
A turboprop is a turbine engine that drives an aircraft propeller.
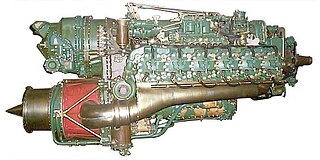
The Napier Nomad is a British diesel aircraft engine designed and built by Napier & Son in 1949. They combined a piston engine with a turbine to recover energy from the exhaust and thereby improve fuel economy. Two versions were tested, the complex Nomad I which used two propellers, each driven by the mechanically independent stages, and the Nomad II, using the turbo-compound principle, coupled the two parts to drive a single propeller. The Nomad II had the lowest specific fuel consumption figures seen up to that time. Despite this the Nomad project was cancelled in 1955 having spent £5.1 million on development, as most interest had passed to turboprop designs.

Centrifugal compressors, sometimes called impeller compressors or radial compressors, are a sub-class of dynamic axisymmetric work-absorbing turbomachinery.

The Theseus was the Bristol Aeroplane Company's first attempt at a gas-turbine engine design. A turboprop delivering just over 2,000 hp (1,500 kW) was chosen rather than compete with companies that were already developing turbojets. A heat exchanger to transfer waste heat from the exhaust to the compressor exit was necessary to meet a requirement for a fuel consumption comparable to a piston engine. The heat exchanger was abandoned after tests showed it had a high pressure loss and saved much less fuel than had been expected.

The Bristol Proteus was the Bristol Engine Company's first mass-produced gas turbine engine design, a turboprop that delivered just over 4,000 hp (3,000 kW). The Proteus was a reverse-flow gas turbine. Because the second turbine drove no compressor stages, but only the propeller, this engine was classified as a free-turbine. It powered the Bristol Britannia airliner, small naval patrol craft, hovercraft and electrical generating sets. It was also used to power a land-speed record car, the Bluebird-Proteus CN7. After the merger of Bristol with Armstrong Siddeley the engine became the Bristol Siddeley Proteus, and later the Rolls-Royce Proteus. The Proteus was to have been superseded by the Bristol Orion which would have given a Britannia a 75% increase in power for cruising faster.

The Rolls-Royce Olympus was the world's second two-spool axial-flow turbojet aircraft engine design, first run in May 1950 and preceded only by the Pratt & Whitney J57, first-run in January 1950. It is best known as the powerplant of the Avro Vulcan and later models in the Concorde SST.

The Pratt & Whitney Canada PT6 is a turboprop aircraft engine produced by Pratt & Whitney Canada. Its design was started in 1958, it first ran in February 1960, first flew on 30 May 1961, entered service in 1964 and has been continuously updated since. It consists of two basic sections: a gas generator with accessory gearbox and a free power turbine with reduction gearbox, and is often seemingly mounted backwards in an aircraft in so far as the intake is at the rear and the exhaust at the front. Many variants of the PT6 have been produced, not only as turboprops but also as turboshaft engines for helicopters, land vehicles, hovercraft, and boats; as auxiliary power units; and for industrial uses. By November 2015, 51,000 had been produced, had logged 400 million flight hours from 1963 to 2016. It is known for its reliability with an in-flight shutdown rate of 1 per 651,126 hours in 2016. The PT6A covers the power range between 580 and 1,940 shp while the PT6B/C are turboshaft variants for helicopters.

The Rolls-Royce RB.39 Clyde was Rolls-Royce's first purpose-designed turboprop engine and the first turboprop engine to pass its civil and military type-tests.

The Metropolitan-Vickers F.2 is an early turbojet engine and the first British design to be based on an axial-flow compressor. It was an extremely advanced design for the era, using a nine-stage axial compressor, annular combustor, and a two-stage turbine.

Turbomachinery, in mechanical engineering, describes machines that transfer energy between a rotor and a fluid, including both turbines and compressors. While a turbine transfers energy from a fluid to a rotor, a compressor transfers energy from a rotor to a fluid.

The Lockheed J37 was one of the first turbojet engines designed in the United States. It was not considered very important when its development was first begun in the 1930s, and it was allowed to languish. By the time it was developed enough for production use, other engines, some British-derived, had surpassed it in performance. The design was later converted to a turboprop, the T35 and still later sold to Wright Aeronautical, where it saw some interest for use on what would become the B-52 Stratofortress, before that design moved to jet power. The J37 and T35 were built to the extent of a number of testbed examples but never entered production.

