Grampound in Cornwall was a borough constituency of the House of Commons of the Parliament of England, then of the Parliament of Great Britain from 1707 to 1800 and of the Parliament of the United Kingdom from 1801 to 1826. It was represented by two Members of Parliament.
Sussex was a constituency of the House of Commons of the Parliament of England then of the Parliament of Great Britain from 1707 to 1800 and of the Parliament of the United Kingdom from 1801 to 1832. It was represented by two Knights of the Shire, elected by the bloc vote system.
Wendover was a borough constituency of the House of Commons of the Parliament of England then of the Parliament of Great Britain from 1707 to 1800 and of the Parliament of the United Kingdom from 1801 to 1832. It was based on the borough of Wendover, was represented by two Members of Parliament, and was considered a classic example of a pocket borough.
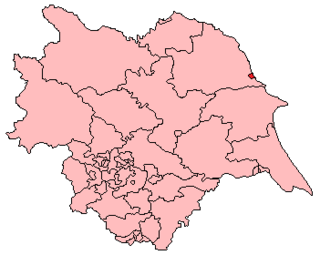
Scarborough was the name of a constituency in Yorkshire, electing Members of Parliament to the House of Commons, at two periods. From 1295 until 1918 it was a parliamentary borough consisting only of the town of Scarborough, electing two MPs until 1885 and one from 1885 until 1918. In 1974 the name was revived for a county constituency, covering a much wider area; this constituency was abolished in 1997.
Pontefract was an English parliamentary constituency centred on the town of Pontefract in the West Riding of Yorkshire, which returned two Members of Parliament to the House of Commons briefly in the 13th century and again from 1621 until 1885, and one member from 1885 to 1974.
Cricklade was a parliamentary constituency named after the town of Cricklade in Wiltshire.
Northallerton was a parliamentary borough in the North Riding of Yorkshire, represented by two Members of Parliament in the House of Commons briefly in the 13th century and again from 1640 to 1832, and by one member from 1832 until 1885.
Knaresborough was a parliamentary constituency which returned two Members of Parliament (MPs) to the Parliament of England, Parliament of Great Britain and the House of Commons of the Parliament of the United Kingdom until 1868, and then one MP until its abolition in 1885.
New Shoreham, sometimes simply called Shoreham, was a parliamentary borough centred on the town of Shoreham-by-Sea in what is now West Sussex. It returned two Members of Parliament (MPs) to the House of Commons of England from 1295 to 1707, then to the House of Commons of Great Britain until 1800, and finally to the House of Commons of the Parliament of the United Kingdom from 1801 until it was abolished by the Redistribution of Seats Act 1885, with effect from the 1885 general election.
Ilchester was a constituency of the House of Commons of the Parliament of England, then of the Parliament of Great Britain from 1707 to 1800 and of the Parliament of the United Kingdom from 1801 to 1832. It was represented by two Members of Parliament until 1832. It was one of the most notoriously corrupt rotten boroughs.
Midhurst was a parliamentary borough in Sussex, which elected two Members of Parliament (MPs) to the House of Commons from 1311 until 1832, and then one member from 1832 until 1885, when the constituency was abolished. Before the Great Reform Act of 1832, it was one of the most notorious of England's rotten boroughs.
Droitwich was the name of a constituency of the House of Commons of England in 1295, and again from 1554, then of the House of Commons of Great Britain from 1707 to 1800 and of the House of Commons of the Parliament of the United Kingdom from 1801 to 1918. It was a parliamentary borough in Worcestershire, represented by two Members of Parliament until 1832, and by one member from 1832 to 1885. The name was then transferred to a county constituency electing one MP from 1885 until 1918.
Plymouth was a parliamentary borough in Devon, which elected two members of parliament (MPs) to the House of Commons in 1298 and again from 1442 until 1918, when the borough was merged with the neighbouring Devonport and the combined area divided into three single-member constituencies.
Downton was a parliamentary borough in Wiltshire, which elected two Members of Parliament (MPs) to the House of Commons from 1295 until 1832, when it was abolished by the Great Reform Act.
Steyning was a parliamentary borough in Sussex, England, which elected two Members of Parliament (MPs) to the House of Commons sporadically from 1298 and continuously from 1467 until 1832. It was a notorious rotten borough, and was abolished by the Great Reform Act.
Whitchurch was a parliamentary borough in the English County of Hampshire, which elected two Members of Parliament (MPs) to the Unreformed House of Commons from 1586 until 1832, when the borough was abolished by the Great Reform Act.
Hindon was a parliamentary borough consisting of the village of Hindon in Wiltshire, which elected two Members of Parliament (MPs) to the House of Commons from 1448 until 1832, when the borough was abolished by the Great Reform Act. It was one of the most notoriously corrupt of the rotten boroughs, and bills to disfranchise Hindon were debated in Parliament on two occasions before its eventual abolition.
Shaftesbury was a parliamentary constituency in Dorset. It returned two Members of Parliament to the House of Commons of England, Great Britain and the House of Commons of the Parliament of the United Kingdom from 1295 until 1832 and one member until the constituency was abolished in 1885.
Sandwich was a parliamentary constituency in Kent, which elected two Members of Parliament (MPs) to the House of Commons from 1366 until 1885, when it was disfranchised for corruption.
Henry Goring was an English soldier and politician who sat in the House of Commons between 1673 and 1685.
