
At 475,440 km2 (183,570 sq mi), Cameroon is the world's 53rd largest country. It is slightly larger than the nation of Sweden and US state of California. It is comparable in size to Papua New Guinea. Cameroon's landmass is 472,710 km2 (182,510 sq mi), with 2,730 km2 (1,050 sq mi) of water.

Bushmeat is meat from wildlife species that are hunted for human consumption in tropical forests. Bushmeat is an important food resource for poor people, particularly in rural areas.

HIV/AIDS is a major public health concern and cause of death in many parts of Africa. Although the continent is home to about 15.2 percent of the world's population, more than two-thirds of the total infected worldwide – some 35 million people – were Africans, of whom 15 million have already died. Sub-Saharan Africa alone accounted for an estimated 69 percent of all people living with HIV and 70 percent of all AIDS deaths in 2011. In the countries of sub-Saharan Africa most affected, AIDS has raised death rates and lowered life expectancy among adults between the ages of 20 and 49 by about twenty years. Furthermore, the life expectancy in many parts of Africa is declining, largely as a result of the HIV/AIDS epidemic with life-expectancy in some countries reaching as low as thirty-four years.

Abong-Mbang is a town and commune in the East Region of Cameroon. Abong-Mbang is located at a crossroads of National Route 10 and the road that leads south to Lomié. Yaoundé, the capital of Cameroon, is 178 km to the west, and Bertoua, the capital of the East Province, lies 108 km to the east. From Ayos, at the border in the Centre Province 145 km (90 mi) from Abong-Mbang, the tar on National Route 10 ends and a dirt road begins. Abong-Mbang is the seat of the Abong-Mbang sub-division and the Haut-Nyong division. The town is headed by a mayor. Gustave Mouamossé has held the post since August 2002. Abong-Mbang is site of one of the East Province's four Courts of First Instance and a prefectural prison. The population was estimated at 18,700 in 2001.
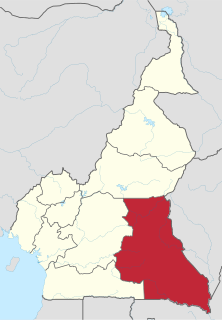
The East Region occupies the southeastern portion of the Republic of Cameroon. It is bordered to the east by the Central African Republic, to the south by Congo, to the north by the Adamawa Region, and to the west by the Centre and South Regions. With 109,002 km² of territory, it is the largest region in the nation as well as the most sparsely populated. Historically, the peoples of the East have been settled in Cameroonian territory for longer than any other of the country's many ethnic groups, the first inhabitants being the Baka pygmies.

The South Region is located in the southwestern and south-central portion of the Republic of Cameroon. It is bordered to the east by the East Region, to the north by the Centre Region, to the northwest by the Littoral Region, to the west by the Gulf of Guinea, and to the south by the countries of Equatorial Guinea, Gabon, and Congo. The South occupies 47,720 km2 of territory, making it the fourth largest region in the nation. The major ethnic groups are the various Beti-Pahuin peoples, such as the Ewondo, Fang, and Bulu.

The Baka people, known in the Congo as Bayaka, are an ethnic group inhabiting the southeastern rain forests of Cameroon, northern Republic of the Congo, northern Gabon, and southwestern Central African Republic. They are sometimes called a subgroup of the Twa, but the two peoples are not closely related. Likewise, the name "Baka" is sometimes mistakenly applied to other peoples of the area who, like the Baka and Twa, have been historically called pygmies, a term that is no longer considered respectful.

AIDS is caused by a human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), which originated in non-human primates in Central and West Africa. While various sub-groups of the virus acquired human infectivity at different times, the global pandemic had its origins in the emergence of one specific strain – HIV-1 subgroup M – in Léopoldville in the Belgian Congo in the 1920s.

Makete District is one of the six districts of Njombe Region of Tanzania. Its administrative seat is the town of Iwawa. It is bordered to the north and west by the Mbeya Region, to theeast by the Njombe District and to the south by the Ludewa District. It is divided into six divisions and 17 wards. Makete District was founded in 1979 with the policy of the Ujamaa. Before, this part of Iringa Region belonged to Njombe District.
This article is a timeline of early AIDS cases.

