Related Research Articles
The centimetre–gram–second system of units is a variant of the metric system based on the centimetre as the unit of length, the gram as the unit of mass, and the second as the unit of time. All CGS mechanical units are unambiguously derived from these three base units, but there are several different ways in which the CGS system was extended to cover electromagnetism.
The litre or liter is a metric unit of volume. It is equal to 1 cubic decimetre (dm3), 1000 cubic centimetres (cm3) or 0.001 cubic metres (m3). A cubic decimetre occupies a volume of 10 cm × 10 cm × 10 cm and is thus equal to one-thousandth of a cubic metre.

Pressure is the force applied perpendicular to the surface of an object per unit area over which that force is distributed. Gauge pressure is the pressure relative to the ambient pressure.

The International System of Units, internationally known by the abbreviation SI, is the modern form of the metric system and the world's most widely used system of measurement. It is the only system of measurement with official status in nearly every country in the world, employed in science, technology, industry, and everyday commerce. The SI system is coordinated by the International Bureau of Weights and Measures which is abbreviated BIPM from French: Bureau international des poids et mesures.
Standard temperature and pressure (STP) or standard conditions for temperature and pressure are various standard sets of conditions for experimental measurements used to allow comparisons to be made between different sets of data. The most used standards are those of the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) and the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), although these are not universally accepted. Other organizations have established a variety of other definitions.
The torr is a unit of pressure based on an absolute scale, defined as exactly 1/760 of a standard atmosphere. Thus one torr is exactly 101325/760 pascals.
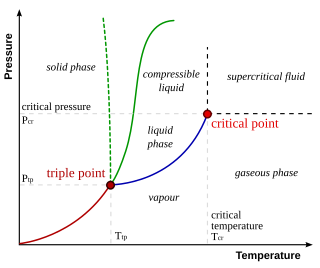
In thermodynamics, the triple point of a substance is the temperature and pressure at which the three phases of that substance coexist in thermodynamic equilibrium. It is that temperature and pressure at which the sublimation, fusion, and vaporisation curves meet. For example, the triple point of mercury occurs at a temperature of −38.8 °C (−37.8 °F) and a pressure of 0.165 mPa.

United States customary units form a system of measurement units commonly used in the United States and most U.S. territories since being standardized and adopted in 1832. The United States customary system developed from English units that were in use in the British Empire before the U.S. became an independent country. The United Kingdom's system of measures evolved by 1824 to create the imperial system, which was officially adopted in 1826, changing the definitions of some of its units. Consequently, while many U.S. units are essentially similar to their imperial counterparts, there are noticeable differences between the systems.

The mole (symbol mol) is a unit of measurement, the base unit in the International System of Units (SI) for amount of substance, an SI base quantity proportional to the number of elementary entities of a substance. One mole is an aggregate of exactly 6.02214076×1023 elementary entities (approximately 602 sextillion or 602 billion times a trillion), which can be atoms, molecules, ions, ion pairs, or other particles. The number of particles in a mole is the Avogadro number (symbol N0) and the numerical value of the Avogadro constant (symbol NA) expressed in mol-1. The value was chosen on the basis of the historical definition of the mole as the amount of substance that corresponds to the number of atoms in 12 grams of 12C, which made the mass of a mole of a compound expressed in grams, numerically equal to the average molecular mass or formula mass of the compound expressed in daltons. With the 2019 revision of the SI, the numerical equivalence is now only approximate but may be assumed for all practical purposes.

The metric system is a system of measurement that standardizes a set of base units and a nomenclature for describing relatively large and small quantities via decimal-based multiplicative unit prefixes. Though the rules governing the metric system have changed over time, the modern definition, the International System of Units (SI), defines the metric prefixes and seven base units: metre (m), kilogram (kg), second (s), ampere (A), kelvin (K), mole (mol), and candela (cd).

The pascal is the unit of pressure in the International System of Units (SI). It is also used to quantify internal pressure, stress, Young's modulus, and ultimate tensile strength. The unit, named after Blaise Pascal, is an SI coherent derived unit defined as one newton per square metre (N/m2). It is also equivalent to 10 barye in the CGS system. Common multiple units of the pascal are the hectopascal, which is equal to one millibar, and the kilopascal, which is equal to one centibar.

The bar is a metric unit of pressure defined as 100,000 Pa (100 kPa), though not part of the International System of Units (SI). A pressure of 1 bar is slightly less than the current average atmospheric pressure on Earth at sea level. By the barometric formula, 1 bar is roughly the atmospheric pressure on Earth at an altitude of 111 metres at 15 °C.

Metrication is the process of introducing the International System of Units, also known as SI units or the metric system, to replace a jurisdiction's traditional measuring units. U.S. customary units have been defined in terms of metric units since the 19th century, and the SI has been the "preferred system of weights and measures for United States trade and commerce" since 1975 according to United States law. However, conversion was not mandatory and many industries chose not to convert, and U.S. customary units remain in common use in many industries as well as in governmental use. There is government policy and metric (SI) program to implement and assist with metrication; however, there is major social resistance to further metrication.
This page provides supplementary data to the article properties of water.
A standard cubic foot (scf) is a unit representing the amount of gas (such as natural gas) contained in a volume of one cubic foot at reference temperature and pressure conditions. It is the unit commonly used when following the customary system, a collection of standards set by the National Institute of Standards and Technology. Another unit used for the same purpose is the standard cubic metre (Sm3), derived from SI units, representing the amount of gas contained in a volume of one cubic meter at different reference conditions. The reference conditions depend on the type of gas and differ from other standard temperature and pressure conditions.

A kilogram-force per square centimetre (kgf/cm2), often just kilogram per square centimetre (kg/cm2), or kilopond per square centimetre (kp/cm2) is a deprecated unit of pressure using metric units. It is not a part of the International System of Units (SI), the modern metric system. 1 kgf/cm2 equals 98.0665 kPa (kilopascals) or 0.980665 bar—2% less than a bar. It is also known as a technical atmosphere.

A vapor barrier is any material used for damp proofing, typically a plastic or foil sheet, that resists diffusion of moisture through the wall, floor, ceiling, or roof assemblies of buildings and of packaging to prevent interstitial condensation. Technically, many of these materials are only vapor retarders as they have varying degrees of permeability.
Inches of water is a non-SI unit for pressure. It is also given as inches of water gauge (iwg or in.w.g.), inches water column (inch wc, in. WC, " wc, etc. or just wc or WC), inAq, Aq, or inH2O. The units are conventionally used for measurement of certain pressure differentials such as small pressure differences across an orifice, or in a pipeline or shaft, or before and after a coil in an HVAC unit.

The metresea water (msw) is a metric unit of pressure used in underwater diving. It is defined as one tenth of a bar.
References
- Michon, Gérard P. (April 29, 2003) "Permeability and permeance". Final Answers: Physics of Gases and Fluids. - accessed August 13, 2007