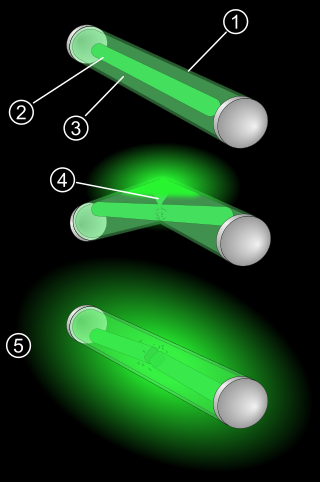
A glow stick, also known as a light stick, chem light, light wand, light rod, and rave light, is a self-contained, short-term light-source. It consists of a translucent plastic tube containing isolated substances that, when combined, make light through chemiluminescence. The light cannot be turned off and can be used only once. The used tube is then thrown away. Glow sticks are often used for recreation, such as for events, camping, outdoor exploration, and concerts. Glow sticks are also used for light in military and emergency services applications. Industrial uses include marine, transportation, and mining.

Oxalic acid is an organic acid with the systematic name ethanedioic acid and chemical formula HO−C(=O)−C(=O)−OH, also written as (COOH)2 or (CO2H)2 or H2C2O4. It is the simplest dicarboxylic acid. It is a white crystalline solid that forms a colorless solution in water. Its name comes from the fact that early investigators isolated oxalic acid from flowering plants of the genus Oxalis, commonly known as wood-sorrels. It occurs naturally in many foods. Excessive ingestion of oxalic acid or prolonged skin contact can be dangerous.
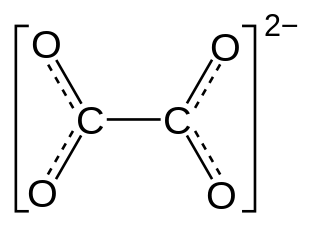
Oxalate is an anion with the chemical formula formula C2O2−4. This dianion is colorless. It occurs naturally, including in some foods. It forms a variety of salts, for example sodium oxalate, and several esters such as dimethyl oxalate. It is a conjugate base of oxalic acid. At neutral pH in aqueous solution, oxalic acid converts completely to oxalate.

Oxalyl chloride is an organic chemical compound with the formula Cl−C(=O)−C(=O)−Cl. This colorless, sharp-smelling liquid, the diacyl chloride of oxalic acid, is a useful reagent in organic synthesis.

Sodium oxalate, or disodium oxalate, is the sodium salt of oxalic acid with the formula Na2C2O4. It is a white, crystalline, odorless solid, that decomposes above 290 °C.

9,10-Bis(phenylethynyl)anthracene (BPEA) is an aromatic hydrocarbon with the chemical formula is C30H18. It displays strong fluorescence and is used as a chemiluminescent fluorophore with high quantum efficiency.

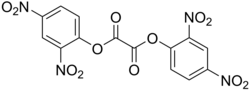
Bis[2,4,5-trichloro-6-(pentyloxycarbonyl)phenyl]oxalate is a solid ester whose oxidation products are responsible for the chemiluminescence in a glowstick. It can be synthesized by reacting 2-carbopentoxy-3,5,6-trichlorophenol with oxalyl chloride.

Barium oxalate is a chemical compound with the chemical formula BaC2O4. It is a barium salt of oxalic acid. It consists of barium cations Ba2+ and oxalate anions C2O2−4. It is a white odorless powder that is sometimes used as a green pyrotechnic colorant generally in specialized pyrotechnic compositions containing magnesium metal powder. Flame color is rich and vivid without additional chlorine donors. Such compositions burn rate is satisfied without commonly used oxidizers as nitrates, chlorates and perchlorates.

Potassium ferrioxalate, also called potassium trisoxalatoferrate or potassium tris(oxalato)ferrate(III) is a chemical compound with the formula K3[Fe(C2O4)3]. It often occurs as the trihydrate K3[Fe(C2O4)3]·3H2O. Both are crystalline compounds, lime green in colour.

Peroxyoxalates are esters initially formed by the reaction of hydrogen peroxide with oxalate diesters or oxalyl chloride, with or without base, although the reaction is much faster with base:

TCPO, or bis(2,4,6-trichlorophenyl) oxalate, is a chemical used in some types of glow sticks.
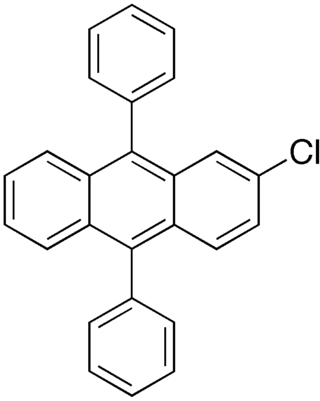
2-Chloro-9,10-diphenylanthracene is a fluorescent dye used in glow sticks for a blue-green glow. It is a chlorinated derivative of 9,10-diphenylanthracene.

Cobalt(II) oxalate is the inorganic compound with the formula of CoC2O4. Like other simple inorganic oxalates, it is a coordination polymer. The oxalate ligands bridge of Co(OH2)2 centres. Each cobalt adopts octahedral coordination geometry.
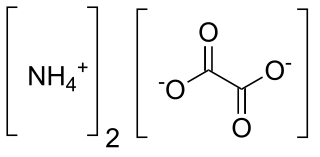
Ammonium oxalate is a chemical compound with the chemical formula [NH4]2C2O4. Its formula is often written as (NH4)2C2O4 or (COONH4)2. It is an ammonium salt of oxalic acid. It consists of ammonium cations ([NH4]+) and oxalate anions (C2O2−4). The structure of ammonium oxalate is ([NH4]+)2[C2O4]2−. Ammonium oxalate sometimes comes as a monohydrate ([NH4]2C2O4·H2O). It is a colorless or white salt under standard conditions and is odorless and non-volatile. It occurs in many plants and vegetables.

Tetrachlorvinphos is an organophosphate insecticide used to kill fleas and ticks.

Caesium oxalate (standard IUPAC spelling) dicesium oxalate, or cesium oxalate (American spelling) is the oxalate of caesium. Caesium oxalate has the chemical formula of Cs2C2O4.

Glowmatography is a laboratory technique for the separation of dyes present in solutions contained in glow sticks. The chemical components of such solutions can be chromatographically separated into polar and nonpolar components. Developed as a laboratory class experiment, it can be used to demonstrate chemistry concepts of polarity, chemical kinetics, and chemiluminescence.
The borate oxalates are chemical compounds containing borate and oxalate anions. Where the oxalate group is bound to the borate via oxygen, a more condensed anion is formed that balances less cations. These can be termed boro-oxalates, bis(oxalato)borates, or oxalatoborates or oxalate borates. The oxalatoborates are heterocyclic compounds with a ring containing -O-B-O-. Bis(oxalato)borates are spiro compounds with rings joined at the boron atom.

Transition metal oxalate complexes are coordination complexes with oxalate (C2O42−) ligands. Some are useful commercially, but the topic has attracted regular scholarly scrutiny. Oxalate (C2O42-) is a kind of dicarboxylate ligand. As a small, symmetrical dinegative ion, oxalate commonly forms five-membered MO2C2 chelate rings. Mixed ligand complexes are known, e.g., [Co(C2O4)(NH3)4]κ+.