The Bristol Orion aero engine was a two-shaft turboprop intended for use in later marks of the Bristol Britannia and the Canadair CL-44. Although the engine was built and underwent a development program, the BE.25 Orion project was cancelled in 1958 by the British Ministry of Supply in favour of the Rolls-Royce Tyne. In addition, interest in turboprop-powered aircraft was beginning to wane, because of the successful introduction of the Boeing 707 and Douglas DC-8 jetliners into airline service.
A swing-piston engine is a type of internal combustion engine in which the pistons move in a circular motion inside a ring-shaped "cylinder", moving closer and further from each other to provide compression and expansion. Generally two sets of pistons are used, geared to move in a fixed relationship as they rotate around the cylinder. In some versions the pistons oscillate around a fixed center, as opposed to rotating around the entire engine. The design has also been referred to as a oscillating piston engine, vibratory engine when the pistons oscillate instead of rotate, or toroidal engine based on the shape of the "cylinder".
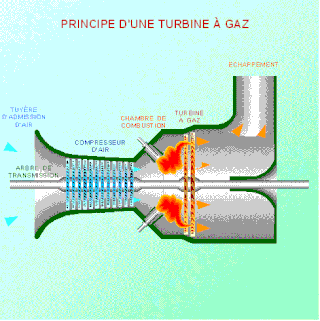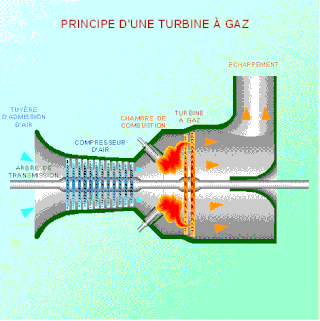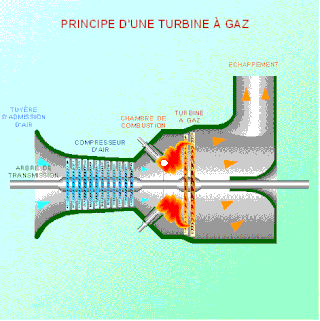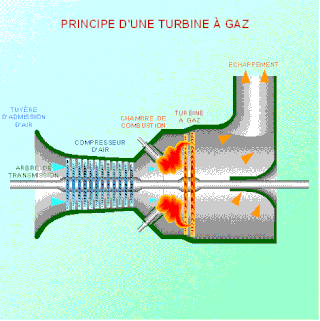
As the name suggests, gas turbine engine compressors provide the compression part of the gas turbine engine thermodynamic cycle. There are three basic categories of gas turbine engine compressor: axial compressor, centrifugal compressor and mixed flow compressor. A fourth, unusual, type is the free-piston gas generator, which combines the functions of compressor and combustion chamber in one unit.

The Allison Model 250, now known as the Rolls-Royce M250, is a highly successful turboshaft engine family, originally developed by the Allison Engine Company in the early 1960s. The Model 250 has been produced by Rolls-Royce since it acquired Allison in 1995.

The Turbomeca Astazou is a highly successful series of turboprop and turboshaft engines, first run in 1957. The original version weighed 110 kg (243 lb) and developed 240 kW (320 shp) at 40,000 rpm. It was admitted for aviation service on May 29, 1961, after a 150-hour test run. The main developing engineer was G. Sporer. It was named after two summits of the Pyrenees.

The Turbomeca Turmo is a family of French turboshaft engines manufacturered for helicopter use. Developed from the earlier Turbomeca Artouste, later versions delivered up to 1,300 kW (1,700 shp). A turboprop version was developed for use with the Bréguet 941 transport aircraft.

The General Electric T31 was the first turboprop engine designed and built in the United States.
The Power Jets WU was a series of three very different experimental jet engines produced and tested by Frank Whittle and his small team in the late 1930s.
The Bristol Phoebus was an early turbojet engine developed by Bristol Engines. It was based on the gas generator core of the Bristol Proteus. The Phoebus was used for development but only a handful were made. As with other Bristol engines, it took its name from classical mythology.
















