Related Research Articles

Landing is the last part of a flight, where a flying animal, aircraft, or spacecraft returns to the ground. When the flying object returns to water, the process is called alighting, although it is commonly called "landing", "touchdown"a or "splashdown" as well. A normal aircraft flight would include several parts of flight including taxi, takeoff, climb, cruise, descent and landing.

In flight dynamics a spin is a special category of stall resulting in autorotation about the aircraft's longitudinal axis and a shallow, rotating, downward path approximately centred on a vertical axis. Spins can be entered intentionally or unintentionally, from any flight attitude if the aircraft has sufficient yaw while at the stall point. In a normal spin, the wing on the inside of the turn stalls while the outside wing remains flying. It is possible for both wings to stall, but the angle of attack of each wing, and consequently its lift and drag, are different.

Aircraft flight control surfaces are aerodynamic devices allowing a pilot to adjust and control the aircraft's flight attitude.

Pilot-induced oscillations (PIOs), as defined by MIL-HDBK-1797A, are sustained or uncontrollable oscillations resulting from efforts of the pilot to control the aircraft. They occur when the pilot of an aircraft inadvertently commands an often increasing series of corrections in opposite directions, each an attempt to cover the aircraft's reaction to the previous input with an overcorrection in the opposite direction. An aircraft in such a condition can appear to be "porpoising" switching between upward and downward directions. As such it is a coupling of the frequency of the pilot's inputs and the aircraft's own frequency. In order to avoid any assumption that oscillation is necessarily the fault of the pilot, new terms have been suggested to replace pilot-induced oscillation. These include aircraft-pilot coupling, pilot–in-the-loop oscillations and pilot-assisted oscillations.

Landing gear is the undercarriage of an aircraft or spacecraft that is used for taxiing, takeoff or landing. For aircraft, it is generally needed for all three of these. It was also formerly called alighting gear by some manufacturers, such as the Glenn L. Martin Company. For aircraft, Stinton makes the terminology distinction undercarriage (British) = landing gear (US).

A slip is an aerodynamic state where an aircraft is moving somewhat sideways as well as forward relative to the oncoming airflow or relative wind. In other words, for a conventional aircraft, the nose will be pointing in the opposite direction to the bank of the wing(s). The aircraft is not in coordinated flight and therefore is flying inefficiently.

Trim tabs are small surfaces connected to the trailing edge of a larger control surface on a boat or aircraft, used to control the trim of the controls, i.e. to counteract hydro- or aerodynamic forces and stabilise the boat or aircraft in a particular desired attitude without the need for the operator to constantly apply a control force. This is done by adjusting the angle of the tab relative to the larger surface.

The Learjet 25 is an American ten-seat, twin-engine, high-speed business jet aircraft manufactured by Learjet. It is a stretched version of the Learjet 24.
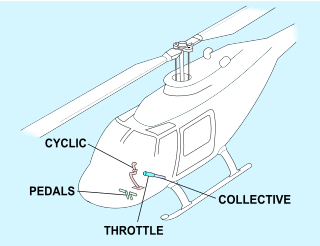
Helicopter flight controls are used to achieve and maintain controlled aerodynamic helicopter flight. Changes to the aircraft flight control system transmit mechanically to the rotor, producing aerodynamic effects on the rotor blades that make the helicopter move in a desired way. To tilt forward and back (pitch) or sideways (roll) requires that the controls alter the angle of attack of the main rotor blades cyclically during rotation, creating differing amounts of lift at different points in the cycle. To increase or decrease overall lift requires that the controls alter the angle of attack for all blades collectively by equal amounts at the same time, resulting in ascent, descent, acceleration and deceleration.

Oakland County International Airport is a county-owned public-use airport located in Waterford Township, Oakland County, Michigan, United States. The airport is located approximately one mile from the center of Waterford Township and Oakland County. It is included in the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) National Plan of Integrated Airport Systems for 2017–2021, in which it is categorized as a non primary commercial service facility.

In aviation, a crosswind landing is a landing maneuver in which a significant component of the prevailing wind is perpendicular to the runway center line.

