Related Research Articles

Maritime archaeology is a discipline within archaeology as a whole that specifically studies human interaction with the sea, lakes and rivers through the study of associated physical remains, be they vessels, shore-side facilities, port-related structures, cargoes, human remains and submerged landscapes. A specialty within maritime archaeology is nautical archaeology, which studies ship construction and use.

Lake Huron is one of the five Great Lakes of North America. Hydrologically, it comprises the easterly portion of Lake Michigan–Huron, having the same surface elevation as its westerly counterpart, to which it is connected by the 5-mile-wide (8.0 km), 20-fathom-deep Straits of Mackinac. It is shared on the north and east by the Canadian province of Ontario and on the south and west by the U.S. state of Michigan. The name of the lake is derived from early French explorers who named it for the Huron people inhabiting the region. The Huronian glaciation was named from evidence collected from Lake Huron region. The northern parts of the lake include the North Channel and Georgian Bay. Saginaw Bay is located in the southwest corner of the lake. The main inlet is the St. Marys River, and the main outlet is the St. Clair River.

The maritime European exploration of Australia consisted of several waves of European seafarers who sailed the edges of the Australian continent. Dutch navigators were the first Europeans known to have explored and mapped the Australian coastline. The first documented encounter was that of Dutch navigator Willem Janszoon, in 1606. Dutch seafarers also visited the west and north coasts of the continent, as did French explorers.

A sailing ship is a sea-going vessel that uses sails mounted on masts to harness the power of wind and propel the vessel. There is a variety of sail plans that propel sailing ships, employing square-rigged or fore-and-aft sails. Some ships carry square sails on each mast—the brig and full-rigged ship, said to be "ship-rigged" when there are three or more masts. Others carry only fore-and-aft sails on each mast—schooners. Still others employ a combination of square and fore-and aft sails, including the barque, barquentine, and brigantine.

Francisco de Orellana Bejarano Pizarro y Torres de Altamirano was a Spanish explorer and conquistador. He completed the first known navigation of the entire length of the Amazon River, which initially had been named "Rio de Orellana" until reports of skirmishes that included the women warriors of the Tapuyas tribe brought about the name change. He also founded the city of Guayaquil in what is now Ecuador.

The Saga of Erik the Red, in Old Norse: Eiríks saga rauða, is an Icelandic saga on the Norse exploration of North America. The original saga is thought to have been written in the 13th century. It is preserved in somewhat different versions in two manuscripts: Hauksbók and Skálholtsbók.
Eudoxus of Cyzicus was a Greek navigator who explored the Arabian Sea for Ptolemy VIII, king of the Hellenistic Ptolemaic dynasty in Egypt.

The Frisian Islands, also known as the Wadden Islands or the Wadden Sea Islands, form an archipelago at the eastern edge of the North Sea in northwestern Europe, stretching from the northwest of the Netherlands through Germany to the west of Denmark. The islands shield the mudflat region of the Wadden Sea from the North Sea.

A ghost ship, also known as a phantom ship, is a vessel with no living crew aboard; it may be a ghostly vessel, such as the Flying Dutchman, or a physical derelict found adrift with its crew missing or dead, like the Mary Celeste. The term is sometimes used for ships that have been decommissioned but not yet scrapped, as well as drifting boats that have been found after breaking loose of their ropes and becoming carried away by the wind or the waves.

Île Saint-Paul is an island forming part of the French Southern and Antarctic Lands in the Indian Ocean, with an area of 6 km2. The island is located about 90 km (56 mi) south of the larger Île Amsterdam, 1,300 kilometres (810 mi) northeast of the Kerguelen Islands, and 3,000 km (1,900 mi) southeast of Réunion. It is the nearest landfall to the antipode of the geographic center of the contiguous United States.

The theory of Portuguese discovery of Australia claims that early Portuguese navigators were the first Europeans to sight Australia between 1521 and 1524, well before the arrival of Dutch navigator Willem Janszoon in 1606 on board the Duyfken who is generally considered to be the first European discoverer. This is based on the following elements:

La Belle was one of Robert de La Salle's four ships when he explored the Gulf of Mexico with the ill-fated mission of starting a French colony at the mouth of the Mississippi River in 1685. La Belle was wrecked in present-day Matagorda Bay the following year, dooming La Salle's Texas colony to failure. The wreckage of La Belle lay forgotten until it was discovered by a team of state archaeologists in 1995. The discovery of La Salle's flagship was regarded as one of the most important archaeological finds of the century in Texas, and a major excavation was launched by the state of Texas that, over a period of about a year, recovered the entire shipwreck and over a million artifacts.

