
Bolshoy Kamen is a town in the south of Primorsky Krai, Russia, located on the opposite side of the Ussuri Bay as seen from Lazurnaya Bay. The town was closed due to its naval base and the Zvezda shipyard, but this status was revoked effective January 1, 2015. Population: 39,257 (2010 Census); 38,394 (2002 Census); 65,621 (1989 Census).

Yakov Permyakov was a Russian seafarer, explorer, merchant, and Cossack.
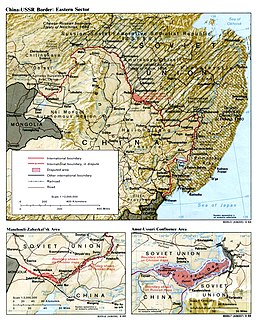
Bolshoi Ussuriysky Island, or Heixiazi Island, is a sedimentary island at the confluence of the Ussuri and Amur rivers. It is divided between the People's Republic of China (PRC) and Russia. It has an area of about 327 to 350 km² and is bounded closely by Yinlong Island, and over ninety islets. Its position at the confluence of the Amur and the Ussuri and right next to the major Russian city of Khabarovsk, has given it great strategic importance.

Maly Semyachik is a stratovolcano located in the eastern part of Kamchatka Peninsula, Russia. It is a compound stratovolcano located in a 10-km-wide caldera within the 15x20 km mid-Pleistocene Stena-Soboliny caldera. Three overlapping stratovolcanoes were constructed sequentially along a NE-SW line, with the youngest cone, Tseno-Semyachik, at the southwest end. A hot, acidic crater lake fills the historically active Troitsky Crater, which formed during a large explosive eruption of Ceno-Semiachik about 400 years ago.
Bolshoy Kekuknaysky is a volcano located in the central part of Kamchatka Peninsula, Russia. It comprises two shield volcanoes: Bolshoy (1301 m) and Kekuknaysky (1401 m). Their lava flows and cinder cones have dammed a valley dissecting the mountain, creating the Bolshoye Goltsovoye and Maloye Goltsovoe lakes. The last eruption occurred at Kekuk Crater, about 7,200 years ago.

Bolshoy Shantar is an island in the Sea of Okhotsk, Russia. It is the main island of the Shantar Islands. Its area is 1766 km². It is about 72 km (44.7 mi) in length and 49 km (30.4 mi) in width. It has a large brackish lake on its north side which is connected to the sea through a narrow passage. Yakshin Bay indents the southwest side of the island.
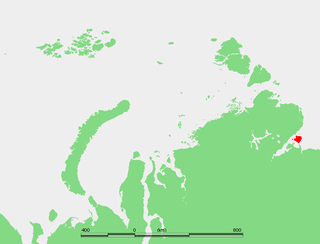
Bolshoy Begichev is an island in the Laptev Sea, Russia.

The Bolshoy Ice Dome is a multi-purpose indoor arena located in Olympic Park, Sochi, Russia. Opened in 2012, the 12,000-seat arena was primarily constructed to host hockey competitions during the 2014 Winter Olympics. Following the Games, it became the home arena of HC Sochi, an expansion team of the KHL. The arena has also hosted concerts and other events. Prior to the Games, the arena hosted the IIHF World U18 Championships and Channel One Cup in 2013.

Большой брат was the Russian version of the reality show Big Brother in Russia. It was produced by Endemol. Unlike most of the other countries it is aired in, Big Brother had only one season in Russia and there are no plans for a second season.
The Bolshoy Anyuy River or Bolshoy Anyui River is a river in the Kolyma River basin in Far East Siberia. It flows roughly westwards and passes through the sparsely populated areas of Chukotka. The Malyi Anyui River joins it from the north near the Sakha Republic border and the combined river properly flows about 20 kilometres (12 mi) to meet the Kolyma at Nizhnekolymsk.
The Aluchin Horst is a mountainous geological formation in the Siberian Far East. It is located right below the Arctic Circle, close to the Baimka River, a left tributary of the Bolshoy Anyui River, about 180 km southwest of Bilibino.

Maly Begichev is an island in the Laptev Sea, Russia. Its area is 15 km². This small island is situated within the Khatanga Gulf.
Bolshoy Yenisei River is a river in the Republic of Tuva, the right source of the Yenisei.
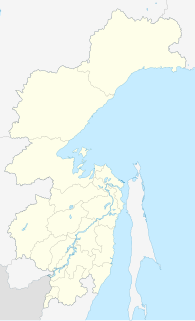
The Chastye Islands is an island group in the southern end of the Sea of Okhotsk. It is located in Tatar Strait, between the mainland shore and the western coast of Sakhalin. Although there are some settlements on the adjacent coast, the Chastye Islands are uninhabited.

The Bolshoy Uzen is a river in Saratov Oblast of Russia and West Kazakhstan Province of Kazakhstan. It is 650 kilometres (400 mi) long, with a drainage basin of 15,600 square kilometres (6,000 sq mi).

Merkury Vagin was a Russian Arctic explorer.

Bolshoy Dom is an office building located at 4 Liteyny Avenue in Saint Petersburg, Russia. It is the headquarters of the local Saint Petersburg and Leningrad Oblast branches of the Federal Security Service of Russia (FSB) and Main Department of the Ministry of Internal Affairs.
The Shantar Sea is a small coastal sea in the northwestern Sea of Okhotsk.

The Smithsonian Institution's Global Volcanism Program (GVP) documents Earth's volcanoes and their eruptive history over the past 10,000 years. The GVP reports on current eruptions from around the world as well as maintaining a database repository on active volcanoes and their eruptions. In this way, a global context for the planet's active volcanism is presented. Smithsonian reporting on current volcanic activity dates back to 1968, with the Center for Short-Lived Phenomena (CSLP). The GVP is housed in the Department of Mineral Sciences, part of the National Museum of Natural History, on the National Mall in Washington, D.C.

The Smithsonian Institution, founded on August 10, 1846 "for the increase and diffusion of knowledge," is a group of museums and research centers administered by the Government of the United States. The institution is named after its founding donor, British scientist James Smithson. Originally organized as the "United States National Museum," that name ceased to exist as an administrative entity in 1967.















