,300 MW come from nuclear power generated at the company's Comanche Peak Nuclear Power Plant, 5,800 MW from coal-fired power plants, and the remainder from natural gas-fired plants. Luminant is also a major purchaser of wind power.
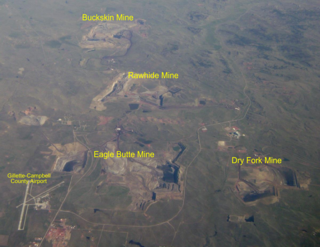
The Rawhide Mine is a coal mine located 10 miles (16.1 km) north of Gillette, Wyoming in the United States in the coal-rich Powder River Basin. The mine is an open pit mine that utilizes a combination of cast blast/dozer push and truck/shovel mining methods to strip an average of 165 feet (50.3m) of overburden off of approximately 105 (32.0m) feet of coal. Rawhide produces a low-sulfur, sub-bituminous coal from the Roland and Smith seams. This coal is used for domestic energy generation and shipped to customers via railroad. The mine is currently owned and operated by Peabody Energy.

Fairfield Lake State Park is a state park located in Freestone County, Texas, United States, northeast of Fairfield on the shores of Fairfield Lake. The park is 1,460 acres (591 ha).

Amyntaio Power Station is a 600 MW coal-fired power station near Amyntaio in Western Macedonia, Greece. Build and commissioned in the mid 1980s, the power station is fuelled by lignite from the adjacent Amyntaio coal mine.

Martin Lake Power Plant is a 2,250-megawatt coal power plant located southwest of Tatum, Texas, in Rusk County, Texas. The plant is owned by Luminant. It began operations in 1977. The plant is also served by the Luminant owned Martin Lake Line, shuttling coal from nearby as well as the Powder River Basin in Wyoming via BNSF.
Sandow Power Plant was a 1.1-gigawatt coal power plant located southwest of Rockdale, Texas in Milam County, Texas. It was operated by Luminant, a subsidiary of Vistra Corp. The plant closed in 2018.
Coffeen Power Station was a 915 megawatt (MW) coal power plant located south of Coffeen, Illinois near Coffeen Lake State Fish and Wildlife Area in Montgomery County, Illinois. The plant was owned by Vistra Energy. Coffeen began operations in 1965 and was shut down on November 1, 2019.
Oak Grove Power Plant is a 1.79-gigawatt, coal power plant located north of Franklin, Texas in Robertson County, Texas. The plant is operated by Luminant, a subsidiary of Vistra Energy. It began operations in 2010.
Çayırhan power station is a 620 MW operational coal fired power station in Turkey and a proposed 800 MW extension, in Ankara Province. In 2019 land was expropriated for another lignite mine, to feed the new plant, which is being opposed as uneconomic and polluting.
Vistra is a Fortune 275 integrated retail electricity and power generation company based in Irving, Texas.