The South Cameroon Plateau or Southern Cameroon Plateau is the dominant geographical feature of Cameroon. The plateau lies south of the Adamawa Plateau and southeast of the Cameroon Range. It slopes south and west until giving way to the Cameroon coastal plain in the southwest and the Congo River basin in the southeast. The plateau is characterised by hills and valleys in the southwest and a more gentle peneplain in the southwest. Isolated massifs occur, especially in the southwest. Metamorphic rocks make up the plain's basement. The soils are ferrallitic and lateritic, with colouration ranging from red or brown in the interior to yellow on the coast. The soils are subjected to silica leeching, so they are not productive without fertiliser.

The wildlife of Cameroon is composed of its flora and fauna. Bordering Nigeria, it is considered one of the wettest parts of Africa and records Africa's second highest concentration of biodiversity. To preserve its wildlife, Cameroon has more than 20 protected reserves comprising national parks, zoos, forest reserves and sanctuaries. The protected areas were first created in the northern region under the colonial administration in 1932; the first two reserves established were Mozogo Gokoro Reserve and the Bénoué Reserve, which was followed by the Waza Reserve on 24 March 1934. The coverage of reserves was initially about 4 percent of the country's area, rising to 12 percent; the administration proposes to cover 30 percent of the land area.
Xenopus boumbaensis, the Mawa clawed frog, is a species of frog in the family Pipidae. It is known from a few localities in central and south-eastern Cameroon, and from north-western Republic of Congo and extreme south-western Central African Republic; it probably occurs more widely in the central African forest belt, but identification is difficult: it is one of the cryptic species that resemble Xenopus fraseri, from which it can be distinguished by chromosome number (2n=72) and a male advertisement call of a single note.
Bankim, M'Bankim,Bamkin or Kimi is a town and commune of the division Mayo-Banyo in Adamaoua in Cameroon. It is about 95 km from Foumban and 125 km from Banyo The area's vegetation is of shrub savanna type.

Many protected areas in Cameroon are still in pristine condition, mostly because there is less tourism in Cameroon than other regions of Africa. According to reported statistics, there were ten protected areas from 1932 to 1960. Six protected areas were added between 1960 and 1980, five more were added between 1980 and 2004, and eight protected areas are under consideration within a final approval process.

Boumba Bek National Park is a national park in extreme southeastern Cameroon, located in its East Province.

Nki National Park is a national park in southeastern Cameroon, located in its East Province. The closest towns to Nki are Yokadouma, Moloundou and Lomie, beyond which are rural lands. Due to its remoteness, Nki has been described as "the last true wilderness." It has a large and varied ecosystem, and it is home to over 265 species of birds, and the forests of Cameroon contain some of the highest population density of forest elephants of any nation with an elephant density of roughly 2.5 per square kilometer for Nki and neighboring Boumba Bek National Park combined. These animals are victims of poaching, which has been a major problem since an economic depression in the 1980s. The indigenous people follow in the footsteps of the poachers, attracted by the financial opportunities. The removal of logging industries from the park, on the other hand, has been a success; it is no longer considered a major threat to Nki's wilderness.

The central chimpanzee or tschego is a subspecies of the common chimpanzee. It occurs mainly in Gabon, Cameroon, and the Republic of the Congo, but also, to a lesser extent, in other regions.

Moloundou is an arrondissement (district) in the Boumba-et-Ngoko Division of southeastern Cameroon's East Province. Mouloundou is close to Boumba Bek and Nki National Parks on the Dja River. It has a mayor and several decentralised administrative services.

Lobéké National Park is a national park of southeastern Cameroon within the Moloundou Arrondissement of East Province. Located in the Congo Basin, it is bounded on the east by the Sangha River which serves as Cameroon's international border with Central African Republic and the Republic of the Congo. It is adjacent to two other reserves in the CAR and Congo. To the northwest is Boumba Bek National Park, another national park in Cameroon's East Province.


















