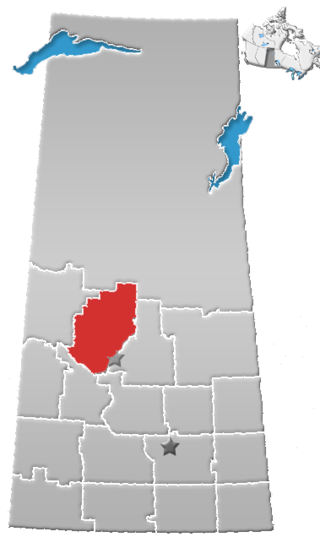
Division No. 16 is one of eighteen census divisions in the province of Saskatchewan, Canada, as defined by Statistics Canada. It is located in the north-central part of the province. The most populous community in this division is North Battleford.

Beaver River is a large river in east-central Alberta and central Saskatchewan, Canada. It flows east through Alberta and Saskatchewan and then turns sharply north to flow into Lac Île-à-la-Crosse on the Churchill River which flows into Hudson Bay.
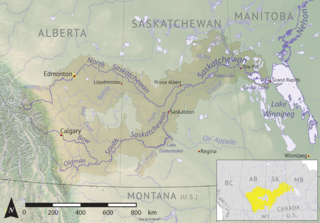
Torch River is a river in the Canadian province of Saskatchewan. The river's source is the dam at Candle Lake, near Candle Lake Provincial Park, and it travels east through boreal forest and muskeg en route to its mouth in the Saskatchewan River Delta. Torch River Provincial Forest, a conservation area, is located along the course of the river, near where White Fox River flows into Torch River. Torch River is a significant tributary of the Saskatchewan River and it is part of the Hudson Bay drainage basin.

Waterhen River is an east-flowing river in the north-west area of the Canadian province of Saskatchewan in the drainage basin of the Beaver River. It is north of and parallel to the east-flowing part of the Beaver River and joins the north-flowing part of that river. Most of the river and its drainage basin is at the southern edge of the boreal forest belt. While the river's source is Lac des Îles, its drainage basin reaches north into the Mostoos Hills and west well into the neighbouring province of Alberta.
Rusty Lake is a lake in Meadow Lake Provincial Park in the Canadian Province of Saskatchewan in the boreal forest ecozone of Canada. The lake is the first of six notable lakes in the Rusty Creek watershed part of Meadow Lake Provincial Park. The other lakes include First Mustus, Second Mustus, Third Mustus, Peitahigan, and Fourth Mustus.
Peitahigan Lake is a lake in Meadow Lake Provincial Park in the Canadian Province of Saskatchewan in the boreal forest ecozone of Canada. The lake is one of six notable lakes in the Rusty Creek watershed. The other lakes include Rusty, First Mustus, Second Mustus, Third Mustus, and Fourth Mustus. Rusty Creek and the lakes are part of the Waterhen River drainage basin. The Waterhen River is a tributary of the Beaver River, which flows north into Lac Île-à-la-Crosse and the Churchill River, a major tributary in the Hudson Bay drainage basin.

Rusty Creek is a river in the Canadian province of Saskatchewan. The river's source is First Mustus Lake, which is a lake in Meadow Lake Provincial Park, and its mouth is along the course of the Waterhen River. It is a south flowing river and the entirety of its course is in Meadow Lake Provincial Park and the boreal forest ecozone. Rusty Creek is a tributary of Waterhen River, which is a major tributary of Beaver River of the Churchill River and in the Hudson Bay drainage basin.

Meadow River is a river in the Canadian province of Saskatchewan. The river's source is Meadow Lake, which is the lake adjacent to the city of Meadow Lake. The river and its drainage basin are in the transition zone between the boreal forest and prairies ecozones of Canada. Meadow River's mouth is at Beaver River, which flows northward into Lac Île-à-la-Crosse, a lake along the course of the Churchill River, which is a major river in the Hudson Bay drainage basin.
Meadow Lake is a small, shallow, oval-shaped lake that is the source of Meadow River and the namesake of Meadow Lake Provincial Park, despite not being within the park's boundaries. The lake is in the transition zone between the boreal forest and prairies ecozones of Canada.

