
The Amiot 143M was a late 1930s French medium bomber designed to meet 1928 specifications for a bomber capable of day/night bombing, long-range reconnaissance and bomber escort.

The Bleriot-SPAD S.51 was a French fighter aircraft developed in 1924 in response to a French Air Force requirement for an aircraft to replace their obsolete Nieuport-Delage NiD.29s.
The Latécoère 611 was a French four-engined maritime reconnaissance flying boat of the Second World War. Although only a single prototype was completed, this served throughout the war, being used by both the Vichy French and Free French navies.

The Potez-CAMS 141 was a French long range reconnaissance flying boat of the late 1930s. Intended to equip the French Navy, only a single prototype was completed before the German invasion of France stopped production. That prototype did, however serve operationally from bases in French North Africa until scrapped in 1943.

The Loire 210 was a French single-seat catapult-launched fighter seaplane designed and built by Loire Aviation for the French Navy.
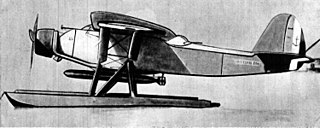
The Latécoère 290 was a torpedo bomber floatplane produced in France during the 1930s. Designed by Latécoère in response to an Aéronavale specification for such an aircraft, the 290 was based on its successful Laté 28.3 mail plane. It was a conventional high-wing, strut-braced monoplane that carried a single torpedo externally under the fuselage.

The Farman NC.470 was a French twin-engined floatplane designed as a crew trainer for the French Navy. It was used in small numbers for both its intended role as a trainer and as a coastal reconnaissance aircraft at the start of World War II.
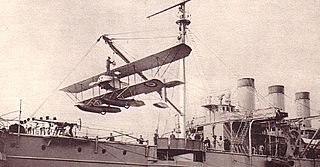
The Caudron J Marine was an amphibious, two-seat, biplane equipped with floats and wheels, simiar to the earlier Caudron J floatplane.

The Loire-Nieuport 10 was a 1930s French prototype long-range maritime reconnaissance and combat floatplane produced by Loire-Nieuport, a joint venture between Loire Aviation and Nieuport-Delage. It was an attempt to answer the requirements for the Navy's programme Hydravion éclaireur de combat for a large floatplane capable of acting as a torpedo bomber or reconnaissance aircraft.
The Latécoère 550 was a four-engined French seaplane, designed in the early 1930s as a bomber/torpedo bomber. Though initial handling problems were partly resolved, the aircraft was deemed too slow and did not go into production.
The Bloch MB.480 was a French twin-engined torpedo-bomber/reconnaissance floatplane designed just before the start of the Second World War by Société des Avions Marcel Bloch. Only two were built, the French Navy deciding to use landplanes instead.

The Bernard H.52 was a French floatplane fighter aircraft of the 1930s. It was a single engine, single-seat monoplane built in the hope of being selected by the French Navy. Two prototypes were built, but no production followed.
The Farman F.420 was a twin engine monoplane, built in France in the mid-1930s to compete in a government contest for an aircraft capable of fulfilling bomber, fighter and reconnaissance roles. Two prototypes were constructed but no production followed.
The SNCASE SE-400 was a prototype French twin-engined coastal patrol floatplane of the Second World War. A single example was flown, but development was abandoned in May 1940 owing to the German invasion of France.

The Blériot-SPAD S.91 was a French light-weight fighter aircraft. It would be later developed into the Blériot-SPAD S.510, the last biplane produced by the French aeronautic industries.

The CAMS 52 was a twin-engined floatplane torpedo-bomber. It was not ordered by the French Navy and only one CAMS 52 was completed. It first flew in the summer of 1930.
The Nieuport-Delage NiD 50 HB.4 was a twin-engined bomber / reconnaissance floatplane, designed in the latter half of the 1920s, to the 1928 HB.4 specification from the Service Technique de l'Aéronautique (STAé), for a four-seat seaplane bomber. Development was cancelled before the first prototype was completed.
The Lioré et Olivier LeO H-46 was a bomber seaplane built in France in 1936.
The Gourdou-Leseurre GL-820 HY family of four-seat single-engined floatplanes were designed and built in France during the latter half of the 1930s by Gourdou-Leseurre. The GL-820 HY and GL-821 HY 02 were shipborne reconnaissance / obeservation aircraft, while the sole GL-821 HY was built as a torpedo carrier.

The Levasseur PL.200 was an observation seaplane built by Levasseur in the mid-1930s. It was a high-wing monoplane with a short, all-metal fuselage nacelle at mid-span, and a wing made of metal.














