Related Research Articles

The lungs are the primary organs of the respiratory system in many animals, including humans. In mammals and most other tetrapods, two lungs are located near the backbone on either side of the heart. Their function in the respiratory system is to extract oxygen from the atmosphere and transfer it into the bloodstream, and to release carbon dioxide from the bloodstream into the atmosphere, in a process of gas exchange. Respiration is driven by different muscular systems in different species. Mammals, reptiles and birds use their musculoskeletal systems to support and foster breathing. In early tetrapods, air was driven into the lungs by the pharyngeal muscles via buccal pumping, a mechanism still seen in amphibians. In humans, the primary muscle that drives breathing is the diaphragm. The lungs also provide airflow that makes vocalisation including speech possible.
A bronchodilator or broncholytic is a substance that dilates the bronchi and bronchioles, decreasing resistance in the respiratory airway and increasing airflow to the lungs. Bronchodilators may be originating naturally within the body, or they may be medications administered for the treatment of breathing difficulties, usually in the form of inhalers. They are most useful in obstructive lung diseases, of which asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease are the most common conditions. They may be useful in bronchiolitis and bronchiectasis, although this remains somewhat controversial. They are often prescribed but of unproven significance in restrictive lung diseases.

Respiratory failure results from inadequate gas exchange by the respiratory system, meaning that the arterial oxygen, carbon dioxide, or both cannot be kept at normal levels. A drop in the oxygen carried in the blood is known as hypoxemia; a rise in arterial carbon dioxide levels is called hypercapnia. Respiratory failure is classified as either Type 1 or Type 2, based on whether there is a high carbon dioxide level, and can be acute or chronic. In clinical trials, the definition of respiratory failure usually includes increased respiratory rate, abnormal blood gases, and evidence of increased work of breathing. Respiratory failure causes an altered state of consciousness due to ischemia in the brain.

The respiratory tract is the subdivision of the respiratory system involved with the process of conducting air to the alveoli for the purposes of gas exchange in mammals. The respiratory tract is lined with respiratory epithelium as respiratory mucosa.

A bronchus is a passage or airway in the lower respiratory tract that conducts air into the lungs. The first or primary bronchi to branch from the trachea at the carina are the right main bronchus and the left main bronchus. These are the widest bronchi, and enter the right lung, and the left lung at each hilum. The main bronchi branch into narrower secondary bronchi or lobar bronchi, and these branch into narrower tertiary bronchi or segmental bronchi. Further divisions of the segmental bronchi are known as fourth order, fifth order, and sixth order segmental bronchi, or grouped together as subsegmental bronchi. The bronchi, when too narrow to be supported by cartilage, are known as bronchioles. No gas exchange takes place in the bronchi.

The bronchioles are the smaller branches of the bronchial airways in the lower respiratory tract. They include the terminal bronchioles, and finally the respiratory bronchioles that mark the start of the respiratory zone delivering air to the gas exchanging units of the alveoli. The bronchioles no longer contain the cartilage that is found in the bronchi, or glands in their submucosa.

Exhalation is the flow of the breath out of an organism. In animals, it is the movement of air from the lungs out of the airways, to the external environment during breathing. This happens due to elastic properties of the lungs, as well as the internal intercostal muscles which lower the rib cage and decrease thoracic volume. As the thoracic diaphragm relaxes during exhalation it causes the tissue it has depressed to rise superiorly and put pressure on the lungs to expel the air. During forced exhalation, as when blowing out a candle, expiratory muscles including the abdominal muscles and internal intercostal muscles generate abdominal and thoracic pressure, which forces air out of the lungs.
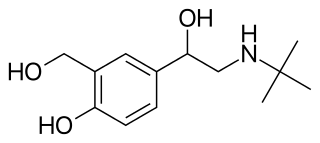
Beta2-adrenergic agonists, also known as adrenergic β2 receptor agonists, are a class of drugs that act on the β2 adrenergic receptor. Like other β adrenergic agonists, they cause smooth muscle relaxation. β2 adrenergic agonists' effects on smooth muscle cause dilation of bronchial passages, vasodilation in muscle and liver, relaxation of uterine muscle, and release of insulin. They are primarily used to treat asthma and other pulmonary disorders. Bronchodilators are considered an important treatment regime for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and are usually used in combination with short acting medications and long acting medications in a combined inhaler.

Bronchoconstriction is the constriction of the airways in the lungs due to the tightening of surrounding smooth muscle, with consequent coughing, wheezing, and shortness of breath.

A respiratory examination, or lung examination, is performed as part of a physical examination, in response to respiratory symptoms such as shortness of breath, cough, or chest pain, and is often carried out with a cardiac examination.

Respiratory diseases, or lung diseases, are pathological conditions affecting the organs and tissues that make gas exchange difficult in air-breathing animals. They include conditions of the respiratory tract including the trachea, bronchi, bronchioles, alveoli, pleurae, pleural cavity, the nerves and muscles of respiration. Respiratory diseases range from mild and self-limiting, such as the common cold, influenza, and pharyngitis to life-threatening diseases such as bacterial pneumonia, pulmonary embolism, tuberculosis, acute asthma, lung cancer, and severe acute respiratory syndromes, such as COVID-19. Respiratory diseases can be classified in many different ways, including by the organ or tissue involved, by the type and pattern of associated signs and symptoms, or by the cause of the disease.