The Antikythera wreck is a Roman-era shipwreck dating from the second quarter of the first century BC.

Levitha, known in classical antiquity as Lebinthus or Lebinthos is a small Greek island located in the east of the Aegean Sea, between Kinaros and Kalymnos, part of the Dodecanese islands. It is part of the municipality of Leros. The island is mentioned in two of Ovid's works Ars Amatoria and the Metamorphoses in connection with the saga of Daedalus and Icarus. While escaping from Crete, Daedalus and Icarus flew over Lebinthus. Besides Ovid, the island is noted by the ancient authors Pliny the Elder, Pomponius Mela, Strabo, and Stephanus of Byzantium. In addition, it is mentioned in the Stadiasmus Maris Magni.

The history of glass-making dates back to at least 3,600 BC in Mesopotamia, however some claim they may have been producing copies of glass objects from Egypt. Other archaeological evidence suggests that the first true glass was made in coastal north Syria, Mesopotamia or Egypt. The earliest known glass objects, of the mid 2,000 BC, were beads, perhaps initially created as the accidental by-products of metal-working (slags) or during the production of faience, a pre-glass vitreous material made by a process similar to glazing. Glass products remained a luxury until the disasters that overtook the late Bronze Age civilizations seemingly brought glass-making to a halt.
The year 2014 in archaeology involved some significant events.

Acts 27 is the twenty-seventh chapter of the Acts of the Apostles in the New Testament of the Christian Bible. It records the journey of Paul from Caesarea heading to Rome, but stranded for a time in Malta. The book containing this chapter is anonymous but early Christian tradition uniformly affirmed that Luke composed this book as well as the Gospel of Luke.

The beeswax wreck is an as-yet-undiscovered shipwreck somewhere off the coast of the U.S. state of Oregon, near Neahkahnie Mountain and the mouth of the Nehalem River in Tillamook County. The ship, thought to be a Spanish Manila galleon that was wrecked in the late-1600s, was carrying a large cargo of beeswax, lumps of which have been found scattered along Oregon's north coast for at least two centuries.

The Gozo Phoenician shipwreck is a seventh-century-BC shipwreck of a Phoenician trade ship lying at a depth of 110 meters (360 ft). The wreck was discovered in 2007 by a team of French scientists during a sonar survey off the coast of Malta's Gozo island. The Gozo shipwreck archaeological excavation is the first maritime archaeological survey to explore shipwrecks beyond a depth of 100 meters (330 ft).
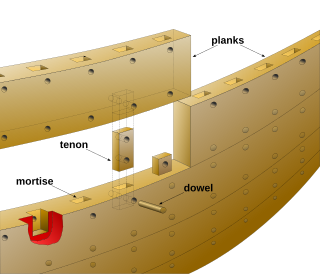
Phoenician joints is a locked mortise and tenon wood joinery technique used in shipbuilding to fasten watercraft hulls. The locked mortise and tenon technique consists of cutting a mortise, or socket, into the edges of two planks and fastening them together with a rectangular wooden knob. The assembly is then locked in place by driving a dowel through one or more holes drilled through the mortise side wall and tenon.
References
- ↑ Cobb, Matthew A. (2018-07-26). Rome and the Indian Ocean Trade from Augustus to the Early Third Century CE. BRILL. p. 45. ISBN 9789004376571.
- ↑ Kleinhenz, Christopher (2004-08-02). Medieval Italy: An Encyclopedia. Routledge. p. 763. ISBN 9781135948801.
- ↑ Sobel, Dava (2010-07-05). Longitude: The True Story of a Lone Genius Who Solved the Greatest Scientific Problem of His Time. Bloomsbury Publishing USA. p. 14. ISBN 9780802779434.
- ↑ Thornton, John K. (2012-09-10). A Cultural History of the Atlantic World, 1250-1820. Cambridge University Press. p. 15. ISBN 9780521727341.