
The Drakensberg is the eastern portion of the Great Escarpment, which encloses the central Southern African plateau. The Great Escarpment reaches its greatest elevation – 2,000 to 3,482 metres within the border region of South Africa and Lesotho.

Mpumalanga is a province of South Africa. The name means "East", or literally "The Place Where the Sun Rises" in the Swazi, Xhosa, Ndebele and Zulu languages. Mpumalanga lies in eastern South Africa, bordering Eswatini and Mozambique. It constitutes 6.5% of South Africa's land area. It shares borders with the South African provinces of Limpopo to the north, Gauteng to the west, the Free State to the southwest, and KwaZulu-Natal to the south. The capital is Mbombela. Mpumalanga was formed in 1994, when the area that was the Eastern Transvaal was merged with the former bantustans KaNgwane, KwaNdebele and parts of Lebowa and Gazankulu. Although the contemporary borders of the province were only formed at the end of apartheid, the region and its surroundings has a history that extends back thousands of years. Much of its history, and current significance is as a region of trade.

The Balkan mountain range is a mountain range in the eastern part of the Balkan Peninsula in Southeastern Europe. The range is conventionally taken to begin at the peak of Vrashka Chuka on the border between Bulgaria and Serbia. It then runs for about 560 kilometres (350 mi), first in a south-easterly direction along the border, then eastward across Bulgaria, forming a natural barrier between the northern and southern halves of the country, before finally reaching the Black Sea at Cape Emine. The mountains reach their highest point with Botev Peak at 2,376 metres (7,795 ft).

Tufa is a variety of limestone formed when carbonate minerals precipitate out of water in unheated rivers or lakes. Geothermally heated hot springs sometimes produce similar carbonate deposits, which are known as travertine. Tufa is sometimes referred to as (meteogene) travertine. It should not be confused with hot spring (thermogene) travertine. Tufa, which is calcareous, should also not be confused with tuff, a porous volcanic rock with a similar etymology that is sometimes also called "tufa".

The Oklahoma City Zoo and Botanical Garden is a zoo and botanical garden located in Oklahoma City's Adventure District in northeast Oklahoma City, Oklahoma.

The American Species Survival Plan or SSP program was developed in 1981 by the (American) Association of Zoos and Aquariums to help ensure the survival of selected species in zoos and aquariums, most of which are threatened or endangered in the wild.

Nature's Valley is a holiday resort and small village on the Garden Route along the southern Cape coast of South Africa. Nature's Valley lies between the Salt River, the foothills of the Tsitsikamma Mountains, the Indian Ocean and the Groot River lagoon. Nature's Valley has a balmy climate and is surrounded by the de Vasselot Nature Reserve which is part of the Tsitsikamma Park, and in turn part of the Garden Route National Park.
The Treur River barb or simply Treur barb is a species of cyprinid fish. It is endemic to northern Mpumalanga, South Africa.

The Berlin Falls is a waterfall in Mpumalanga, South Africa. They are located close to God's Window and the highest waterfall in South Africa's Mpumalanga province, Lisbon Falls. They are less than a tenth of the height of South Africa's tallest waterfall, the Tugela Falls, and are better known for their beauty.

Blyde River Canyon Nature Reserve is situated in the Drakensberg escarpment region of eastern Mpumalanga, South Africa. The reserve protects the Blyde River Canyon, including sections of the Ohrigstad and Blyde Rivers and the geological formations around Bourke's Luck Potholes, where the Treur River tumbles into the Blyde below. Southwards of the canyon, the reserve follows the escarpment, to include the Devil's and God's Window, the latter a popular viewpoint to the lowveld at the reserve's southern extremity.

Blyderivierpoort Dam is a gravity-arch dam on the Blyde River, in the lower Blyde River Canyon, near Hoedspruit in Mpumalanga, South Africa. It also floods the lower reaches of the Blyde's Ohrigstad River tributary. The dam was completed in 1974. The 71 m high dam wall and 22 m deep is situated 3 km from Swadini resort by road.

The Motlatse River, Blyde River, or Umdhlazi River is a river in the Mpumalanga and Limpopo provinces of South Africa. It has a northwards course in steep-sided valleys and ravines of the Mpumalanga Drakensberg, before it enters the lowveld region of the Limpopo province. It has its ultimate origins at around 2,000 m altitude in the Hartebeesvlakte conservation area, to the north of Long Tom Pass. It runs through the Blyde River Canyon.
The Kruger to Canyons Biosphere Region is a biosphere reserve situated in the north eastern region of South Africa, straddling Limpopo and Mpumalanga Provinces. In 2001, under the supervision of the then Department of Environmental Affairs (DEA), the Kruger to Canyons Biosphere Region was officially ratified by UNESCO as part of the Man and the Biosphere (MaB) Programme. UNESCO's Man and the Biosphere Programme provides a framework for exploring local solutions to challenges by mainstreaming biodiversity conservation and sustainable development, integrating economic, social and environmental aspects and recognizing their vital linkages within specific learning landscapes adjacent to Protected Areas.

Hingol National Park or Hungol National Park is the largest national park in Pakistan, located in the Makran coastal region. The park covers an area of about 6,100 square kilometres (2,400 sq mi) and is located 190 km from Karachi in the three districts of Gwadar, Lasbela and Awaran in Balochistan. Hingol was declared a national park in 1988.

The Lisbon Falls are falls in the Lisbon Creek, a right bank tributary of the Blyde River. They are situated a short distance north of Graskop beside the R532 road, and are the highest waterfalls in Mpumalanga, South Africa. The waterfalls are 94 metres (308 ft) high and were named for the Lisbon Creek and the Farm Lisbon, on which the falls are located.

Zoom Torino is a zoo and amusement park in Cumiana, near Turin, northern Italy, created in 2007. It covers 180,000 square metres.
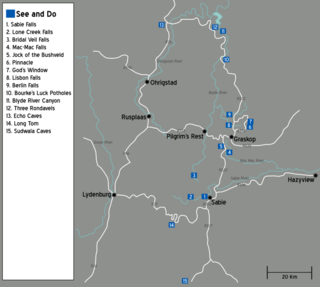
The Panorama Route is a scenic road in South Africa connecting several cultural and natural points of interest. The route, steeped in the history of South Africa, is in Mpumalanga province, centred around the Blyde River Canyon, the world's third largest canyon. It features numerous waterfalls, one of the largest afforested areas in South Africa, and several natural landmarks. The route starts at the foot of the Long Tom Pass just outside Lydenburg, following the natural descent from the Great Escarpment to the Lowveld, and ending at the border of the Mpumalanga and Limpopo provinces near the Echo Caves.
Afroedura rondavelica, also known as the Blyde River flat gecko or rondavel rock gecko, is a species of African geckos, first found in the Limpopo and Mpumalanga provinces of South Africa. Its specific and common name refers to the rondavel, a southern African hut-type structure.




