Britannia Airways Flight 226A was an international passenger flight from Cardiff, Wales to Girona, Spain, operated by charter airliner Britannia Airways. On 14 September 1999, the Boeing 757-204 aircraft suffered a crash landing and broke apart during a thunderstorm in Girona-Costa Brava Airport. Of the 236 passengers and nine crew on board, two were seriously injured and 41 sustained minor injuries. One of the passengers who had apparently sustained only minor injuries died five days later of unsuspected internal injuries. The aircraft involved in the crash, Boeing 757-204 registration G-BYAG, was damaged beyond economical repair and scrapped.

FedEx Express Flight 14 was a scheduled cargo flight from Singapore to Newark, New Jersey, via Malaysia, Taiwan, and Alaska. On July 31, 1997, the aircraft flying this route crashed during landing on its final segment at Newark International Airport (EWR), inverting and catching fire, injuring all five people on board.
Supermaneuverability is the capability of fighter aircraft to execute tactical maneuvers that are not possible with purely aerodynamic techniques. Such maneuvers can involve controlled side-slipping or angles of attack beyond maximum lift.

FedEx Express Flight 80 was a scheduled cargo flight from Guangzhou Baiyun International Airport in China, to Narita International Airport in Narita, Chiba Prefecture, Japan. On March 23, 2009, the McDonnell Douglas MD-11F (N526FE) operating the flight crashed at 6:48 am JST, while attempting a landing on Runway 34L in gusty wind conditions. The aircraft became destabilized at flare and touchdown resulting in an unrecovered "bounced" landing with structural failure of the landing gear and airframe following pilot error due to poor training for bounced landings. The plane came to rest off the runway, inverted, and burning fiercely. The captain and first officer, the jet's only occupants, were both killed.

A flight control mode or flight control law is a computer software algorithm that transforms the movement of the yoke or joystick, made by an aircraft pilot, into movements of the aircraft control surfaces. The control surface movements depend on which of several modes the flight computer is in. In aircraft in which the flight control system is fly-by-wire, the movements the pilot makes to the yoke or joystick in the cockpit, to control the flight, are converted to electronic signals, which are transmitted to the flight control computers that determine how to move each control surface to provide the aircraft movement the pilot ordered.

Malaysia Airlines Flight 2133 (MH2133/MAS2133) was a scheduled domestic passenger flight from Kota Kinabalu to Tawau, operated by Malaysia's flag carrier Malaysia Airlines. On 15 September 1995, the Fokker 50 carrying 53 people flew into a shanty town after the pilots failed to stop the aircraft while landing in Tawau, killing 32 of the 49 passengers and 2 of the 4 crew on board. This was the first hull loss of a Fokker 50.

A falling leaf is a maneuver in which an aircraft performs a wings-level stall which begins to induce a spin. This spin is countered with the rudder, which begins a spin in the opposite direction that must be countered with rudder, and the process is repeated as many times as the pilot determines. During the maneuver, the plane resembles a leaf falling from the sky; first slipping to one side, stopping, and then slipping to the other direction; continuing a side-to-side motion as it drifts toward the ground.

The CubCrafters CC19 XCub is an American light aircraft, designed and produced by Cub Crafters of Yakima, Washington, introduced in June 2016. The aircraft is supplied complete and ready-to-fly.

Loganair Flight 6780 was a scheduled domestic flight from Aberdeen Airport to Sumburgh Airport in the Shetland Islands, Scotland. On 15 December 2014, the Saab 2000 operating the flight was struck by lightning during the approach, and then plunged faster than the aircraft's maximum operating speed. The aircraft came within 1,100 feet (340 m) of the North Sea before the pilots recovered and returned to Aberdeen. All 33 passengers and crew were unharmed.
References
- ↑ "Ballooning During Roundout". avstop.com. Retrieved 7 May 2019.
- ↑ "Activities, Courses, Seminars & Webinars - ALC_Content - FAA - FAASTeam - FAASafety.gov". www.faasafety.gov. Retrieved 7 May 2019.
- ↑ "How To Recover From A Bounced Landing". www.boldmethod.com. Retrieved 7 May 2019.
- ↑ "Василий Васильевич Ершов. Практика полетов на самолете Ту-154". lib.ru. Retrieved 7 May 2019.