This article needs additional citations for verification .(March 2009) |
The Big Salmon River is a tributary of the Yukon River The encampment of Big Salmon Village lies at the confluence of the Big Salmon and Yukon Rivers.
This article needs additional citations for verification .(March 2009) |
The Big Salmon River is a tributary of the Yukon River The encampment of Big Salmon Village lies at the confluence of the Big Salmon and Yukon Rivers.
Black spruce is a dominant tree in the Big Salmon River watershed. [1] [2] This locale near the Seward Peninsula represents the near westernmost limit of the Black Spruce, Picea mariana , [3] one of the most widespread conifers in northern North America.

The Yukon River is a major watercourse of northwestern North America. From its source in British Columbia, Canada, it flows through Canada's territory of Yukon. The lower half of the river continues westwards through the U.S. state of Alaska. The river is 3,190 kilometres (1,980 mi) long and empties into the Bering Sea at the Yukon–Kuskokwim Delta. The average flow is 6,400–7,000 m3/s (230,000–250,000 cu ft/s). The total drainage area is 833,000 km2 (321,500 sq mi), of which 323,800 km2 (125,000 sq mi) lies in Canada. The total area is more than 25% larger than Texas or Alberta.

Picea mariana, the black spruce, is a North American species of spruce tree in the pine family. It is widespread across Canada, found in all 10 provinces and all 3 territories. It is the official tree of the province of Newfoundland and Labrador and is that province's most numerous tree. The range of the black spruce extends into northern parts of the United States: in Alaska, the Great Lakes region, and the upper Northeast. It is a frequent part of the biome known as taiga or boreal forest.

The Charley River is an 88-mile (142 km) tributary of the Yukon River in the U.S. state of Alaska. Flowing generally northeast from the Mertie Mountains in the northeastern part of the state, the river lies entirely within Yukon–Charley Rivers National Preserve. The Charley River enters the larger river downstream and 55 miles (89 km) northwest of Eagle.

Picea glauca, the white spruce, is a species of spruce native to the northern temperate and boreal forests in North America. Picea glauca is native from central Alaska all through the east, across southern/central Canada to the Avalon Peninsula in Newfoundland, and south to Montana, Minnesota, Wisconsin, Michigan, Upstate New York and Vermont, along with the mountainous and immediate coastal portions of New Hampshire and Maine, where temperatures are just barely cool and moist enough to support it. There is also an isolated population in the Black Hills of South Dakota and Wyoming. It is also known as Canadian spruce, skunk spruce, cat spruce, Black Hills spruce, western white spruce, Alberta white spruce, and Porsild spruce.
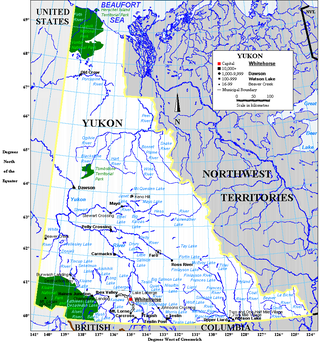
Yukon is in the northwestern corner of Canada and is bordered by Alaska and the Northwest Territories. The sparsely populated territory abounds with natural scenic beauty, with snowmelt lakes and perennial white-capped mountains, including many of Canada's highest mountains. The territory's climate is Arctic in territory north of Old Crow, subarctic in the region, between Whitehorse and Old Crow, and humid continental climate south of Whitehorse and in areas close to the British Columbia border. Most of the territory is boreal forest with tundra being the main vegetation zone only in the extreme north and at high elevations.

Hoh Rainforest is one of the largest temperate rainforests in the U.S., located on the Olympic Peninsula in western Washington state. It includes 24 miles (39 km) of low elevation forest 394 to 2,493 feet along the Hoh River. The Hoh River valley was formed thousands of years ago by glaciers.

The Teslin River is a river in southern Yukon Territory and northwestern British Columbia, Canada, that flows 632 kilometres (393 mi) from its source south of Teslin Lake to its confluence with the Yukon River.

Pleurozium schreberi, the red-stemmed feathermoss or Schreber's big red stem moss, is a moss with a loose growth pattern. The root name pleuro comes from the Latin for ribs, possibly describing how the parts branch from the stem.
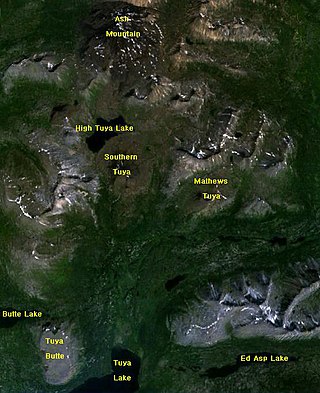
The Tuya Range is a mountain range in the Stikine Ranges of the Cassiar Mountains in the far north of the Canadian province of British Columbia, near its border with the Yukon Territory and to the southwest of Watson Lake, Yukon, which is the nearest major settlement.

Krummholz — also called knieholz — is a type of stunted, deformed vegetation encountered in the subarctic and subalpine tree line landscapes, shaped by continual exposure to fierce, freezing winds. Under these conditions, trees can only survive where they are sheltered by rock formations or snow cover. As the lower portion of these trees continues to grow, the coverage becomes extremely dense near the ground. In Newfoundland and Labrador, the formation is known as tuckamore. Krummholz trees are also found on beaches such as the Oregon coast, where trees can become much taller than their subalpine cousins.
The Jennings River is a river in far northern British Columbia, Canada. It is approximately 150 kilometres (93 mi) long. The river was named for William T. Jennings (1846-1906), a civil engineer who, in 1897, assessed various road and railroad routes from the Pacific Ocean to the Yukon.

Ptilium is a genus of mosses with very broad worldwide occurrence. This genus is within the family Hypnaceae, in the class Bryopsida, subclass Bryidae and order Hypnales.

Hypnaceae is a large family of moss with broad worldwide occurrence in the class Bryopsida, subclass Bryidae and order Hypnales. Genera include Hypnum, Phyllodon, and Taxiphyllum.

Ptilium crista-castrensis, the knights plume moss or ostrich-plume feathermoss, is a moss species within the family Pylaisiaceae, in the class Bryopsida, subclass Bryidae and order Hypnales.
Keller Lake is a surface water body in the Northwest Territories of Canada. It is located 85 kilometers (53 mi) south of the Great Bear Lake and 220 kilometers (140 mi) north of Fort Simpson, at an elevation of 255 meters (837 ft). The lake has a triangular shape, a surface area of 380 square kilometers (150 sq mi), and it empties through the Johnny Hoe River into the Great Bear Lake.

Dactylina arctica is a species of fungus within the family Parmeliaceae. Common names for this lichen are finger lichen and Arctic finger lichen. A specific area in which this lichen occurs is represented by the boreal forests of Canada.

The Cook Inlet taiga is a taiga and boreal forests ecoregion in Alaska.

The Yukon Interior dry forests is a taiga ecoregion of Canada.

The interior Alaska–Yukon lowland taiga is an ecoregion in the taiga and boreal forests biome, of far northern North America.

The Port-Cartier-Sept-Îles Wildlife Reserve is a wildlife reserve in the province of Quebec, Canada.
Coordinates: 61°52′50″N134°55′18″W / 61.8806°N 134.9217°W