Related Research Articles
The history of Senegal is commonly divided into a number of periods, encompassing the prehistoric era, the precolonial period, colonialism, and the contemporary era.

Baol or Bawol was a kingdom in what is now central Senegal. Founded in the 11th century, it was a vassal of the Jolof Empire before becoming independent in the mid-16th century. The ruler bore the title of Teigne and reigned from the capital in Lambaye. The kingdom encompassed a strip of land extending east from the ocean and included the towns of Touba, Diourbel, and Mbacke. It was directly south of the Kingdom of Cayor and north of the Kingdom of Sine.
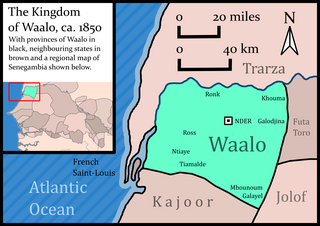
Waalo was a kingdom on the lower Senegal River in West Africa, in what is now Senegal and Mauritania. It included parts of the valley proper and areas north and south, extending to the Atlantic Ocean. To the north were Moorish emirates; to the south was the kingdom of Cayor; to the east was Jolof.
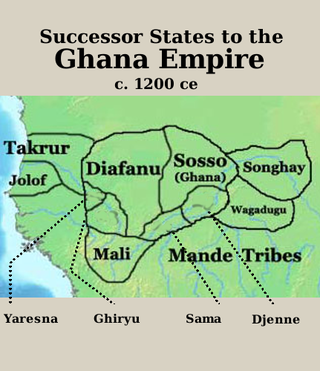
Takrur, Tekrur or Tekrour was a state based in the Senegal River valley in West Africa which was at its height in the 10th and 11th centuries, roughly parallel to the Ghana Empire, but lasted in some form into the 18th century.
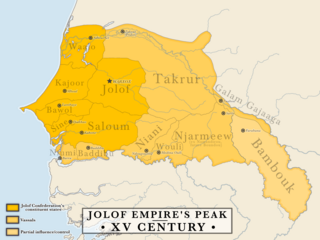
The Jolof Empire, also known as Great Jolof, or the WolofEmpire, was a Wolof and Sereer confederacy state that ruled parts of West Africa, most precisely modern-day Senegal, Mali, Gambia and Mauritania from around the 12th century to 1549. Following the 1549 battle of Danki, its vassal states were fully or de facto independent; in this period it is known as the Jolof Kingdom.
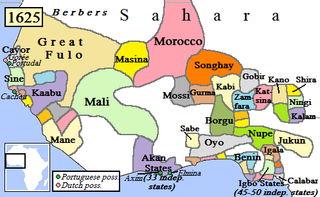
The Empire of Great Fulo, also known as the Denanke Kingdom or Denianke Kingdom, was a Pulaar kingdom of Senegal, which dominated the Futa Toro region from the early 16th century to 1776.

The Kingdom of Sine was a post-classical Serer kingdom along the north bank of the Saloum River delta in modern Senegal. The inhabitants are called Siin-Siin or Sine-Sine.

The Kingdom of Jolof, also known as Wolof and Wollof, was a West African rump state located in what is today the nation of Senegal. For nearly two hundred years, the Wolof rulers of the Jolof Empire collected tribute from vassal kings' states who voluntarily agreed to the confederacy. At the 1549 Battle of Danki, however, the Buurba Jolof was defeated by the lord of Kayor, resulting in the rapid disintegration of the empire. Jolof survived as a rump state, unable to access the Atlantic trade between its former vassal territories and the Portuguese.

