
The atmospheric engine was invented by Thomas Newcomen in 1712, and is often referred to as the Newcomen fire engine or simply as a Newcomen engine. The engine was operated by condensing steam drawn into the cylinder, thereby creating a partial vacuum which allowed the atmospheric pressure to push the piston into the cylinder. It was historically significant as the first practical device to harness steam to produce mechanical work. Newcomen engines were used throughout Britain and Europe, principally to pump water out of mines. Hundreds were constructed throughout the 18th century.

A cable railway is a railway that uses a cable, rope or chain to haul trains. It is a specific type of cable transportation.

A capstan is a vertical-axled rotating machine developed for use on sailing ships to multiply the pulling force of seamen when hauling ropes, cables, and hawsers. The principle is similar to that of the windlass, which has a horizontal axle.

A steam donkey or donkey engine is a steam-powered winch once widely used in logging, mining, maritime, and other industrial applications.

A line shaft is a power-driven rotating shaft for power transmission that was used extensively from the Industrial Revolution until the early 20th century. Prior to the widespread use of electric motors small enough to be connected directly to each piece of machinery, line shafting was used to distribute power from a large central power source to machinery throughout a workshop or an industrial complex. The central power source could be a water wheel, turbine, windmill, animal power or a steam engine. Power was distributed from the shaft to the machinery by a system of belts, pulleys and gears known as millwork.

A horse mill is a mill, sometimes used in conjunction with a watermill or windmill, that uses a horse engine as the power source. Any milling process can be powered in this way, but the most frequent use of animal power in horse mills was for grinding grain and pumping water. Other animal engines for powering mills are powered by dogs, donkeys, oxen or camels. Treadwheels are engines powered by humans.
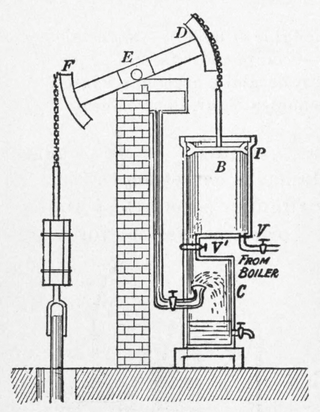
A beam engine is a type of steam engine where a pivoted overhead beam is used to apply the force from a vertical piston to a vertical connecting rod. This configuration, with the engine directly driving a pump, was first used by Thomas Newcomen around 1705 to remove water from mines in Cornwall. The efficiency of the engines was improved by engineers including James Watt, who added a separate condenser; Jonathan Hornblower and Arthur Woolf, who compounded the cylinders; and William McNaught, who devised a method of compounding an existing engine. Beam engines were first used to pump water out of mines or into canals but could be used to pump water to supplement the flow for a waterwheel powering a mill.

A windlass is a machine used on ships that is used to let-out and heave-up equipment such as a ship's anchor or a fishing trawl. On some ships, it may be located in a specific room called the windlass room.

A hoist is a device used for lifting or lowering a load by means of a drum or lift-wheel around which rope or chain wraps. It may be manually operated, electrically or pneumatically driven and may use chain, fiber or wire rope as its lifting medium. The most familiar form is an elevator, the car of which is raised and lowered by a hoist mechanism. Most hoists couple to their loads using a lifting hook. Today, there are a few governing bodies for the North American overhead hoist industry which include the Hoist Manufactures Institute, ASME, and the Occupational Safety and Health Administration. HMI is a product counsel of the Material Handling Industry of America consisting of hoist manufacturers promoting safe use of their products.

