Related Research Articles

An artery is a blood vessel in humans and most animals that takes blood away from the heart to one or more parts of the body. Most arteries carry oxygenated blood; the two exceptions are the pulmonary and the umbilical arteries, which carry deoxygenated blood to the organs that oxygenate it. The effective arterial blood volume is that extracellular fluid which fills the arterial system.
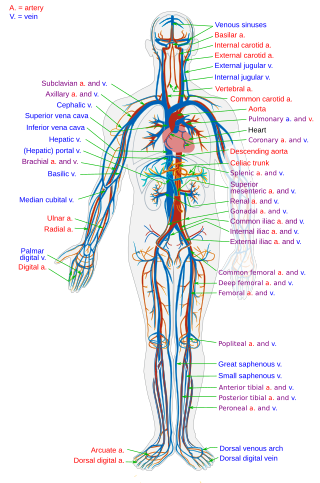
The blood vessels are the components of the circulatory system that transport blood throughout the human body. These vessels transport blood cells, nutrients, and oxygen to the tissues of the body. They also take waste and carbon dioxide away from the tissues. Blood vessels are needed to sustain life, because all of the body's tissues rely on their functionality.

Blood pressure (BP) is the pressure of circulating blood against the walls of blood vessels. Most of this pressure results from the heart pumping blood through the circulatory system. When used without qualification, the term "blood pressure" refers to the pressure in the large arteries. Blood pressure is usually expressed in terms of the systolic pressure over diastolic pressure in the cardiac cycle. It is measured in millimeters of mercury (mmHg) above the surrounding atmospheric pressure.

The respiratory system is a biological system consisting of specific organs and structures used for gas exchange in animals and plants. The anatomy and physiology that make this happen varies greatly, depending on the size of the organism, the environment in which it lives and its evolutionary history. In land animals the respiratory surface is internalized as linings of the lungs. Gas exchange in the lungs occurs in millions of small air sacs; in mammals and reptiles these are called alveoli, and in birds they are known as atria. These microscopic air sacs have a very rich blood supply, thus bringing the air into close contact with the blood. These air sacs communicate with the external environment via a system of airways, or hollow tubes, of which the largest is the trachea, which branches in the middle of the chest into the two main bronchi. These enter the lungs where they branch into progressively narrower secondary and tertiary bronchi that branch into numerous smaller tubes, the bronchioles. In birds the bronchioles are termed parabronchi. It is the bronchioles, or parabronchi that generally open into the microscopic alveoli in mammals and atria in birds. Air has to be pumped from the environment into the alveoli or atria by the process of breathing which involves the muscles of respiration.
Diffusing capacity of the lung (DL) measures the transfer of gas from air in the lung, to the red blood cells in lung blood vessels. It is part of a comprehensive series of pulmonary function tests to determine the overall ability of the lung to transport gas into and out of the blood. DL, especially DLCO, is reduced in certain diseases of the lung and heart. DLCO measurement has been standardized according to a position paper by a task force of the European Respiratory and American Thoracic Societies.
Gas exchange is the physical process by which gases move passively by diffusion across a surface. For example, this surface might be the air/water interface of a water body, the surface of a gas bubble in a liquid, a gas-permeable membrane, or a biological membrane that forms the boundary between an organism and its extracellular environment.

Pulmonary edema, also known as pulmonary congestion, is excessive liquid accumulation in the tissue and air spaces of the lungs. It leads to impaired gas exchange and may cause hypoxemia and respiratory failure. It is due to either failure of the left ventricle of the heart to remove oxygenated blood adequately from the pulmonary circulation, or an injury to the lung tissue directly or blood vessels of the lung.

A pulmonary artery is an artery in the pulmonary circulation that carries deoxygenated blood from the right side of the heart to the lungs. The largest pulmonary artery is the main pulmonary artery or pulmonary trunk from the heart, and the smallest ones are the arterioles, which lead to the capillaries that surround the pulmonary alveoli.
Vascular resistance is the resistance that must be overcome to push blood through the circulatory system and create flow. The resistance offered by the systemic circulation is known as the systemic vascular resistance (SVR) or may sometimes be called by the older term total peripheral resistance (TPR), while the resistance offered by the pulmonary circulation is known as the pulmonary vascular resistance (PVR). Systemic vascular resistance is used in calculations of blood pressure, blood flow, and cardiac function. Vasoconstriction increases SVR, whereas vasodilation decreases SVR.

