Related Research Articles

A Nissen hut is a prefabricated steel structure originally for military use, especially as barracks, made from a 210° portion of a cylindrical skin of corrugated iron. It was designed during the First World War by the Canadian-American-British engineer and inventor Major Peter Norman Nissen. It was used also extensively during the Second World War and was adapted as the similar Quonset hut in the United States.

A Quonset hut is a lightweight prefabricated structure of corrugated galvanized steel with a semi-circular cross-section. The design was developed in the United States based on the Nissen hut introduced by the British during World War I. Hundreds of thousands were produced during World War II, and military surplus was sold to the public. The name comes from the site of their first deployment at Quonset Point at the Davisville Naval Construction Battalion Center in Davisville, Rhode Island.

Peter Norman Nissen,, was a Canadian-American-British mining engineer, inventor and army officer. He held a number of patents for his inventions and developed the Nissen hut prefabricated shelter during the First World War.

A hut is a small dwelling, which may be constructed of various local materials. Huts are a type of vernacular architecture because they are built of readily available materials such as wood, snow, ice, stone, grass, palm leaves, branches, clay, hides, fabric, or mud using techniques passed down through the generations.

British hardened field defences of World War II were small fortified structures constructed as a part of British anti-invasion preparations. They were popularly known as pillboxes, a reference to their shape.
The Bellman Hangar was designed in the United Kingdom in 1936 by the Directorate of Works structural engineer, N. S. Bellman, as a temporary aircraft hangar capable of being erected or dismantled by unskilled labour with simple equipment and to be easily transportable. Commercial manufacturing rights were acquired by Head Wrightson & Co of Teesdale Iron Works, Thornaby-on-Tees. By November 1938, 10 had even been supplied to Russia.

Breddan Aerodrome is a heritage-listed abandoned aerodrome at Gregory Developmental Road, Breddan, Charters Towers Region, Queensland, Australia. It is located 15 kilometres (9.3 mi) north of Charters Towers. It was built from 1942 to 1943 by Allied Works Council and Queensland Main Roads Commission. The airfield was constructed for the USAAF 38th Bomb Group in August 1942 as a satellite field for Charters Towers Airport, and later used by the Royal Australian Air Force (RAAF) during World War II as a maintenance base. Consisting of two runways, the airfield was abandoned after 1948. Today, the remains of the airfield consist of some deteriorating runways, taxiways and hardstands, mostly being reclaimed by grassland and shrub. No buildings have survived. It is also known as Breddan Airfield and Breddan WWII Aircraft Maintenance, Repair and Salvage Depot. It was added to the Queensland Heritage Register on 16 April 2010.

A Dymaxion deployment unit (DDU) or Dymaxion House, is a structure designed in 1940 by Buckminster Fuller consisting of a 20-foot circular hut constructed of corrugated steel looking much like a yurt or the top of a metal silo. The interior was insulated and finished with wallboard, portholes and a door. The dome-like ceiling has a hole in the top and a cap for ventilation.

The Great North Road is a large road tunnel in the British Overseas Territory of Gibraltar. It was constructed by the British military during World War II inside the Rock of Gibraltar and remains property of the Ministry of Defence to this day. The road allowed lorries to travel from the north to the south of Gibraltar entirely within the Rock. The tunnel still contains the remains of World War II buildings such as Nissen huts, kitchens, offices as well as a generating station and period anti-submarine nets.

The tunnels of Gibraltar were constructed over the course of nearly 200 years, principally by the British Army. Within a land area of only 2.6 square miles (6.7 km2), Gibraltar has around 34 miles (55 km) of tunnels, nearly twice the length of its entire road network. The first tunnels, excavated in the late 18th century, served as communication passages between artillery positions and housed guns within embrasures cut into the North Face of the Rock. More tunnels were constructed in the 19th century to allow easier access to remote areas of Gibraltar and accommodate stores and reservoirs to deliver the water supply of Gibraltar.
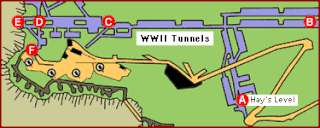
Fordham's Accommodation are underground parallel chambers within the Rock of Gibraltar built during the Second World War. These are part of the extensive tunnels of Gibraltar. The chambers were named after Colonel H M Fordham OBE, MC, who was Chief Engineer in Gibraltar. The chambers were based on Liddell's Union Tunnel.