A Cornish engine is a type of steam engine developed in Cornwall, England, mainly for pumping water from a mine. It is a form of beam engine that uses steam at a higher pressure than the earlier engines designed by James Watt. The engines were also used for powering man engines to assist the underground miners' journeys to and from their working levels, for winching materials into and out of the mine, and for powering on-site ore stamping machinery.
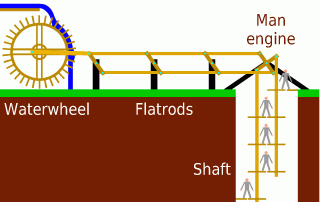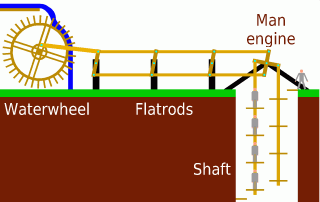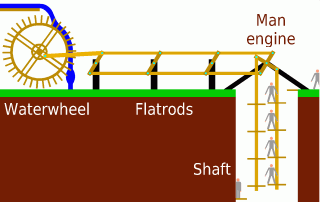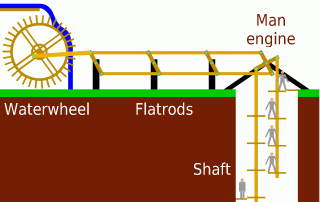
A man engine is a mechanism of reciprocating ladders and stationary platforms installed in mines to assist the miners' journeys to and from the working levels. It was invented in Germany in the 19th century and was a prominent feature of tin and copper mines in Cornwall until the beginning of the twentieth century.

A gin gang, wheelhouse, roundhouse or horse-engine house is a structure built to enclose a horse engine, usually circular but sometimes square or octagonal, attached to a threshing barn. Most were built in England in the late 18th and early 19th centuries. The threshing barn held a small threshing machine which was connected to the gin gang via wooden gears, drive shafts and drive belt, and was powered by a horse which walked round and round inside the gin gang.

Mining in the Upper Harz region of central Germany was a major industry for several centuries, especially for the production of silver, lead, copper, and, latterly, zinc as well. Great wealth was accumulated from the mining of silver from the 16th to the 19th centuries, as well as from important technical inventions. The centre of the mining industry was the group of seven Upper Harz mining towns of Clausthal, Zellerfeld, Sankt Andreasberg, Wildemann, Grund, Lautenthal und Altenau.

A mine railway, sometimes pit railway, is a railway constructed to carry materials and workers in and out of a mine. Materials transported typically include ore, coal and overburden. It is little remembered, but the mix of heavy and bulky materials which had to be hauled into and out of mines gave rise to the first several generations of railways, at first made of wooden rails, but eventually adding protective iron, steam locomotion by fixed engines and the earliest commercial steam locomotives, all in and around the works around mines.
A torque amplifier is a mechanical device that amplifies the torque of a rotating shaft without affecting its rotational speed. It is mechanically related to the capstan seen on ships. Its most widely known use is in power steering on automobiles. Another use is on the differential analyser, where it was used to increase the output torque of the otherwise limited ball-and-disk integrator. The term is also applied to some gearboxes used on tractors, although this is unrelated. It differs from a torque converter, in which the rotational speed of the output shaft decreases as the torque increases.
Resolution was an early beam engine, installed between 1781 and 1782 at Coalbrookdale as a water-returning engine to power the blast furnaces and ironworks there. It was one of the last water-returning engines to be constructed, before the rotative beam engine made this type of engine obsolete.

The Racecourse Colliery is an exhibit located at the Black Country Living Museum.

A team boat, horse boat, or horse ferry, is a watercraft powered by horses or mules, generally using a treadmill, which serves as a horse engine. Team boats were popular as ferries in the United States from the mid-1810s to the 1850s.

Calvert's Engine or the Newbridge Colliery Engine is a beam engine of 1845, now preserved on the campus of the University of Glamorgan, South Wales.

The Wanlockhead beam engine is located close to the Wanlock Water below Church Street on the B797 in the village of Wanlockhead, Parish of Sanquhar, Dumfries and Galloway, Scotland. The site is in the Lowther Hills above the Mennock Pass, a mile south of Leadhills in the Southern Uplands. This is the only remaining original water powered beam engine in the United Kingdom and still stands at its original location. It ceased working circa 1910 after installation circa 1870.


















