
Rondavel is a style of African hut known in literature as cone on cylinder or cone on drum. The word comes from the Afrikaans rondawel. [1] [2]

Rondavel is a style of African hut known in literature as cone on cylinder or cone on drum. The word comes from the Afrikaans rondawel. [1] [2]
The rondavel is usually round or oval in shape and is traditionally made with materials that can be locally found in raw form. [3] Its walls are often constructed from stones. The mortar may consist of sand, soil, or combinations of these, mixed with cow dung. The floor of a traditional rondavel is finished with a dung mixture to make it hard and smooth. The main roofing elements of a rondavel are spars or poles taken from tree limbs, which have been harvested and cut to length. The roof covering is of thatch that is sewn to the poles with grass rope. The process of completing the thatch can take as little as one weekend or up to a year if made by a skilled artisan, as it must be sewn in one section at a time, starting from the bottom working towards the top. As each section is sewn, it may be weathered and aged to form a complete weatherproof seal.


Rondavels can be found in the countries of Southern Africa, [4] including: South Africa, Lesotho (where the hut is also known as a mokhoro), Eswatini, Botswana, and others. In Réunion they exist only in public places, for picnics for example. In different areas, there are small local variations in wall height, roof pitch and general finish. Some people elaborately carve, paint, or decorate the outside wall that has been finished off with dung. In other places, people leave their rondavels undecorated.
In recent times, with the availability of modern construction materials, the appearance and construction of rondavels have changed. They may have concrete foundations, be built with cement blocks or brick, mortared with cement, and/or roofed with corrugated tin. While the traditional rondavel did not have running water, electricity, and/or other modern amenities, many are now equipped with or have been adapted to accommodate these services.
Today, complete homes built in the rondavel architecture are common, and rondavels are fairly popular as outbuildings on smallholdings and commercial farms (e.g. tool sheds, milk rooms, staff accommodation, etc.). Rondavels are also quite common as holiday cottages. Apart from pre-fabricated rondavels, the roofing material is nearly always thatch, because it is difficult to make a neat conical roof out of other materials.
Structurally, no internal struts are required. The principals (wooden poles running radially out from the apex of the roof to the top of the rondavel's wall) are fully supported by the circular purlins: First, the principals do not sag in the middle, because sagging only puts the purlins near the middle of the principals under compression. Second, the principals do not splay at the bottom (push the top of the walls over to the outside) because splaying only puts the purlins near the bottom of the principals under tension. Thus it is possible to build a large rondavel without internal bracing for the roof. Traditional African rondavels range in size depending on the availability of building and construction materials.

A roof is the top covering of a building, including all materials and constructions necessary to support it on the walls of the building or on uprights, providing protection against rain, snow, sunlight, extremes of temperature, and wind. A roof is part of the building envelope.

Thatching is the craft of building a roof with dry vegetation such as straw, water reed, sedge, rushes, heather, or palm branches, layering the vegetation so as to shed water away from the inner roof. Since the bulk of the vegetation stays dry and is densely packed—trapping air—thatching also functions as insulation. It is a very old roofing method and has been used in both tropical and temperate climates. Thatch is still employed by builders in developing countries, usually with low-cost local vegetation. By contrast, in some developed countries it is the choice of some affluent people who desire a rustic look for their home, would like a more ecologically friendly roof, or who have purchased an originally thatched abode.

Building material is material used for construction. Many naturally occurring substances, such as clay, rocks, sand, wood, and even twigs and leaves, have been used to construct buildings. Apart from naturally occurring materials, many man-made products are in use, some more and some less synthetic. The manufacturing of building materials is an established industry in many countries and the use of these materials is typically segmented into specific specialty trades, such as carpentry, insulation, plumbing, and roofing work. They provide the make-up of habitats and structures including homes.
This page is a list of construction topics.

A wigwam, wickiup, wetu (Wampanoag), or wiigiwaam is a semi-permanent domed dwelling formerly used by certain Native American tribes and First Nations people and still used for ceremonial events. The term wickiup is generally used to refer to these kinds of dwellings in the Southwestern United States and Western United States and Northwest Alberta, Canada, while wigwam is usually applied to these structures in the Northeastern United States as well as Ontario and Quebec in central Canada. The names can refer to many distinct types of Indigenous structures regardless of location or cultural group. The wigwam is not to be confused with the Native Plains tipi, which has a different construction, structure, and use.