Pulmonary hypertension is a condition of increased blood pressure in the arteries of the lungs. Symptoms include shortness of breath, fainting, tiredness, chest pain, swelling of the legs, and a fast heartbeat. The condition may make it difficult to exercise. Onset is typically gradual.

Cerebral circulation is the movement of blood through a network of cerebral arteries and veins supplying the brain. The rate of cerebral blood flow in an adult human is typically 750 milliliters per minute, or about 15% of cardiac output. Arteries deliver oxygenated blood, glucose and other nutrients to the brain. Veins carry "used or spent" blood back to the heart, to remove carbon dioxide, lactic acid, and other metabolic products. Because the brain would quickly suffer damage from any stoppage in blood supply, the cerebral circulatory system has safeguards including autoregulation of the blood vessels. The failure of these safeguards may result in a stroke. The volume of blood in circulation is called the cerebral blood flow. Sudden intense accelerations change the gravitational forces perceived by bodies and can severely impair cerebral circulation and normal functions to the point of becoming serious life-threatening conditions.
Compliance is the ability of a hollow organ (vessel) to distend and increase volume with increasing transmural pressure or the tendency of a hollow organ to resist recoil toward its original dimensions on application of a distending or compressing force. It is the reciprocal of "elastance", hence elastance is a measure of the tendency of a hollow organ to recoil toward its original dimensions upon removal of a distending or compressing force.

Hypoxemia is an abnormally low level of oxygen in the blood. More specifically, it is oxygen deficiency in arterial blood. Hypoxemia has many causes, and often causes hypoxia as the blood is not supplying enough oxygen to the tissues of the body.
In respiratory physiology, the ventilation/perfusion ratio is a ratio used to assess the efficiency and adequacy of the matching of two variables:
A pulmonary shunt is the passage of deoxygenated blood from the right side of the heart to the left without participation in gas exchange in the pulmonary capillaries. It is a pathological condition that results when the alveoli of parts of the lungs are perfused with blood as normal, but ventilation fails to supply the perfused region. In other words, the ventilation/perfusion ratio of those areas is zero.
The factors that determine the values for alveolar pO2 and pCO2 are:
The multiple inert gas elimination technique (MIGET) is a medical technique used mainly in pulmonology that involves measuring the concentrations of various infused, inert gases in mixed venous blood, arterial blood, and expired gas of a subject. The technique quantifies true shunt, physiological dead space ventilation, ventilation versus blood flow ratios, and diffusion limitation.
The Alveolar–arterial gradient, is a measure of the difference between the alveolar concentration (A) of oxygen and the arterial (a) concentration of oxygen. It is a useful parameter for narrowing the differential diagnosis of hypoxemia.
The Shunt equation quantifies the extent to which venous blood bypasses oxygenation in the capillaries of the lung. “Shunt” and “dead space“ are terms used to describe conditions where either blood flow or ventilation do not interact with each other in the lung, as they should for efficient gas exchange to take place. These terms can also be used to describe areas or effects where blood flow and ventilation are not properly matched, though both may be present to varying degrees. Some references refer to “shunt-effect” or “dead space-effect” to designate the ventilation/perfusion mismatch states that are less extreme than absolute shunt or dead space.

Ventilation-perfusion coupling is the relationship between ventilation and perfusion processes, which take place in the respiratory and cardiovascular systems. Ventilation is the movement of gas during breathing, and perfusion is the process of pulmonary blood circulation, which delivers oxygen to body tissues. Anatomically, the lung structure, alveolar organization, and alveolar capillaries contribute to the physiological mechanism of ventilation and perfusion. Ventilation-perfusion coupling maintains a constant ratio near 0.8 on average, while the regional variation exists within the lungs due to gravity. When the ratio gets above or below 0.8, it is considered abnormal ventilation-perfusion coupling, also known as a ventilation-perfusion mismatch. Lung diseases, cardiac shunts, and smoking can cause a ventilation-perfusion mismatch that results in significant symptoms and diseases, which can be treated through treatments like bronchodilators and oxygen therapy.
References
- ↑ West J, Dollery C, Naimark A (1964). "Distribution of blood flow in isolated lung; relation to vascular and alveolar pressures". J Appl Physiol. 19 (4): 713–24. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1964.19.4.713 . PMID 14195584.
- ↑ Permutt S, Bromberger-Barnea B, Bane HN (1962). "Alveolar Pressure, Pulmonary Venous Pressure, and the Vascular Waterfall". Med. Thorac. 19 (4): 239–269. doi:10.1159/000192224. PMID 13942495.