
The Socratic method is a form of argumentative dialogue between individuals, based on asking and answering questions.

Dialogue is a written or spoken conversational exchange between two or more people, and a literary and theatrical form that depicts such an exchange. As a philosophical or didactic device, it is chiefly associated in the West with the Socratic dialogue as developed by Plato, but antecedents are also found in other traditions including Indian literature.

David Joseph Bohm was an American scientist who has been described as one of the most significant theoretical physicists of the 20th century and who contributed unorthodox ideas to quantum theory, neuropsychology and the philosophy of mind. Among his many contributions to physics is his causal and deterministic interpretation of quantum theory known as De Broglie–Bohm theory.

Conversation is interactive communication between two or more people. The development of conversational skills and etiquette is an important part of socialization. The development of conversational skills in a new language is a frequent focus of language teaching and learning. Conversation analysis is a branch of sociology which studies the structure and organization of human interaction, with a more specific focus on conversational interaction.

Brainstorming is a creativity technique in which a group of people interact to suggest ideas spontaneously in response to a prompt. Stress is typically placed on the volume and variety of ideas, including ideas that may seem outlandish or "off-the-wall". Ideas are noted down during the activity, but not assessed or critiqued until later. The absence of criticism and assessment is intended to avoid inhibiting participants in their idea production. The term was popularized by advertising executive Alex Faickney Osborn in the classic work Applied Imagination (1953).

Uppaluri Gopala Krishnamurti was a philosopher and orator who questioned the state of spiritual liberation. Having pursued a religious path in his youth and eventually rejecting it, U.G. claimed to have experienced a devastating biological transformation on his 49th birthday, an event he refers to as "the calamity". He emphasized that this transformation back to "the natural state" is a rare, acausal, biological occurrence with no religious context. Because of this, he discouraged people from pursuing the "natural state" as a spiritual goal.
Implicate order and explicate order are ontological concepts for quantum theory coined by theoretical physicist David Bohm during the early 1980s. They are used to describe two different frameworks for understanding the same phenomenon or aspect of reality. In particular, the concepts were developed in order to explain the bizarre behaviors of subatomic particles which quantum physics describes and predicts with elegant precision but struggles to explain.

Plato's problem is the term given by Noam Chomsky to "the problem of explaining how we can know so much" given our limited experience. Chomsky believes that Plato asked how we should account for the rich, intrinsic, common structure of human cognition, when it seems underdetermined by extrinsic evidence presented to a person during human development. In linguistics this is referred to as the "argument from poverty of the stimulus" (APS). Such arguments are common in the natural sciences, where a developing theory is always "underdetermined by evidence". Chomsky's approach to Plato's problem involves treating cognition as a normal research topic in the natural sciences, so cognition can be studied to elucidate intertwined genetic, developmental, and biophysical factors. Plato's problem is most clearly illustrated in the Meno dialogue, in which Socrates demonstrates that an uneducated boy nevertheless understands geometric principles.
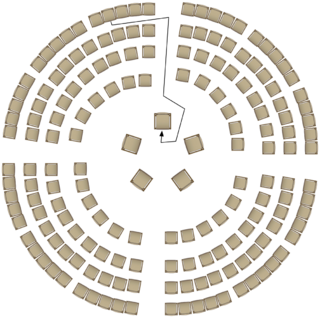
A fishbowl conversation is a form of dialogue that can be used when discussing topics within large groups. Fishbowl conversations are sometimes also used in participatory events such as unconferences. The advantage of fishbowl is that it allows the entire group to participate in a conversation. Several people can join the discussion.
Collaborative methods are processes, behaviors, and conversations that relate to the collaboration between individuals. These methods specifically aim to increase the success of teams as they engage in collaborative problem solving. Forms, rubrics, charts and graphs are useful in these situations to objectively document personal traits with the goal of improving performance in current and future projects.

The hermeneutic circle describes the process of understanding a text hermeneutically. It refers to the idea that one's understanding of the text as a whole is established by reference to the individual parts and one's understanding of each individual part by reference to the whole. The circle is a metaphor for the procedure of transforming one's understanding of the part and the whole through iterative recontextualization.
The term "unsaid" refers what is not explicitly stated, what is hidden and/or implied in the speech of an individual or a group of people.

