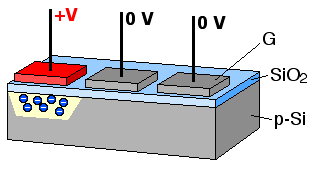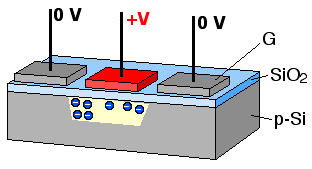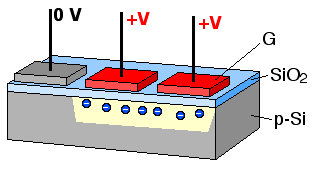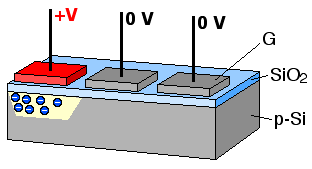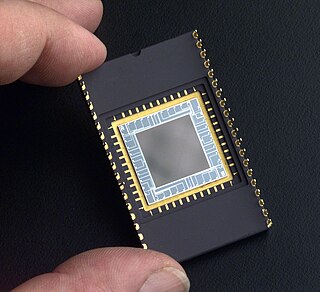
A charge-coupled device (CCD) is an integrated circuit containing an array of linked, or coupled, capacitors. Under the control of an external circuit, each capacitor can transfer its electric charge to a neighboring capacitor. CCD sensors are a major technology used in digital imaging.
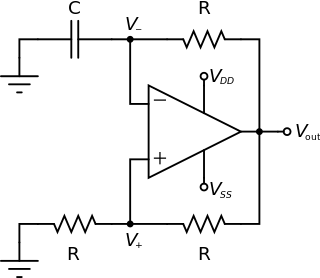
An electronic oscillator is an electronic circuit that produces a periodic, oscillating electronic signal, often a sine wave or a square wave or a triangle wave. Oscillators convert direct current (DC) from a power supply to an alternating current (AC) signal. They are widely used in many electronic devices ranging from simplest clock generators to digital instruments and complex computers and peripherals etc. Common examples of signals generated by oscillators include signals broadcast by radio and television transmitters, clock signals that regulate computers and quartz clocks, and the sounds produced by electronic beepers and video games.

In electronics, an analog-to-digital converter is a system that converts an analog signal, such as a sound picked up by a microphone or light entering a digital camera, into a digital signal. An ADC may also provide an isolated measurement such as an electronic device that converts an analog input voltage or current to a digital number representing the magnitude of the voltage or current. Typically the digital output is a two's complement binary number that is proportional to the input, but there are other possibilities.

Capacitive coupling is the transfer of energy within an electrical network or between distant networks by means of displacement current between circuit(s) nodes, induced by the electric field. This coupling can have an intentional or accidental effect.
A low-pass filter is a filter that passes signals with a frequency lower than a selected cutoff frequency and attenuates signals with frequencies higher than the cutoff frequency. The exact frequency response of the filter depends on the filter design. The filter is sometimes called a high-cut filter, or treble-cut filter in audio applications. A low-pass filter is the complement of a high-pass filter.
An analog sampled filter an electronic filter that is a hybrid between an analog and a digital filter. The input is an analog signal, and usually stored in capacitors. The time domain is discrete, however. Distinct analog samples are shifted through an array of holding capacitors as in a bucket brigade. Analog adders and amplifiers do the arithmetic in the signal domain, just as in an analog computer.
Delay-line memory is a form of computer memory, now obsolete, that was used on some of the earliest digital computers. Like many modern forms of electronic computer memory, delay-line memory was a refreshable memory, but as opposed to modern random-access memory, delay-line memory was sequential-access.

CV/gate is an analog method of controlling synthesizers, drum machines, and similar equipment with external sequencers. The control voltage typically controls pitch and the gate signal controls note on-off.

In electronics, a sample and hold circuit is an analog device that samples the voltage of a continuously varying analog signal and holds its value at a constant level for a specified minimum period of time. Sample and hold circuits and related peak detectors are the elementary analog memory devices. They are typically used in analog-to-digital converters to eliminate variations in input signal that can corrupt the conversion process. They are also used in electronic music, for instance to impart a random quality to successively-played notes.
In electronic instrumentation and signal processing, a time-to-digital converter (TDC) is a device for recognizing events and providing a digital representation of the time they occurred. For example, a TDC might output the time of arrival for each incoming pulse. Some applications wish to measure the time interval between two events rather than some notion of an absolute time.

A pulse generator is either an electronic circuit or a piece of electronic test equipment used to generate rectangular pulses. Pulse generators are used primarily for working with digital circuits; related function generators are used primarily for analog circuits.

Analogue electronics are electronic systems with a continuously variable signal, in contrast to digital electronics where signals usually take only two levels. The term "analogue" describes the proportional relationship between a signal and a voltage or current that represents the signal. The word analogue is derived from the Greek: word ανάλογος pronounced [n](analogos) meaning "proportional".
Delta-sigma modulation is a method for encoding analog signals into digital signals as found in an analog-to-digital converter (ADC). It is also used to convert high bit-count, low-frequency digital signals into lower bit-count, higher-frequency digital signals as part of the process to convert digital signals into analog as part of a digital-to-analog converter (DAC).

Moogerfooger is the trademark for a series of analog effects pedals manufactured by Moog Music. There are currently eight different pedals produced; however, one of these models is designed for processing control voltages rather than audio signal. A sixth model, the Analog Delay, was released in a limited edition of 1000 units and has become a collector's item. Moog Music announced on August 28, 2018, that the Moogerfooger, CP-251, Minifooger, Voyager synthesizers, and some other product lines were being built using the remaining parts on hand and discontinued thereafter.

A variable capacitor is a capacitor whose capacitance may be intentionally and repeatedly changed mechanically or electronically. Variable capacitors are often used in L/C circuits to set the resonance frequency, e.g. to tune a radio, or as a variable reactance, e.g. for impedance matching in antenna tuners.

An analog delay line is a network of electrical components connected in cascade, where each individual element creates a time difference between its input and output. It operates on analog signals whose amplitude varies continuously. In the case of a periodic signal, the time difference can be described in terms of a change in the phase of the signal. One example of an analog delay line is a bucket-brigade device.

The Logan String Melody designed by Ing. Giuliano Costantini for Logan was a portable keyboard produced in two versions from 1973 to 1982. Manufactured in Italy, it was sold under both the Logan brand name and re-badged as both a Hohner and Vox product. The Vox version was called The String Thing but still featured the Logan brand name on the back of the case.

An oscilloscope is a type of electronic test instrument that graphically displays varying electrical voltages as a two-dimensional plot of one or more signals as a function of time. The main purposes are to display repetitive or single waveforms on the screen that would otherwise occur too briefly to be perceived by the human eye. The displayed waveform can then be analyzed for properties such as amplitude, frequency, rise time, time interval, distortion, and others. Originally, calculation of these values required manually measuring the waveform against the scales built into the screen of the instrument. Modern digital instruments may calculate and display these properties directly.

Capacitors have many uses in electronic and electrical systems. They are so ubiquitous that it is rare that an electrical product does not include at least one for some purpose.

The Reticon Corporation was incorporated in January 1971 in Sunnyvale CA. It is one of several semiconductor companies formed in the '60s and '70s by former employees of Fairchild Semiconductor. Intel, another one of these companies, was an early investor, holding a 22% share in the company.