
Myrmicinae is a subfamily of ants, with about 140 extant genera; their distribution is cosmopolitan. The pupae lack cocoons. Some species retain a functional sting. The petioles of Myrmicinae consist of two nodes. The nests are permanent and in soil, rotting wood, under stones, or in trees.

Dolichoderinae is a subfamily of ants, which includes species such as the Argentine ant, the erratic ant, the odorous house ant, and the cone ant. The subfamily presents a great diversity of species throughout the world, distributed in different biogeographic regions, from the Palearctic, Nearctic, Afrotropical region and Malaysia, to the Middle East, Australian, and Neotropical regions.

Tapinoma is a genus of ants that belongs to the subfamily Dolichoderinae. The genus currently comprises 74 described species distributed worldwide in tropical and temperate regions. Members of are generalized foragers, nesting in a wide variety of habitats, ranging from grasslands, open fields, woodlands, to inside buildings. The majority of species nest in the ground under objects such as stones or tree logs, other species build nests under bark of logs and stumps, in plant cavities, insect galls or refuse piles.

The wildlife of Tunisia is composed of its flora and fauna. It has 84 species of mammals and 375 species of birds. Tunisia is well documented for its addax and Dama Gazelle population.

Aphaenogaster is a genus of myrmicine ants. About 200 species have been described, including 18 fossil species. They occur worldwide except in South America south of Colombia, Sub-Saharan Africa, and Antarctica.

Crematogaster is an ecologically diverse genus of ants found worldwide, which are characterised by a distinctive heart-shaped gaster (abdomen), which gives them one of their common names, the Saint Valentine ant. Members of this genus are also known as cocktail ants because of their habit of raising their abdomens when alarmed. Most species are arboreal. These ants are sometimes known as acrobat ants.

Strumigenys is a genus of ants in the subfamily Myrmicinae.

Tetramorium is a genus of ants in the subfamily Myrmicinae that includes more than 520 species.

Aenictus is a large army ant genus distributed in the Old World tropics and subtropics. It contains about 181 species, making it one of the larger ant genera of the world.

Technomyrmex is a genus of ants in the subfamily Dolichoderinae. With 98 species, it is one of the largest and most diverse ant genera in the Dolichoderinae. The genus distributed throughout the tropical and subtropical zones with most species occurring in the Oriental-Malesian and Afrotropical regions. One species, Technomyrmex albipes is a tramp ant now widespread throughout the tropics due to human activities.
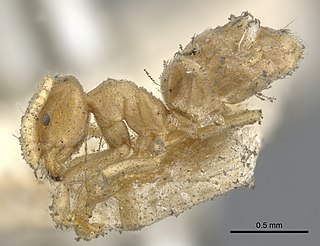
Chronoxenus is a genus of ants in the subfamily Dolichoderinae. The genus is known from Asia.
Bothriomyrmex anastasiae is a species of ant in the genus Bothriomyrmex. Described by Dubovikov in 2002, the species is endemic to the Russian Federation.

Bothriomyrmex atlantis is a species of ant in the genus Bothriomyrmex. Described by Forel in 1894, the species is endemic to Algeria.
Bothriomyrmex emarginatus is a species of ant in the genus Bothriomyrmex. Described by Santschi in 1911, the species is endemic to Tunisia.
Bothriomyrmex pubens is a species of ant in the genus Bothriomyrmex. Described by Santschi in 1919, the species is endemic to Algeria and Tunisia.
Bothriomyrmex regicidus is a species of ant in the genus Bothriomyrmex. Described by Santschi in 1919, the species is endemic to Algeria and Tunisia.
Bothriomyrmex urartus is a species of ant in the genus Bothriomyrmex. Described by Dubovikov in 2002, the species is endemic to Armenia.