A rafter is one of a series of sloped structural members such as wooden beams that extend from the ridge or hip to the wall plate, downslope perimeter or eave, and that are designed to support the roof shingles, roof deck and its associated loads. A pair of rafters is called a couple. In home construction, rafters are normally made of wood. Exposed rafters are a feature of some traditional roof styles.

Roof shingles are a roof covering consisting of individual overlapping elements. These elements are typically flat, rectangular shapes laid in courses from the bottom edge of the roof up, with each successive course overlapping the joints below. Shingles are held by the roof rafters and are made of various materials such as wood, slate, flagstone, metal, plastic, and composite materials such as fibre cement and asphalt shingles. Ceramic roof tiles, which still dominate in Europe and some parts of Asia, are still usually called tiles. Roof shingles may deteriorate faster and need to repel more water than wall shingles. They are a very common roofing material in the United States.

A batten is most commonly a strip of solid material, historically wood but can also be of plastic, metal, or fiberglass. Battens are variously used in construction, sailing, and other fields.

A purlin is a longitudinal, horizontal, structural member in a roof. In traditional timber framing there are three basic types of purlin: purlin plate, principal purlin, and common purlin.

A hut is a small dwelling, which may be constructed of various local materials. Huts are a type of vernacular architecture because they are built of readily available materials such as wood, snow, ice, stone, grass, palm leaves, branches, hides, fabric, or mud using techniques passed down through the generations.
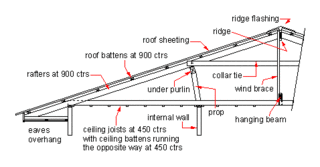
Domestic roof construction is the framing and roof covering which is found on most detached houses in cold and temperate climates. Such roofs are built with mostly timber, take a number of different shapes, and are covered with a variety of materials.

A tin can wall is a wall constructed from tin cans, which are not a common building source. The cans can be laid in concrete, stacked vertically on top of each other, and crushed or cut and flattened to be used as shingles. They can also be used for furniture.

Indian vernacular architecture the informal, functional architecture of structures, often in rural areas of India, built of local materials and designed to meet the needs of the local people. The builders of these structures are unschooled in formal architectural design and their work reflects the rich diversity of India's climate, locally available building materials, and the intricate variations in local social customs and craftsmanship. It has been estimated that worldwide close to 90% of all building is vernacular, meaning that it is for daily use for ordinary, local people and built by local craftsmen.

Pole framing or post-frame construction is a simplified building technique that is an alternative to the labor-intensive traditional timber framing technique. It uses large poles or posts buried in the ground or on a foundation to provide the vertical structural support, along with girts to provide horizontal support. The method was developed and matured during the 1930s as agricultural practices changed, including the shift toward engine-powered farm equipment and the demand for cheaper, larger barns and storage areas.

The vernacular architecture of the Carpathians draws on environmental and cultural sources to create unique designs.

Roof tiles are designed mainly to keep out rain, and are traditionally made from locally available materials such as terracotta or slate. Modern materials such as concrete, metal and plastic are also used and some clay tiles have a waterproof glaze.

A slab hut is a kind of dwelling or shed made from slabs of split or sawn timber. It was a common form of construction used by settlers in Australia and New Zealand during their nations' colonial periods.

Roofline is used to describe the fascia, soffits, bargeboards, antefixes and cladding that forms the frontage immediately below the roof and the eaves of many homes and buildings. These are traditionally made from wood, but can be made of a variety of different materials, including plastic, such as polyvinyl chloride.

A grouted roof is a form of slate roof. It has developed as a form of vernacular architecture associated with the West coast of the British Isles.

The African round hut known in literature as cone on cylinder or cone on drum hut. The hut has different names in various African languages. It is constructed usually with a conical foundation and peaked thatched roof. It is most commonly made out of mud and its roof is often made with grass and with local materials. It has been constructed for thousands of years. The thatched-roofed, plastered type mud houses construction was found early East Africa, where various local indigenous tribes built them, using them as homestead alongside lifestyle with agriculture and farming. The mud hut is extremely common throughout rural parts of the African continent. They can be different in shape and size depending on the region in which they are built.