| Br 941 | |
|---|---|
 | |
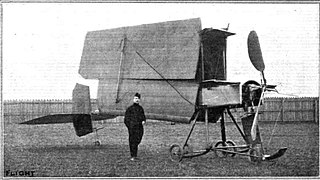
| The prototype as the McDonnell 188 | |
| Role | STOL Transport |
| Manufacturer | Breguet |
| First flight | 21 May 1958 (Breguet 940) 1 June 1961 (Breguet 941) |
| Introduction | 1967 |
| Retired | 1974 |
| Primary user | French Air Force |
| Number built | 1 (940) + 1 (941) + 4 (941S) |
The Breguet 941 was a French four-engine turboprop STOL transport aircraft developed by Breguet in the 1960s. Although widely evaluated, it was not built in large numbers, with only one prototype and four production aircraft being built.

France, officially the French Republic, is a country whose territory consists of metropolitan France in Western Europe and several overseas regions and territories. The metropolitan area of France extends from the Mediterranean Sea to the English Channel and the North Sea, and from the Rhine to the Atlantic Ocean. It is bordered by Belgium, Luxembourg and Germany to the northeast, Switzerland and Italy to the east, and Andorra and Spain to the south. The overseas territories include French Guiana in South America and several islands in the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian oceans. The country's 18 integral regions span a combined area of 643,801 square kilometres (248,573 sq mi) and a total population of 67.3 million. France, a sovereign state, is a unitary semi-presidential republic with its capital in Paris, the country's largest city and main cultural and commercial centre. Other major urban areas include Lyon, Marseille, Toulouse, Bordeaux, Lille and Nice.

STOL is an acronym for a short takeoff and landing aircraft, which have short runway requirements for takeoff and landing. Many STOL-designed aircraft also feature various arrangements for use on runways with harsh conditions. STOL aircraft, including those used in scheduled passenger airline operations, have also been operated from STOLport airfields which feature short runways.

A prototype is an early sample, model, or release of a product built to test a concept or process or to act as a thing to be replicated or learned from. It is a term used in a variety of contexts, including semantics, design, electronics, and software programming. A prototype is generally used to evaluate a new design to enhance precision by system analysts and users. Prototyping serves to provide specifications for a real, working system rather than a theoretical one. In some design workflow models, creating a prototype is the step between the formalization and the evaluation of an idea.