The Saltigue, are Serer high priests and priestesses who preside over the religious ceremonies and affairs of the Serer people, such as the Xooy ceremony, the biggest event in the Serer religious calendar. They usually come from ancient Serer paternal families, and the title is inherited by birthright. In Serer country, Saltigue are always diviners.
Lamane or laman (Serer: Laamaan or Lamaan, mean "master of the land" in Serer. The name was also sometimes the title of chiefs or kings of the Serer people of the Senegambia region which includes modern day Senegal and the Gambia. This title was also used by some kings of the Wolof kingdoms. The title is sometimes used interchangeably with the old title Maad. After the Guelowars' migration to the Sine and the foundation of the Kingdom of Sine, "lamane" denotes a provincial chief answerable to the King of Sine and Saloum.
Alioune Sarr was a Senegalese historian, author and politician whose family gained prominence in the Serer precolonial Kingdom of Sine and Saloum around the 14th century. They also made up the "sulbalƃe" class of Futa Toro. Sarr was born at Foundiougne. His father was a former Chief of Foundiougne, Gandoune, former head of the constituency of Ndiaye-Ndiaye and former prime minister of Diognick in Senegal. Although Sarr was a prominent politician like his father during the colonial era, he is best known as a historian and author especially after his famous work Histoire du Sine-Saloum which was officially published in 1949 and peer reviewed by historians.

Buumi was a royal title in the pre-colonial Serer Kingdoms of Sine, Saloum and Baol, as well as in the Jolof Empire.
Koli Tenguella was a Fulani warrior and leader who was pivotal in establishing the Empire of Great Fulo.
Tenguella was a Fula silatigi or chief who founded a short-lived state in the upper Senegal river valley, a precursor of the Empire of Great Fulo. He was referred to as the Great Fulo or Great king of the Fulos in Portuguese documents of the time.
Tyukuli N'Diklam, also spelled Cukuli Njiklaan, was the fourth ruler, or Burba, of the Jolof Empire. Stewart places his rule between c.1420 and c.1440. Senegalese scholar Oumar Kane, however, proposes that he was born in 1433 and identifies him as the 'Zucholin' who appears in Alvise Cadamosto's account of his visit to Senegambia. This timeline would place him on the throne as late at 1460, when he conquered Takrur and Namandirou and attacked the Kingdom of Sine. This identification is disputed, however, with Rokhaya Fall and Jean Boulegue believing that Birayma N'dyeme Eler was responsible.
N'Dyelen Mbey Leeyti was the sixth ruler, or Burba, of the Jolof Empire. He, like his next two successors, was a member of the Jonai maternal lineage.
Birayma Kuran Kan, also spelled Biram Kura Kan was the ninth ruler, or Burba, of the Jolof Empire. He was the son of Jeleen Mbay Leyti and nephew of Biram Njeme Eler, both earlier burbas, and like them was a member of the Baol-Baol Jonaï maternal lineage.

Jeleen Yatta Ntanye, more commonly known as Jelen, Jeléen, or Bemoim, was a buumi of the Jolof Empire who attempted to take control of the state with help from the Portuguese in the late 15th century.

Namandirou, also known as Njarmeew or Geremeo, was a kingdom in what is now eastern Senegal.
References
- ↑ Stewart, John (2014). African States and Rulers. Jefferson: McFarland. p. 76. ISBN 978-0-78649-564-1.
- 1 2 3 Fall, Rokhaya (2013). "De la nécessité de réactualiser le recours à la « tradition orale » dans l'écriture du passé africain". In Fauvelle-Aymar, François-Xavier; Hirsch, Bertrand (eds.). Les ruses de l'historien. Essais d'Afrique et d'ailleurs en hommage à Jean Boulègue. Hommes et sociétés (in French). Paris: Karthala. pp. 15–29. doi:10.3917/kart.fauve.2013.01.0015. ISBN 978-2-8111-0939-4 . Retrieved 8 January 2024.
- ↑ Kane, Oumar (2004). "Chapitre IV. Les lawakooɓe et la formation du royaume deeniyaŋke". La première hégémonie peule. Le Fuuta Tooro de Koli Teηella à Almaami Abdul. Hommes et sociétés. Paris: Karthala. pp. 114–157. ISBN 978-2-84586-521-1.