McDougal Creek is a river in the Canadian province of Saskatchewan. The river's source is at the southern end of Divide Lake at the northern end of Narrow Hills Provincial Park in a hilly plateau called Cub Hills. The landforms of the Cub Hills, such as the lakes, streams, steeply rolling hills, and flat lowlands, were formed over 10,000 years ago during the last ice age. The entire course of the river is in the boreal forest ecozone of Canada.

White Gull Creek is a river in the Canadian province of Saskatchewan. The river's source is White Gull Lake, near the south-western boundary of Narrow Hills Provincial Park and near the southern slopes of the Cub Hills. The river travels through boreal forest and muskeg en route to its mouth at the Torch River. The Torch River is a tributary of the Saskatchewan River as it flows into one of North America's largest inland fresh water deltas, the Saskatchewan River Delta. There are no communities nor settlements along the river.
The Cub Hills are a hilly plateau located south-east of the geographical centre of the Canadian province of Saskatchewan. The hills are in the boreal forest ecozone of Canada and the landforms of the hills were shaped more than 10,000 years ago during last ice age. Throughout the Cub Hills, there are dozens of lakes and rivers and several parks. The Cubs Hills are 150 km (93 mi) north-east of Prince Albert and are in the Northern Saskatchewan Administration District and Census Division #18. Several highways criss-cross the plateau to provide access to the various parks and other amenities.

Piwei River is a river in the east-central part of the Canadian province of Saskatchewan in the boreal forest ecozone of Canada. It begins at the western end of the Porcupine Hills at Piwei Lakes and heads in an easterly direction through a glacier-formed valley and into the Etomami River, which is a tributary of the Red Deer River.

Yorkton Creek, formally known as Little Whitesand River, is a river in the south-east region of the Canadian province of Saskatchewan. The river begins at Leech Lake, south of Yorkton, and flows north into the Whitesand River. The Whitesand River flows east into the Assiniboine River, which is a major tributary of the Red River. While Yorkton Creek begins at Leech Lake, its main tributary, Crescent Creek, has its headwaters in the Beaver Hills to the west.

Crescent Creek is a river in the south-east region of the Canadian province of Saskatchewan. The river begins in the Beaver Hills and flows in an easterly direction into Crescent Lake. Crescent Creek is a tributary of Yorkton Creek, which flows north into the Whitesand River–a tributary of the Assiniboine River.

Cowan River is a river in the west-central part of the Canadian province of Saskatchewan in the boreal forest ecozone of Canada. The river begins at Cowan Lake Dam near the northern end of Cowan Lake and flows north-west through muskeg and forest to meet Beaver River. Beaver River then flows into Lac Île-à-la-Crosse and the Churchill River. The entirety of Cowen River is within the Northern Saskatchewan Administration District and while there are no communities along its course, the towns of Big River and Spiritwood are in its watershed.
Waskesiu Upland is a hilly plateau in the central region of the Canadian province of Saskatchewan. Waskesiu means red deer or elk in the Cree language. The plateau is just south-west of the geographical centre of the province and consists of two main ranges — the Waskesiu Hills to the south and the Thunder Hills to the north. The Thunder Hills cover an area of about 225,000 acres. Several notable rivers begin from the upland with ones headed south flowing into the North Saskatchewan River and ones headed north flowing into the Churchill River. Much of the plateau is carpeted in boreal forests and most of the Waskesiu Hills range is within Prince Albert National Park. Besides the national park, there are several provincial recreation sites in and around the upland. The northern part of the upland is part of the Northern Saskatchewan Administration District and is sparsely populated.

Armit River is a river in the Canadian provinces of Manitoba and Saskatchewan in the Nelson River drainage basin. The river begins in the Porcupine Hills of the Manitoba Escarpment at Armit Lake and flows in a northerly direction closely following the Manitoba / Saskatchewan border and into Red Deer Lake along the course of the Red Deer River.
Delaronde Lake is a lake in the Canadian province of Saskatchewan. It is situated at the western edge of the Waskesiu Upland in the boreal forest ecozone of Canada. Delaronde Lake is within the Churchill River drainage basin of the Hudson Bay.

MacLennan River is a river in the Canadian province of Saskatchewan. It begins at MacLennan Lake in the Thunder Hills of the Northern Saskatchewan Administration District. It then flows generally south-east out of the hills, through a section of Prince Albert National Park, and on to Montreal Lake. MacLennan River is within the Churchill River drainage basin and is in the Mid-Boreal Upland ecozone of Canada.