
Ton is any of several units of measure of mass, volume or force. It has a long history and has acquired several meanings and uses.

United States customary units form a system of measurement units commonly used in the United States and most U.S. territories, since being standardized and adopted in 1832. The United States customary system developed from English units that were in use in the British Empire before the U.S. became an independent country. The United Kingdom's system of measures was overhauled in 1824 to create the imperial system, which was officially adopted in 1826, changing the definitions of some of its units. Consequently, while many U.S. units are essentially similar to their imperial counterparts, there are noticeable differences between the systems.

Avoirdupois is a measurement system of weights that uses pounds and ounces as units. It was first commonly used in the 13th century AD and was updated in 1959.
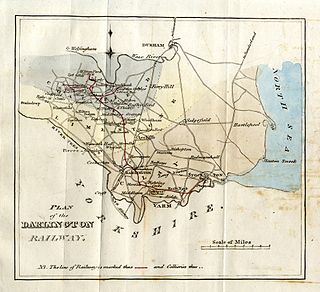
The Stockton and Darlington Railway (S&DR) was a railway company that operated in north-east England from 1825 to 1863. The world's first public railway to use steam locomotives, its first line connected collieries near Shildon with Darlington and Stockton in County Durham, and was officially opened on 27 September 1825. The movement of coal to ships rapidly became a lucrative business, and the line was soon extended to a new port at Middlesbrough. While coal waggons were hauled by steam locomotives from the start, passengers were carried in coaches drawn by horses until carriages hauled by steam locomotives were introduced in 1833.
The long ton, also known as the imperial ton or displacement ton, is a measurement unit equal to 2,240 pounds (1,016.0 kg). It is the name for the unit called the "ton" in the avoirdupois system of weights or Imperial system of measurements. It was standardised in the 13th century. It is used in the United States for bulk commodities.

A bushel is an imperial and US customary unit of volume based upon an earlier measure of dry capacity. The old bushel is equal to 2 kennings (obsolete), 4 pecks, or 8 dry gallons, and was used mostly for agricultural products, such as wheat. In modern usage, the volume is nominal, with bushels denoting a mass defined differently for each commodity.

The hundredweight, formerly also known as the centum weight or quintal, is a British imperial and United States customary unit of weight or mass. Its value differs between the United States customary and British imperial systems. The two values are distinguished in American English as the short and long hundredweight and in British English as the cental and imperial hundredweight.

The stone or stone weight is an English and British imperial unit of mass equal to 14 avoirdupois pounds (6.35 kg). The stone continues in customary use in the United Kingdom and Ireland for body weight.
English units were the units of measurement used in England up to 1826, which evolved as a combination of the Anglo-Saxon and Roman systems of units. Various standards have applied to English units at different times, in different places, and for different applications.

Both the British imperial measurement system and United States customary systems of measurement derive from earlier English unit systems used prior to 1824 that were the result of a combination of the local Anglo-Saxon units inherited from Germanic tribes and Roman units.

Weights and Measures Acts are acts of the British Parliament determining the regulation of weights and measures. It also refers to similar royal and parliamentary acts of the Kingdoms of England and Scotland and the medieval Welsh states. The earliest of these were originally untitled but were given descriptive glosses or titles based upon the monarch under whose reign they were promulgated. Several omnibus modern acts have the short title "Weights and Measures Act" and are distinguished by the year of their enactment.
The Alloa Waggonway, also known as the Alloa Railway was an early tramway. It was 2+1⁄2 miles (4 km) miles long and connected coal pits above Alloa with the harbour and a bottle manufacturer at Alloa in Clackmannanshire, Scotland. The track was wooden with an iron running surface, and wagons were drawn by horses.
The Stanhope and Tyne Railway was an early British mineral railway that ran from Stanhope to South Shields at the mouth of the River Tyne in County Durham, England. It ran through the towns of Birtley, Chester Le Street, West Stanley and Consett. The object was to convey limestone from Stanhope and coal from West Consett and elsewhere to the Tyne, and to local consumers. Passengers were later carried on parts of the line.

The imperial and US customary measurement systems are both derived from an earlier English system of measurement which in turn can be traced back to Ancient Roman units of measurement, and Carolingian and Saxon units of measure.
The quarter was used as the name of several distinct English units based on ¼ sizes of some base unit.
Keel was a unit used to measure coal in the northeast of England, being the quantity of coal carried by a keelboat on the Tyne and Wear rivers. In 1750 it was said to be equal to 8 Newcastle chaldrons (waggons), a measure of volume, or a weight of 21 (long) tons 4 cwt.
The sack was an English unit of weight or mass used for coal and wool. It has also been used for other commodities by weight, commodities by volume, and for both weight and volume in the United States.
The load, also known as a fodder, fother, and charrus, is a historic English unit of weight or mass of various amounts, depending on the era, the substance being measured, and where it was being measured. The term was in use by the 13th century, and disappeared with legislation from the 1820s onwards. Modern equivalents of historical weights and measures are often very difficult to determine, and figures given here should be treated with caution.
A number of units of measurement were used in South Africa to measure quantities like length, mass, capacity, etc. The Imperial system of measurements was made standard in 1922 and the metric system was adopted in 1961.