Dialogic learning is learning that takes place through dialogue. It is typically the result of egalitarian dialogue; in other words, the consequence of a dialogue in which different people provide arguments based on validity claims and not on power claims.
In the social sciences, coordinated management of meaning (CMM) provides an understanding of how individuals create, coordinate and manage meanings in their process of communication. Generally, CMM is "how individuals establish rules for creating and interpreting the meaning and how those rules are enmeshed in a conversation where meaning is constantly being coordinated", and where "human communication is viewed as a flexible, open and mutable process evolving in an ongoing joint interaction, which enables movement, shifts and evolving ways with each other". CMM embodies this vision and allows interpersonal connection and open conversation among individuals or groups, and can be applicable across multiple academic fields and social scenarios.
Positive deconstruction, in relation to Christian apologetics, is a term first used by Nick Pollard in Evangelism Made Slightly Less Difficult, to describe a methodology for engaging with worldviews in Christian apologetics. The process is one of deconstruction because it involves 'dismantling' the worldview in order to identify areas of conflict with a Christian worldview. It is positive because the intention is not to destroy a person's ideas and belief system, but to build on areas of agreement between the two worldviews in order to argue for the truth of the Christian worldview.
Grounding in communication is a concept proposed by Herbert H. Clark and Susan E. Brennan. It comprises the collection of "mutual knowledge, mutual beliefs, and mutual assumptions" that is essential for communication between two people. Successful grounding in communication requires parties "to coordinate both the content and process". The concept is also common in philosophy of language.
Civil discourse is the practice of deliberating about matters of public concern in a way that seeks to expand knowledge and promote understanding. The word "civil" relates directly to civic in the sense of being oriented toward public life, and less directly to civility, in the sense of mere politeness. Discourse is defined as the use of written or spoken communications, similar to having a conversation. Civil discourse includes the practice of deliberating about things that are of concern to society in a way that seeks to help all participants understand each other. It is an essential part of democratic citizenship and is thus a fundamental aspect of freedom of speech, characterized by dialogue that supports the societal good." For civil discourse to truly be effective as a democratic tool, all people need to be heard and share their viewpoints. Civil discourse involves more than just politeness; it involves disagreement without disrespect, seeking common ground, listening beyond preconceptions, and remaining present in dialogues despite deep disagreements. This can help develop better public policies that benefit all people of a society. Members of the U.S. Supreme Court session in 2011 aptly described civil discourse as "robust, honest, frank and constructive dialogue and deliberation that seeks to advance the public interest." Viewpoints are grounded in reason and evidence, adhering to strict guidelines for the appropriate behavior to be practiced. In contrast, uncivil discourse contains direct insults, unwarranted attributions of motive, and open contempt." Civil discourse has its foundation on several key values:

Jiddu Krishnamurti or J. Krishnamurti, was a writer and speaker on philosophical and spiritual issues including psychological revolution, the nature of the mind, meditation, human relationships, and bringing about positive social change. He came to early prominence thanks to claims, made on his behalf, that he was to be a Messiah. As a young man he repudiated these claims and declared himself unbound by any tradition or philosophy. He spent the rest of his life presenting a uniquely expressed philosophy of life around the world in talks, discussions, and writings.
Paavo Pylkkänen is a Finnish philosopher of mind. He is an Associate Professor of Philosophy at the University of Skövde and a university lecturer in theoretical philosophy at the University of Helsinki. He is known for his work on mind-body studies, building on David Bohm's interpretation of quantum mechanics, in particular Bohm's view of the cosmos as an enfolding and unfolding whole including mind and matter.
Text and conversation is a theory in the field of organizational communication illustrating how communication makes up an organization. In the theory's simplest explanation, an organization is created and defined by communication. Communication "is" the organization and the organization exists because communication takes place. The theory is built on the notion, an organization is not seen as a physical unit holding communication. Text and conversation theory puts communication processes at the heart of organizational communication and postulates, an organization doesn't contain communication as a "causal influence", but is formed by the communication within. This theory is not intended for direct application, but rather to explain how communication exists. The theory provides a framework for better understanding organizational communication.










