The Glorieuses or Glorioso Islands are a group of French islands and rocks totaling 5 square kilometres. They are controlled by France as part of the Scattered Islands in the Indian Ocean in the French Southern and Antarctic Lands, a French overseas territory, but are also claimed by Comoros and Seychelles. They are geographically part of the Comoro Islands between the French overseas region of Mayotte and the nation of Madagascar.
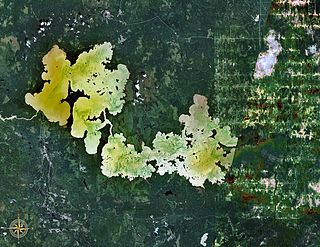
Lake Abitibi is a shallow lake in northeastern Ontario and western Quebec, Canada. The lake, which lies within the vast Clay Belt, is separated in two distinct portions by a short narrows, making it actually 2 lakes. Its total area is 931 square kilometres (359 sq mi), and net area 903 square kilometres (349 sq mi). The lake is shallow and studded with islands. Its shores and vicinity are covered with small timber.

The Gulf of St. Lawrence is the outlet of the North American Great Lakes via the St. Lawrence River into the Atlantic Ocean. The gulf is a semi-enclosed sea, covering an area of about 226,000 square kilometres (87,000 sq mi) and containing about 34,500 cubic kilometres (8,300 cu mi) of water, which results in an average depth of 152 metres (499 ft).

Banks Island is one of the larger members of the Arctic Archipelago. Situated in the Inuvik Region, and part of the Inuvialuit Settlement Region, of the Northwest Territories, it is separated from Victoria Island to its east by the Prince of Wales Strait and from the mainland by Amundsen Gulf to its south. The Beaufort Sea lies to its west, and to its northeast M'Clure Strait separates the island from Prince Patrick Island and Melville Island.

The Ottawa River is a river in the Canadian provinces of Ontario and Quebec. It is named in honour of the Algonquin word 'to trade', as it was the major trade route of Eastern Canada at the time. For most of its length, it defines the border between these two provinces. It is a major tributary of the St. Lawrence River and the longest river in Quebec.

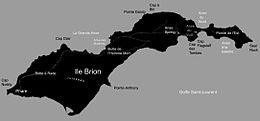
The Magdalen Islands are a small archipelago in the Gulf of Saint Lawrence with a land area of 205.53 square kilometres (79.36 sq mi). While part of the Province of Quebec, the islands are in fact closer to the Maritime provinces and Newfoundland than to the Gaspé Peninsula on the Quebec mainland. The islands are part of the homeland territories, or Mi'kma'ki, of the Mi'kmaw Nation who call the islands Menagoesenog.

Sept-Îles is a city in the Côte-Nord region of eastern Quebec, Canada. It is among the northernmost locales with a paved connection to the rest of Quebec's road network. The population was 25,686 as of the Canada 2011 Census. The town is called Uashat, meaning "bay," in the Innu language.

Sir Frederick Haldimand, KB was a military officer best known for his service in the British Army in North America during the Seven Years' War and the American Revolutionary War. From 1778 to 1786, he served as Governor of the Province of Quebec, during which time he oversaw military operations against the northern frontiers in the war, and engaged in ultimately fruitless negotiations to establish the independent Vermont Republic as a new British province. His administration of Quebec was at times harsh, with the detention of numerous political dissidents and agitators.

Akimiski Island is the largest island in James Bay, Canada, which is part of the Qikiqtaaluk Region of the territory of Nunavut. It has an area of 3,001 km2 (1,159 sq mi), making it the 163rd largest island in the world, and Canada's 29th largest island. Akimiski Island is 19 km (12 mi) from the province of Ontario. From the western side of the island, the Ontario coastline is visible.

Les Îles-de-la-Madeleine is one of two municipalities forming the urban agglomeration of Magdalen Islands in Quebec, Canada. It is part of the Gaspésie–Îles-de-la-Madeleine region and its population was 12,010 as of the 2016 Census.
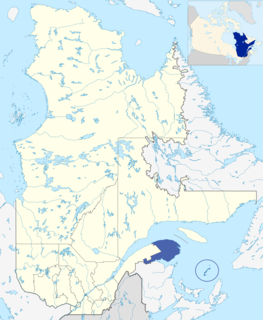
Gaspésie–Îles-de-la-Madeleine is an administrative region of Quebec consisting of the Gaspé Peninsula (Gaspésie) and the Îles-de-la-Madeleine. It lies in the Gulf of Saint Lawrence at the eastern extreme of southern Quebec. The predominant economic activities are fishing, forestry and tourism.

Batchawana Bay is a small bay in Algoma District in Northeastern Ontario, Canada. It is on the eastern shore of Lake Superior, approximately 50 kilometres (31 mi) north of Sault Ste. Marie.
Walrus Island may refer to:

Charron Island is an island in the Saint Lawrence River, the westernmost of the Îles de Boucherville archipelago, near Îles-de-Boucherville National Park to the northeast of Montreal. It is connected to the mainland by the Louis-Hippolyte Lafontaine Bridge–Tunnel which carries Quebec Autoroute 25 and the Trans-Canada Highway.

The Géologie Archipelago, also known as the Pointe Géologie Archipelago, Geology Archipelago or Cape Geology Archipelago, is a small archipelago of rocky islands and rocks close to the north of Cape Géodésie and Astrolabe Glacier Tongue, extending from Helene Island on the west to the Dumoulin Islands on the east, in Adélie Land, Antarctica.
Presqu'ile is a tombolo on the north shore of Lake Ontario in Northumberland County. When proglacial Lake Iroquois drained, leaving the lower Lake Ontario five limestone islands, the largest of which was Presqu'ile Island reduced the speed of currents carrying sand and silt, causing the dynamic sand spit to grow. The spit eventually engulfed Presqu'ile Island, and two small islands. Gull and High Bluff islands remain unattached,

The Gravel River is a river in Quebec, Canada, to the north of the lower St. Lawrence River. It is a tributary of the Aux Rochers River in the Lac-Walker territory of Côte-Nord.

The Sept Îles Archipelago Regional Park is a proposed protected area in the Côte-Nord region of Quebec, Canada. The islands are important to migratory sea birds, and are also of interest to tourists. The management plan was prepared in 2008.

The Gros Mécatina River is a salmon river in the Côte-Nord region of Quebec, Canada. It empties into the Gulf of Saint Lawrence.

The Gros-Mécatina Migratory Bird Sanctuary is a protected area in Quebec, Canada. It consists of four islands and a reef in the Gulf of Saint Lawrence that are used as nesting sites by seabirds.