17 Port and Maritime Regiment is a regiment of the British Army's Royal Logistic Corps. The unit is the Army's only regular Port & Maritime capability, though it is twinned with 165 Port and Maritime Regiment RLC, of the Army Reserve.

The Romney hut is a prefabricated steel structure used by the British military, developed during World War II to supersede the Iris hut.

Gona Barracks is a heritage-listed barracks at 3, 7, 12, 25 & 26 Gona Parade, Kelvin Grove, City of Brisbane, Queensland, Australia. It was built from c. 1914 to 1960s. It is also known as Kelvin Grove Military Reserve and Kelvin Grove Training Area. It was added to the Queensland Heritage Register on 7 February 2005.

Coen Carrier Station is a heritage-listed telegraph station at Coleman Close, Coen, Shire of Cook, Queensland, Australia. It was designed and built in 1942 by the Postmaster-General's Department. It is also known as Coen Telegraph Station and Coen Carrier Repeater Station. It was added to the Queensland Heritage Register on 27 May 1997.
Atherton Performing Arts Theatre is a heritage-listed former military depot and now theatre at 6 Silo Street, Atherton, Tablelands Region, Queensland, Australia. It was built in 1943. It is also known as Atherton WWII Igloo. It was added to the Queensland Heritage Register on 9 October 2015.

The Dubbo RAAF Stores Depot is a heritage-listed former Royal Australian Air Force (RAAF) stores depot located at Cobra Street, Dubbo in the Dubbo Regional Council local government area of New South Wales, Australia. The depot was designed by Sidney Williams & Co and built from 1940 to 1943. It is also known as Dubbo RAAF Stores Depot (former) and was formerly named No. 5 Stores Depot (1942); No. 6 Stores Depot (1942–52); No. 2 Stores Depot Detachment D (1952–92) and Defence National Storage and Distribution Centre Detachment (1992–1995). The property is owned by private companies, Andorra Developments and Belmorgan Property Development. The depot was added to the New South Wales State Heritage Register on 29 June 2004.
The Williamtown RAAF Base Group is a heritage-listed group of Royal Australian Air Force (RAAF) buildings and other items at RAAF Base Williamtown in New South Wales, Australia. It was added to the Australian Commonwealth Heritage List on 22 June 2004.
Macrossan Stores Depot Group is a heritage-listed military installation at Flinders Highway, Macrossan (Dotswood), Charters Towers Region, Queensland, Australia. It was added to the Australian Commonwealth Heritage List on 22 June 2004.

The Twynham hut was developed by the British War Office in 1959 as a replacement for the Nissen hut which was first used in 1916. It was constructed of individual 8-foot (2.4 m) bays which made the roof stronger than that of its predecessor. Huts are known to have been constructed in lengths between 16 feet (4.9 m) and 128 feet (39 m). Although four times the cost of Nissen huts the Twynham hut was considered more comfortable and aesthetically pleasing; it also had twice the design life and could be fitted with air conditioning. The huts remained in use until at least 1982.
References
- ↑ Rose, Edward P.F. (2000). "Fortress Gibraltar". In Rose, Edward P.F.; Nathanail, C. Paul (eds.). Geology and Warfare: Examples of the Influence of Terrain and Geologists on Military Operations. Geological Society. p. 258. ISBN 9781862390652.
- 1 2 3 Historic England. "Details from listed building database (1412391)". National Heritage List for England . Retrieved 13 June 2013.
- ↑ The Civil Engineer in War: Airfields, Roads, Railways, and Bridges. Institution of Civil Engineers. 1948. p. 90.
- ↑ Smith, David J. (1981). Action Stations: Military airfields of Wales and the North-West. Stephens. ISBN 0850594855.
- ↑ Dobinson, Colin (2001). AA Command: Britain's anti-aircraft defences of World War II. Methuen. p. 325. ISBN 9780413765406.
- ↑ Beck, Alfred M. (1985). Technical Services, the Corps of Engineers, the War Against Germany. Government Printing Office. p. 52. ISBN 9780160019388.