Levosalbutamol, also known as levalbuterol, is a short-acting β2 adrenergic receptor agonist used in the treatment of asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Evidence is inconclusive regarding the efficacy of levosalbutamol versus salbutamol or salbutamol-levosalbutamol combinations, though levosalbutamol is believed to have a better safety profile due to its more selective binding to β2 receptors versus β1.
Bronchial thermoplasty is a treatment for severe asthma approved by the FDA in 2010 involving the delivery of controlled, therapeutic radiofrequency energy to the airway wall, thus heating the tissue and reducing the amount of smooth muscle present in the airway wall. This reduces the capacity of the immune system to cause bronchoconstriction through nitric oxide signalling, which is the main root cause of asthma symptoms. Bronchial thermoplasty is normally used to treat patients with severe persistent asthma who do not respond well to typical pharmacotherapy regimens.

Pulmonary function testing (PFT) is a complete evaluation of the respiratory system including patient history, physical examinations, and tests of pulmonary function. The primary purpose of pulmonary function testing is to identify the severity of pulmonary impairment. Pulmonary function testing has diagnostic and therapeutic roles and helps clinicians answer some general questions about patients with lung disease. PFTs are normally performed by a pulmonary function technologist, respiratory therapist, respiratory physiologist, physiotherapist, pulmonologist, or general practitioner.
Pulmonary rehabilitation, also known as respiratory rehabilitation, is an important part of the management and health maintenance of people with chronic respiratory disease who remain symptomatic or continue to have decreased function despite standard medical treatment. It is a broad therapeutic concept. It is defined by the American Thoracic Society and the European Respiratory Society as an evidence-based, multidisciplinary, and comprehensive intervention for patients with chronic respiratory diseases who are symptomatic and often have decreased daily life activities. In general, pulmonary rehabilitation refers to a series of services that are administered to patients of respiratory disease and their families, typically to attempt to improve the quality of life for the patient. Pulmonary rehabilitation may be carried out in a variety of settings, depending on the patient's needs, and may or may not include pharmacologic intervention.

Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a type of progressive lung disease characterized by chronic respiratory symptoms and airflow limitation. GOLD 2024 defined COPD as a heterogeneous lung condition characterized by chronic respiratory symptoms due to abnormalities of the airways and/or alveoli (emphysema) that cause persistent, often progressive, airflow obstruction.

Ventilation–perfusion coupling is the relationship between ventilation and perfusion processes, which take place in the respiratory system and the cardiovascular system. Ventilation is the movement of gas during breathing, and perfusion is the process of pulmonary blood circulation, which delivers oxygen to body tissues. Anatomically, the lung structure, alveolar organization, and alveolar capillaries contribute to the physiological mechanism of ventilation and perfusion. Ventilation–perfusion coupling maintains a constant ventilation/perfusion ratio near 0.8 on average, while the regional variation exists within the lungs due to gravity. When the ratio gets above or below 0.8, it is considered abnormal ventilation-perfusion coupling, also known as a ventilation–perfusion mismatch. Lung diseases, cardiac shunts, and smoking can cause a ventilation-perfusion mismatch that results in significant symptoms and diseases, which can be treated through treatments like bronchodilators and oxygen therapy.
Tedral, or theophylline/ephedrine/phenobarbital, is a medicine formerly used to treat respiratory diseases such as asthma, chronic obstructive lung disease (COPD), chronic bronchitis, and emphysema. It is a combination drug containing three active ingredients - theophylline, ephedrine, phenobarbital. This medication relaxes the smooth muscle of the airways, making breathing easier. The common side effects of Tedral include gastrointestinal disturbances, dizziness, headache and lightheadedness. However, at high dose, it may lead to cardiac arrhythmias, hypertension, seizures or other serious cardiovascular and/or central nervous system adverse effects. Tedral is contraindicated in individuals with hypersensitivity to theophylline, ephedrine and/or phenobarbital. It should be also used in caution in patients with cardiovascular complications, such as ischemic heart disease and heart failure and/or other disease conditions. It can cause a lot of drug–drug interactions. Therefore, before prescribing patient with Tedral, drug interactions profile should be carefully checked if the patient had other concurrent medication(s). Being used as a treatment option for respiratory diseases for decades, Tedral was withdrawn from the US market in 2006 due to safety concerns.

Airway remodelling, or airway remodeling, is a potential complication of certain endotypes (subtypes) of asthma. It is the sum of changes that occur in the airways of some asthmatic people compared to people without the disease.
Airway tone, short for airway smooth muscle tone, is the degree of sustained contractile activation of airway smooth muscle. The airways have a tone baseline, and consequently a baseline level of contraction of their smooth musculature. Airway tone is a key determinant of lung function and the presence of respiratory symptoms in obstructive lung diseases such as asthma, where baseline airway tone is elevated. The upper extreme of the spectrum of airway tone represents bronchoconstriction, wherein the airway smooth muscles are significantly contracted, while the lower extreme represents bronchodilatation, wherein the muscles are relatively relaxed.
References
- 1 2 Almadhoun, Khaled; Sharma, Sandeep (2023), "Bronchodilators", StatPearls, Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing, PMID 30085570 , retrieved 2023-12-20
- 1 2 Prakash, Y. S. (2013-12-15). "Airway smooth muscle in airway reactivity and remodeling: what have we learned?". American Journal of Physiology. Lung Cellular and Molecular Physiology. 305 (12): L912–L933. doi:10.1152/ajplung.00259.2013. ISSN 1040-0605. PMC 3882535 . PMID 24142517.