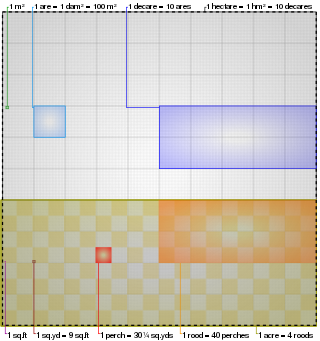
The acre is a unit of land area used in the British imperial and the United States customary systems. It is traditionally defined as the area of one chain by one furlong, which is exactly equal to 10 square chains, 1⁄640 of a square mile, 4,840 square yards, or 43,560 square feet, and approximately 4,047 m2, or about 40% of a hectare. Based upon the international yard and pound agreement of 1959, an acre may be declared as exactly 4,046.8564224 square metres. The acre is sometimes abbreviated ac but is usually spelled out as the word "acre".

The mile, sometimes the international mile or statute mile to distinguish it from other miles, is a British imperial unit and United States customary unit of distance; both are based on the older English unit of length equal to 5,280 English feet, or 1,760 yards. The statute mile was standardised between the Commonwealth of Nations and the United States by an international agreement in 1959, when it was formally redefined with respect to SI units as exactly 1,609.344 metres.

The yard is an English unit of length in both the British imperial and US customary systems of measurement equalling 3 feet or 36 inches. Since 1959 it has been by international agreement standardized as exactly 0.9144 meter. A distance of 1,760 yards is equal to 1 mile.

A fathom is a unit of length in the imperial and the U.S. customary systems equal to 6 feet (1.8288 m), used especially for measuring the depth of water. The fathom is neither an international standard (SI) unit, nor an internationally accepted non-SI unit. Historically it was the maritime measure of depth in the English-speaking world but, apart from within the US, charts now use metres.

The foot is a unit of length in the British imperial and United States customary systems of measurement. The prime symbol, ′, is commonly used to represent the foot. In both customary and imperial units, one foot comprises 12 inches, and one yard comprises three feet. Since an international agreement in 1959, the foot is defined as equal to exactly 0.3048 meters.

A unit of length refers to any arbitrarily chosen and accepted reference standard for measurement of length. The most common units in modern use are the metric units, used in every country globally. In the United States the U.S. customary units are also in use. British Imperial units are still used for some purposes in the United Kingdom and some other countries. The metric system is sub-divided into SI and non-SI units.
The rod, perch, or pole is a surveyor's tool and unit of length of various historical definitions. In British imperial and US customary units it is defined as 16+1⁄2 feet, equal to exactly 1⁄320 of a mile, or 5+1⁄2 yards, and is exactly 5.0292 meters. The rod is useful as a unit of length because integer multiples of it can form one acre of square measure (area). The 'perfect acre' is a rectangular area of 43,560 square feet, bounded by sides 660 feet long and 66 feet wide or, equivalently, 40 rods by 4 rods. An acre is therefore 160 square rods or 10 square chains.

The chain is a unit of length equal to 66 feet, used in both the US customary and Imperial unit systems. It is subdivided into 100 links. There are 10 chains in a furlong, and 80 chains in one statute mile. In metric terms, it is 20.1168 m long. By extension, chainage is the distance along a curved or straight survey line from a fixed commencing point, as given by an odometer.
A system of units of measurement, also known as a system of units or system of measurement, is a collection of units of measurement and rules relating them to each other. Systems of measurement have historically been important, regulated and defined for the purposes of science and commerce. Instances in use include the International System of Units or SI, the British imperial system, and the United States customary system.
The following systems arose from earlier systems, and in many cases utilise parts of much older systems. For the most part they were used to varying degrees in the Middle Ages and surrounding time periods. Some of these systems found their way into later systems, such as the Imperial system and even SI.

Gunter's chain is a distance-measuring device used for surveying. It was designed and introduced in 1620 by English clergyman and mathematician Edmund Gunter (1581–1626). It enabled plots of land to be accurately surveyed and plotted, for legal and commercial purposes.

The link, sometimes called a Gunter’s link, is a unit of length formerly used in many English-speaking countries. In US customary units modern definition, the link is exactly 66⁄100 of a US survey foot, or exactly 7.92 inches or approximately 20.12 cm.
English units were the units of measurement used in England up to 1826, which evolved as a combination of the Anglo-Saxon and Roman systems of units. Various standards have applied to English units at different times, in different places, and for different applications.

The earliest recorded systems of weights and measures originate in the 3rd or 4th millennium BC. Even the very earliest civilizations needed measurement for purposes of agriculture, construction and trade. Early standard units might only have applied to a single community or small region, with every area developing its own standards for lengths, areas, volumes and masses. Often such systems were closely tied to one field of use, so that volume measures used, for example, for dry grains were unrelated to those for liquids, with neither bearing any particular relationship to units of length used for measuring cloth or land. With development of manufacturing technologies, and the growing importance of trade between communities and ultimately across the Earth, standardized weights and measures became critical. Starting in the 18th century, modernized, simplified and uniform systems of weights and measures were developed, with the fundamental units defined by ever more precise methods in the science of metrology. The discovery and application of electricity was one factor motivating the development of standardized internationally applicable units.

Both the British imperial measurement system and United States customary systems of measurement derive from earlier English unit systems used prior to 1824 that were the result of a combination of the local Anglo-Saxon units inherited from Germanic tribes and Roman units.
There are a number of Spanish units of measurement of length or area that are virtually obsolete due to metrication. They include the vara, the cordel, the league and the labor. The units of area used to express the area of land are still encountered in some transactions in land today.

A rood is a historic English and international inch-pound measure of area, as well as an archaic English measure of length.

The imperial and US customary measurement systems are both derived from an earlier English system of measurement which in turn can be traced back to Ancient Roman units of measurement, and Carolingian and Saxon units of measure.
The History of measurement systems in Pakistan begins in early Indus Valley civilization when pastoral societies used barter to exchange goods or services and needed units of measurement.
A number of different units of measurement were historically used in Cyprus to measure quantities like length, mass, area and capacity. Before the Metric system, the Imperial system was used. In between 1986-1988, metric system was adopted in Cyprus.














