
The Aberdeen Bestiary is a 12th-century English illuminated manuscript bestiary that was first listed in 1542 in the inventory of the Old Royal Library at the Palace of Westminster. Due to similarities, it is often considered to be the "sister" manuscript of the Ashmole Bestiary. The connection between the ancient Greek didactic text Physiologus and similar bestiary manuscripts is also often noted. Information about the manuscript's origins and patrons are circumstantial, although the manuscript most likely originated from the 13th century and was owned by a wealthy ecclesiastical patron from north or south England. Currently, the Aberdeen Bestiary resides in the Aberdeen University Library in Scotland.

The amphisbaena is a mythological, ant-eating serpent with a head at each end. The creature is alternatively called the amphisbaina, amphisbene, amphisboena, amphisbona, amphista, amfivena, amphivena, or anphivena, and is also known as the "Mother of Ants". Its name comes from the Greek words amphis, meaning "both ways", and bainein, meaning "to go".

A bestiary is a compendium of beasts. Originating in the ancient world, bestiaries were made popular in the Middle Ages in illustrated volumes that described various animals and even rocks. The natural history and illustration of each beast was usually accompanied by a moral lesson. This reflected the belief that the world itself was the Word of God and that every living thing had its own special meaning. For example, the pelican, which was believed to tear open its breast to bring its young to life with its own blood, was a living representation of Jesus. Thus the bestiary is also a reference to the symbolic language of animals in Western Christian art and literature.

The unicorn is a legendary creature that has been described since antiquity as a beast with a single large, pointed, spiraling horn projecting from its forehead.

The manticore or mantichore is a Persian legendary creature similar to the Egyptian sphinx that proliferated in western European medieval art as well. It has the head of a human, the body of a lion and a tail of venomous spines similar to porcupine quills, while other depictions have it with the tail of a scorpion. There are some accounts that the spines can be shot like arrows, thus making the manticore a lethal predator.

The catoblepas is a legendary creature from Ethiopia (Africa), first described by Pliny the Elder and later by Claudius Aelianus.

The Yale or Centicore is a mythical beast found in European mythology and heraldry.

The jaculus is a small mythical serpent or dragon. It can be shown with wings and sometimes has front legs. It is also sometimes known as the javelin snake.

The crocotta or corocotta, crocuta, or leucrocotta is a mythical dog-wolf of India or Aethiopia, linked to the hyena and said to be a deadly enemy of men and dogs.

The cinnamon bird, also known as Cinnamologus, Cinomolgus, or Cynnamolgus is a mythical creature described in various bestiaries as a giant bird that collected cinnamon to build its nests.
The salamander is an amphibian of the order Urodela which, as with many real creatures, often has been ascribed fantastic and sometimes occult qualities by pre-modern authors not possessed by the real organism. The legendary salamander is often depicted as a typical salamander in shape with a lizard-like form, but is usually ascribed an affinity with fire, sometimes specifically elemental fire.
The idea that there are specific marine counterparts to land creatures, inherited from the writers on natural history in Antiquity, was firmly believed in Islam and in Medieval Europe. It is exemplified by the creatures represented in the medieval animal encyclopedias called bestiaries, and in the parallels drawn in the moralising attributes attached to each. "The creation was a mathematical diagram drawn in parallel lines," T. H. White said a propos the bestiary he translated. "Things did not only have a moral they often had physical counterparts in other strata. There was a horse in the land and a sea-horse in the sea. For that matter there was probably a Pegasus in heaven". The idea of perfect analogies in the fauna of land and sea was considered part of the perfect symmetry of the Creator's plan, offered as the "book of nature" to mankind, for which a text could be found in Job:
But ask the animals, and they will teach you, or the birds of the air, and they will tell you; or speak to the earth, and it will teach you, or let the fish of the sea inform you. Which of all these does not know that the hand of the Lord has done this? In his hand is the life of every creature and the breath of all mankind.

A pard is the Greek word for the leopard, which is listed in medieval bestiaries and in Pliny the Elder's book Natural History. Over the years, there have been many different depictions of the creature including some adaptations with and without manes and some in later years with shorter tails. However, one consistent representation shows them as large felines often with spots.
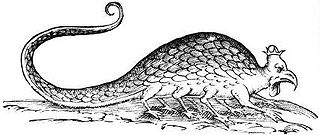
In European bestiaries and legends, a basilisk is a legendary reptile reputed to be a serpent king, who causes death to those who look into its eyes. According to the Naturalis Historia of Pliny the Elder, the basilisk of Cyrene is a small snake, "being not more than twelve inches in length", that is so venomous, it leaves a wide trail of deadly venom in its wake, and its gaze is likewise lethal.

The Forest Bull, also known Ethiopian Bull and Ethiopian Forest Bull, is an animal from ancient and medieval bestiaries. According to Pliny the Elder, they were a breed of ferocious, tawny cattle living in Ethiopia, with mouths gaping open to the ears. Their horns, like a Yale's, could swivel in any direction. To fight, they raised them, after which the horns remained in this position. According to Aelian, they were called "flesh eaters" and were the most ferocious and savage of all animals. They were twice the size of regular bulls and could run at great speeds. He cites their hair as being red. No weapon could physically hurt the bulls, be it spears or arrows because even iron deflected from their skin. The forest bulls hunted herds of wild animals and horses. To protect their flocks, herdsmen who lived in the area dug deep ditches, in which the bulls would fall and consequently choke on their rage. The Troglodytae (cave-dwellers), a nearby tribe, supposedly "judged [this] to be the king of beasts, and rightly so, for it possesses the courage of a lion, the speed of a horse, the strength of a bull, and is stronger than iron."

A legendary creature is a type of fantasy entity, typically a hybrid, that has not been proven and that is described in folklore, but may be featured in historical accounts before modernity.

The Rochester Bestiary is a richly illuminated manuscript copy of a medieval bestiary, a book describing the appearance and habits of a large number of familiar and exotic animals, both real and legendary. The animals' characteristics are frequently allegorised, with the addition of a Christian moral.
Theow, also called thos, thea or thoye, is a hybrid heraldic beast, represented by a wolf with goat's hooves.

The barnacle goose myth is a myth about the origin of the barnacle goose and brant goose.

















